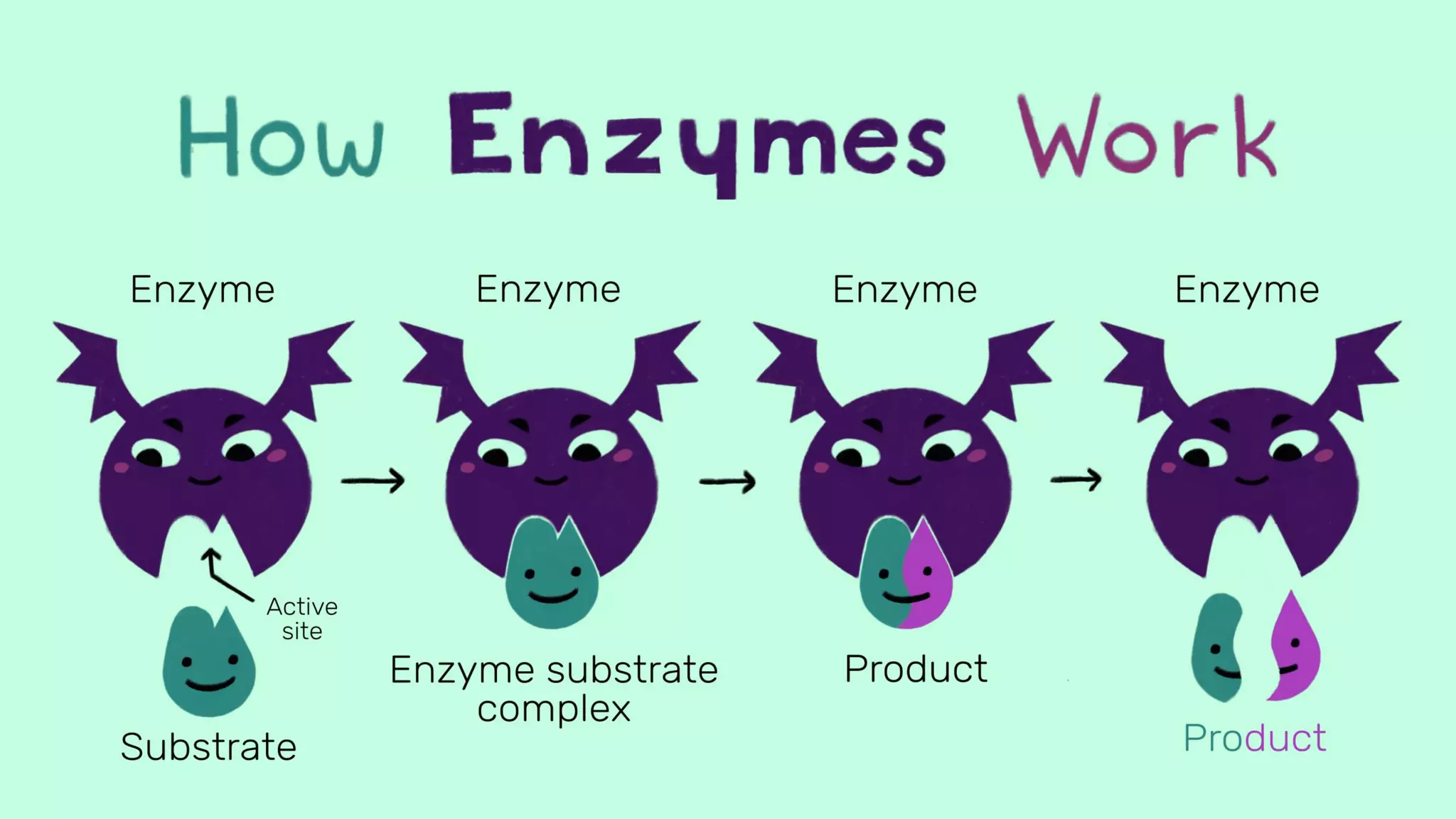
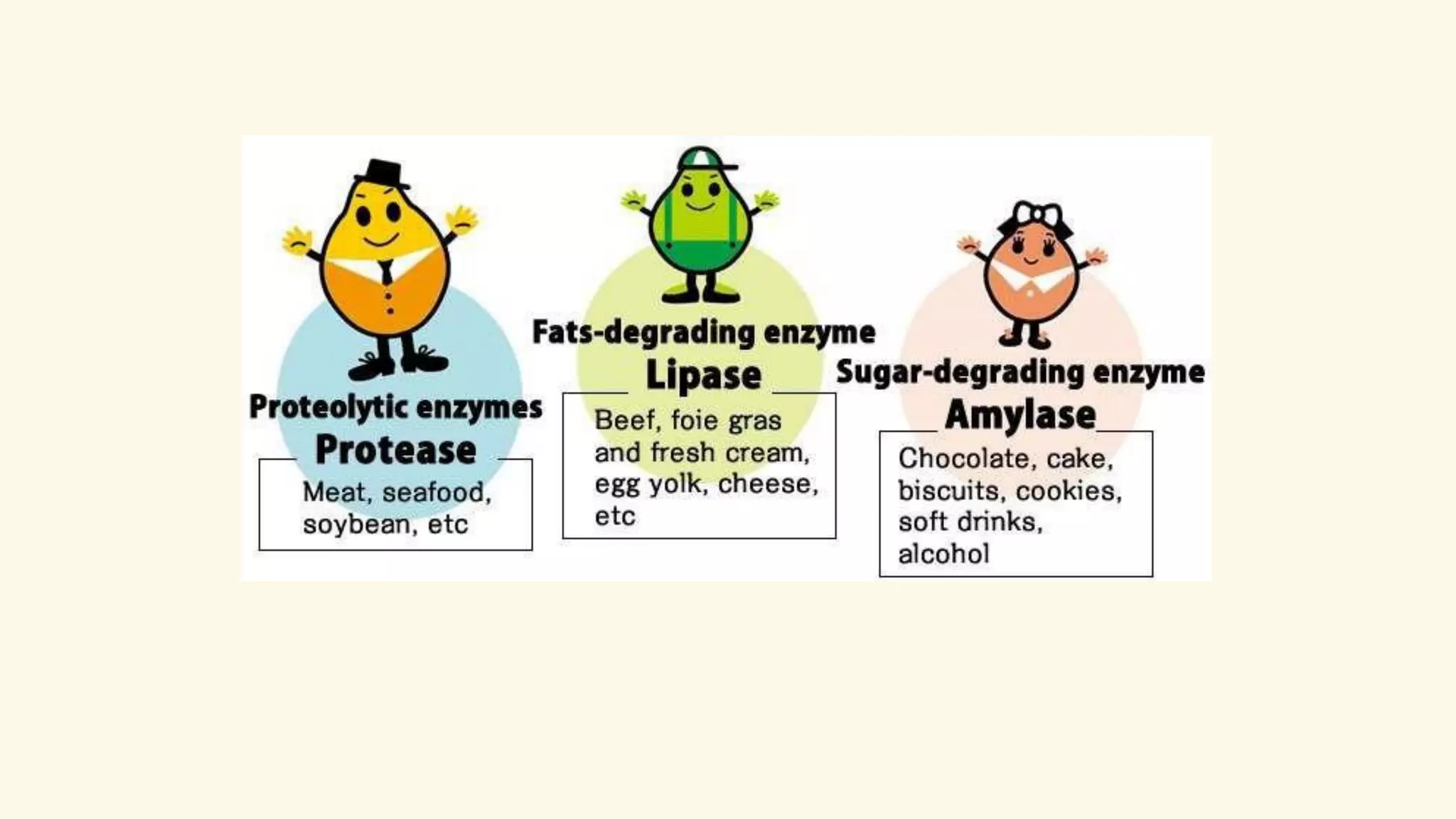
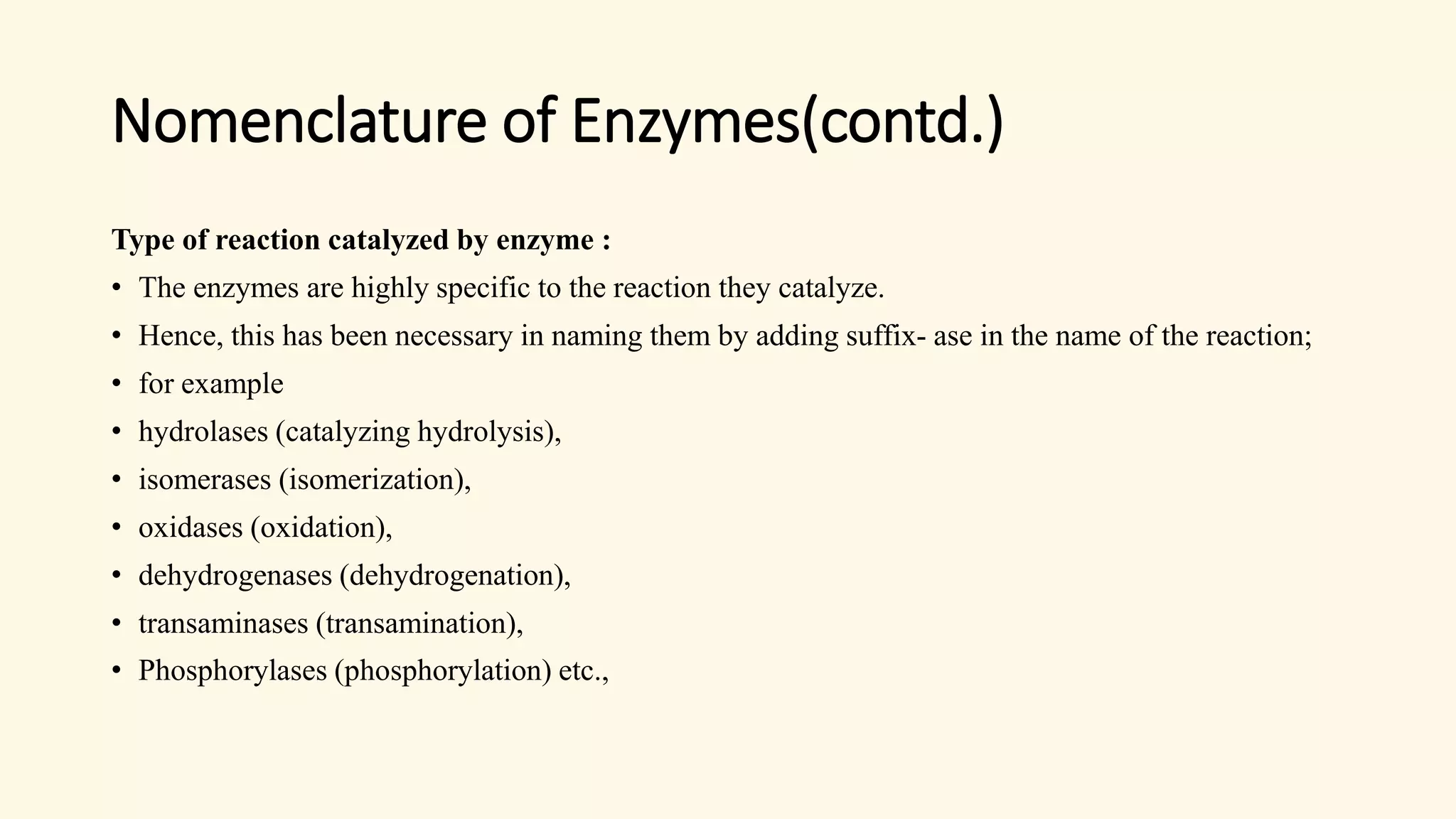
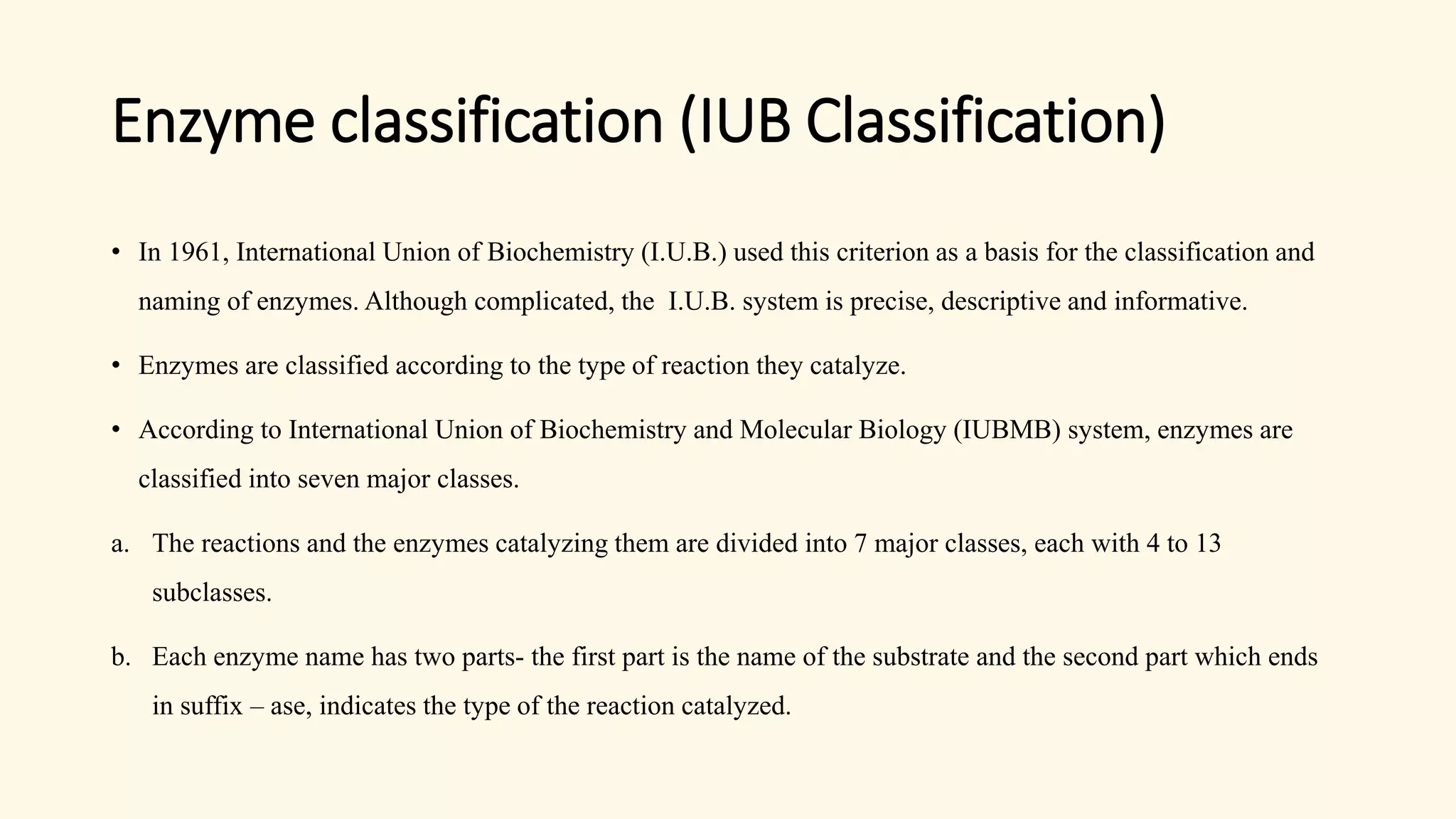
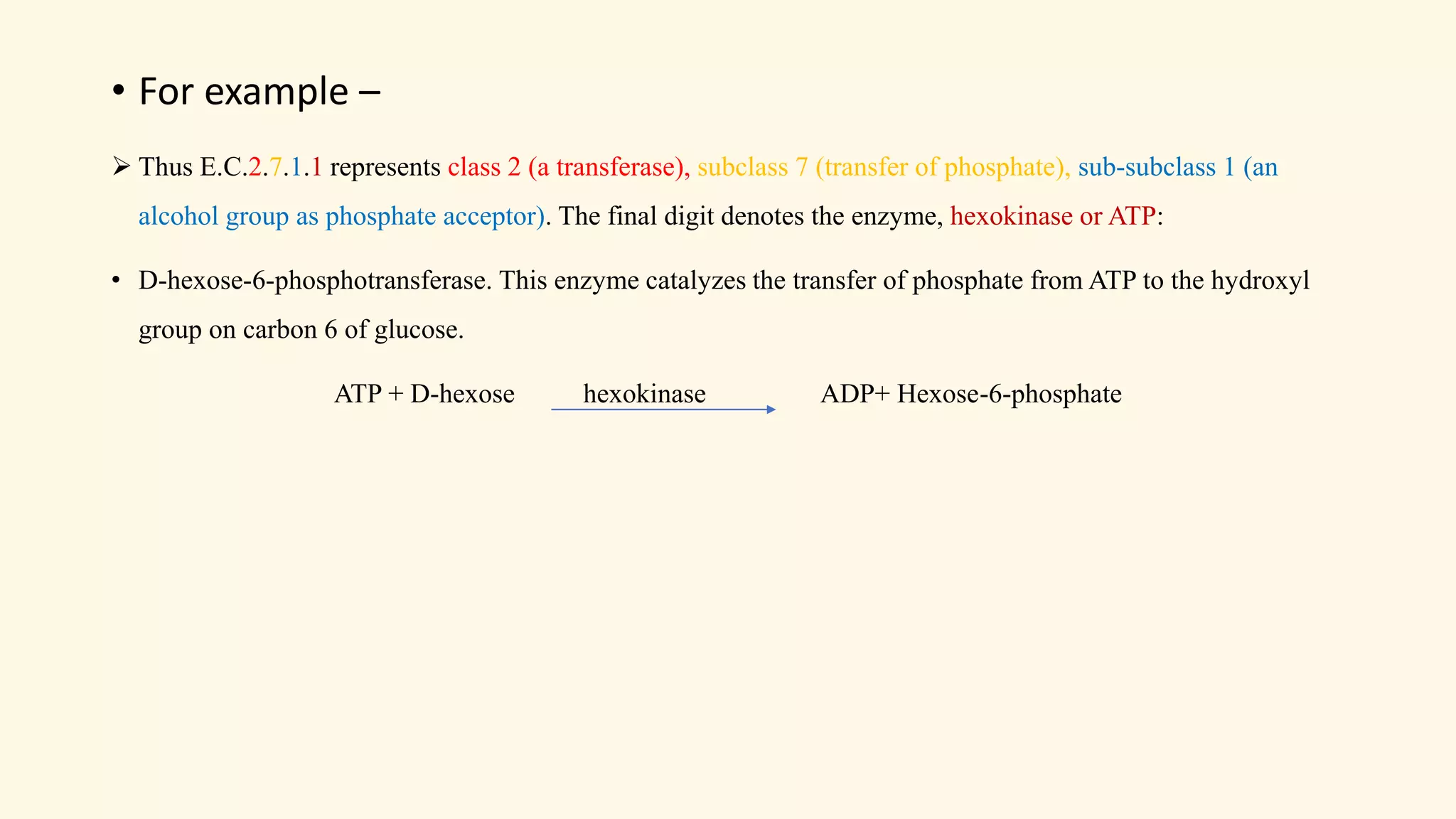
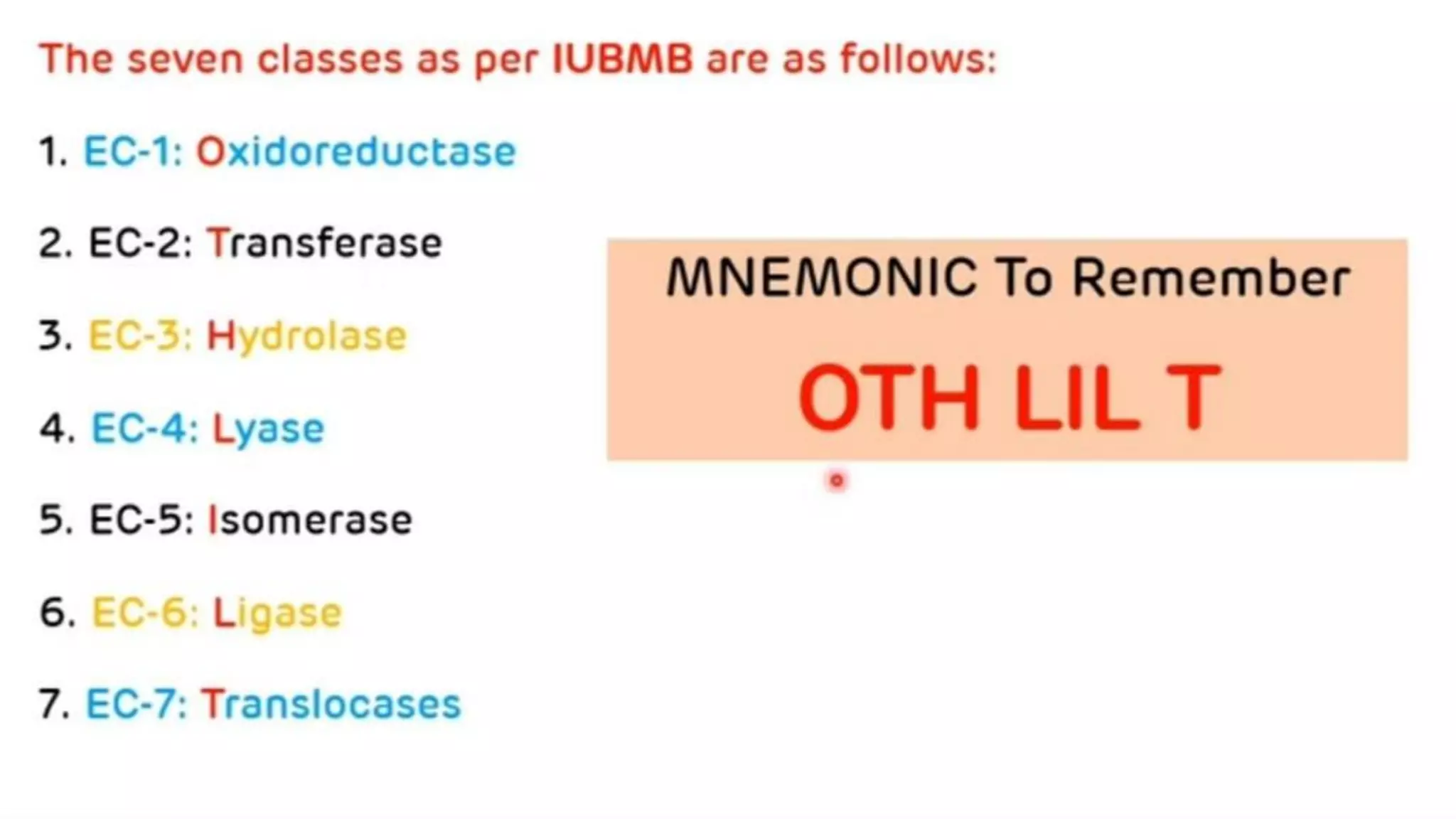
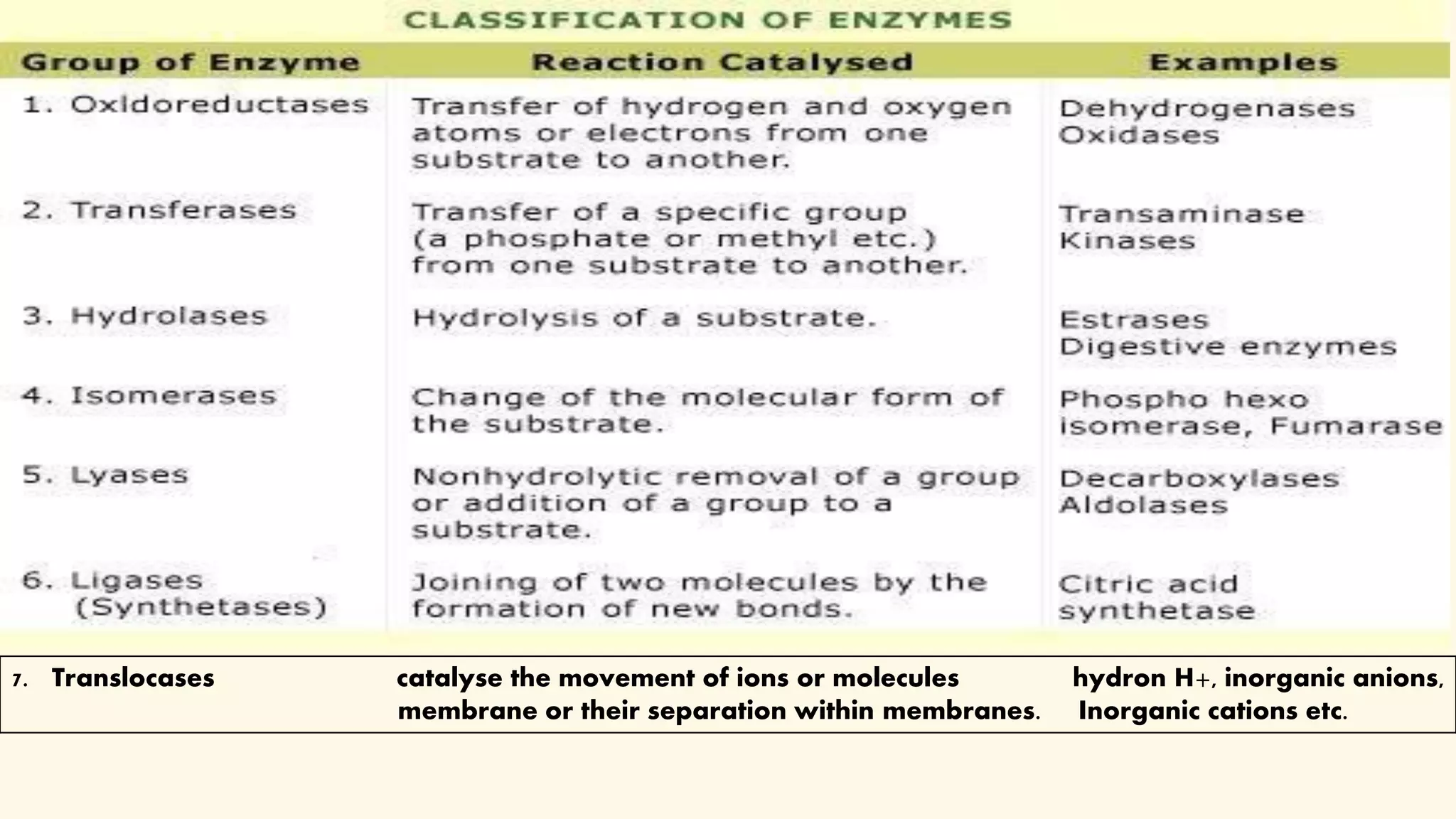
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins made from amino acids that fold into unique three-dimensional shapes. Enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions, allowing reactions to occur more quickly and at mild temperatures within cells. They are highly specific and only catalyze one type of reaction. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology classifies enzymes into seven major classes based on the type of reaction they catalyze and assigns each enzyme a unique identification number.