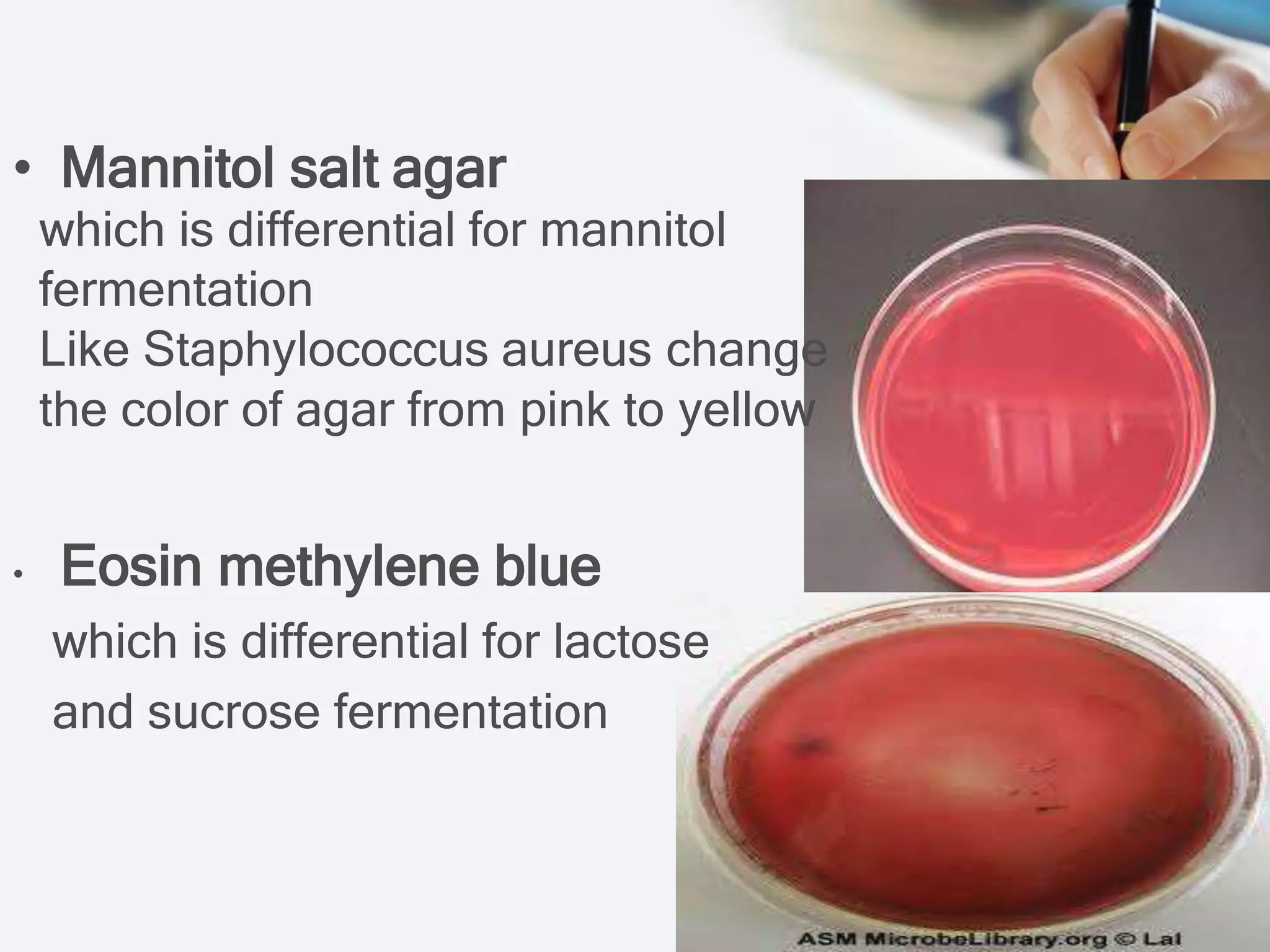
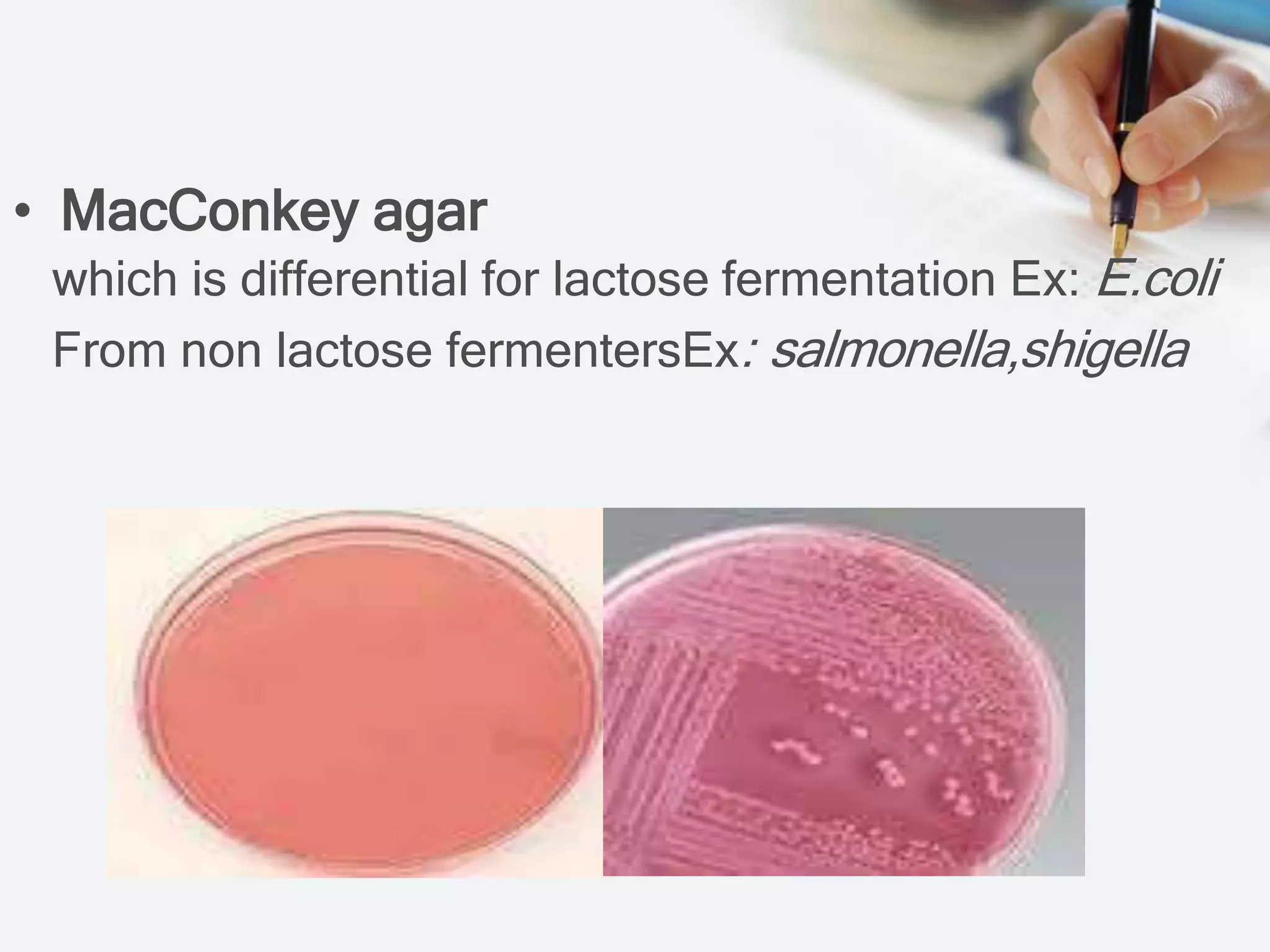
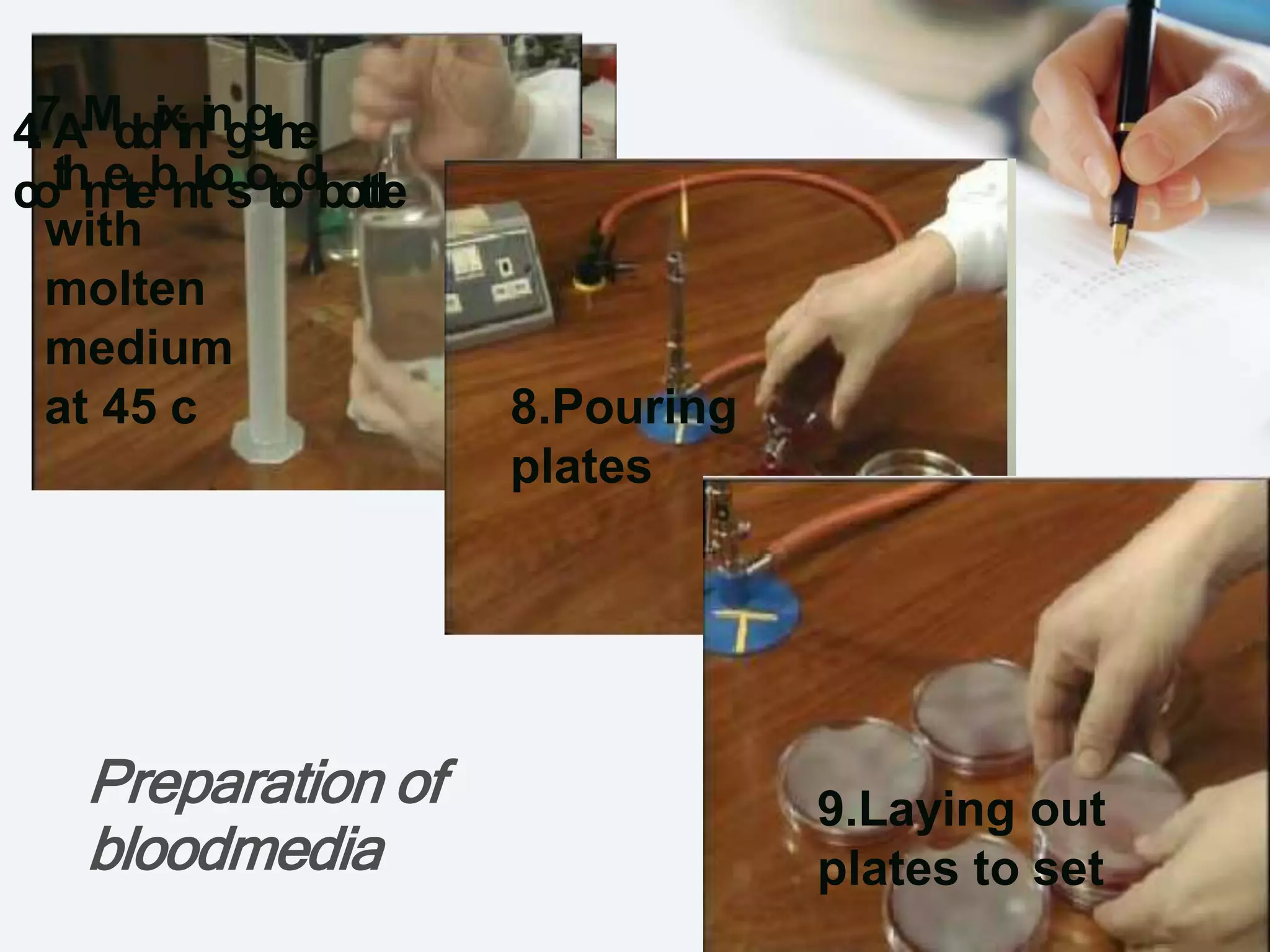
The document outlines the nutritional requirements, preparation, classification, and physical parameters for culture media used in cultivating microorganisms. It details various types of media, including basic, selective, differential, enriched, and transport media, highlighting their components and specific uses in microbiology. Key components for growth are also addressed, including chemical and physical requirements such as nutrients and environmental conditions.