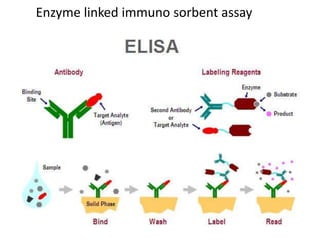
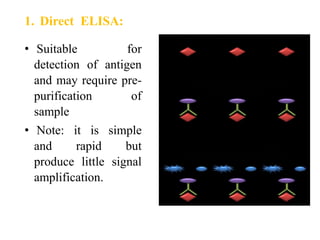
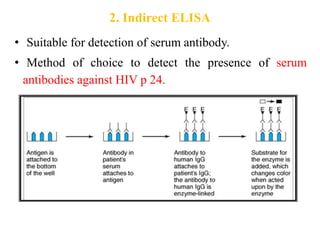
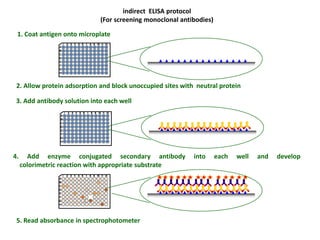
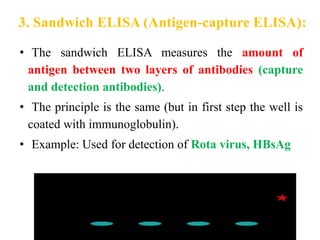
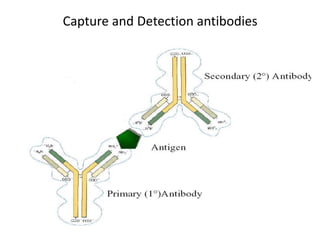
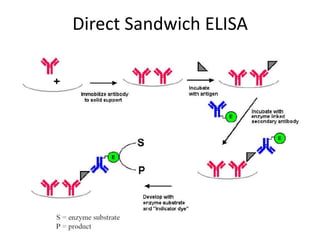
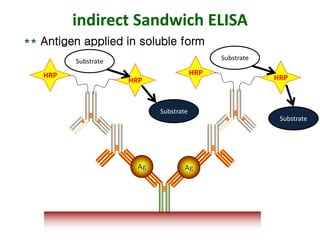
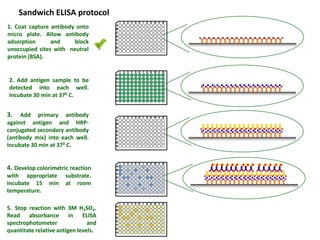
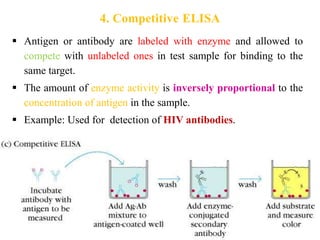
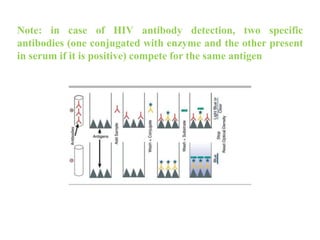
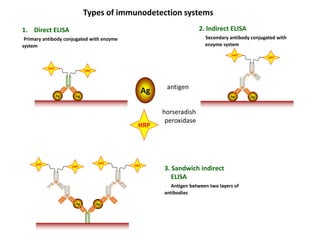
The document outlines the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), a biochemical technique used to detect antigens or antibodies in patient specimens through enzyme-linked antibodies that produce a color change. It details the different types of ELISA methods, including direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISA, and their applications in measuring antibodies, detecting viruses, hormonal changes, and inflammatory markers. Additionally, it discusses the advantages of ELISA, including sensitivity, quantitative results, and reproducibility, as well as limitations such as cost and potential cross-contamination issues.