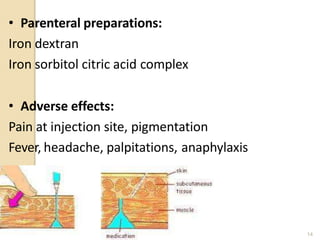
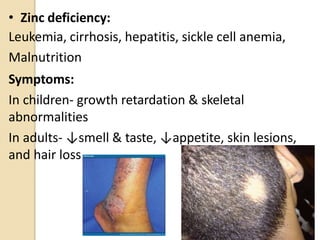
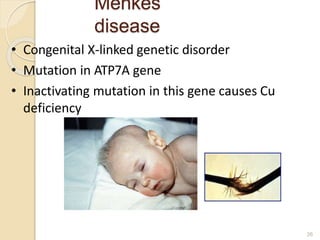
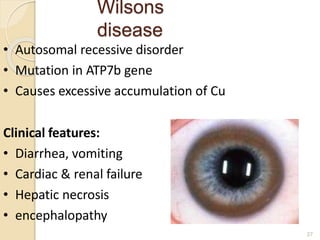
This document provides an overview of essential trace elements, including their classification, functions, dietary sources, deficiency and toxicity symptoms, and treatment. It discusses the trace elements iron, zinc, copper, chromium, fluoride, iodine, manganese, molybdenum, selenium, vanadium, tin, boron, lithium, and xenon. For each element, it summarizes their role in the body, recommended intake amounts, and conditions related to deficiency or excess. The document aims to inform about these important micronutrients and their significance for human health.