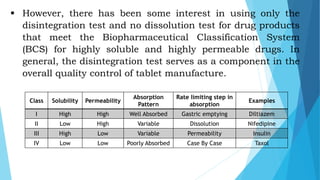
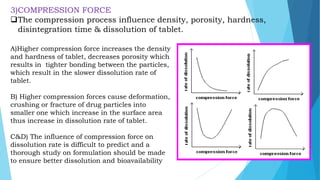
The three main rate limiting steps in drug absorption from oral solid dosage forms are disintegration, dissolution, and gastric emptying. Disintegration involves the breakdown of the solid dosage form into smaller particles so that the drug can be released. Dissolution is the process by which the drug becomes dissolved in water to be absorbed. Gastric emptying determines how quickly the drug formulation moves from the stomach into the intestines, where most absorption occurs. Several drug and formulation properties can impact these steps and influence overall drug absorption.