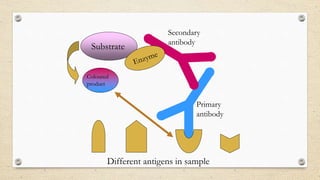
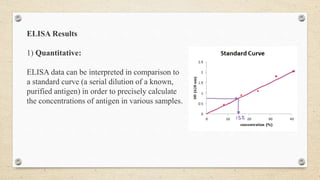
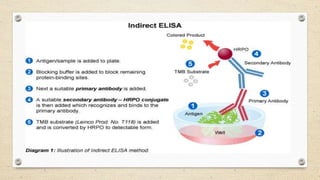
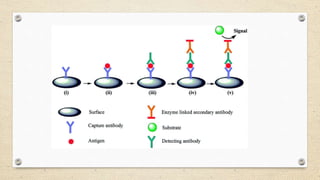
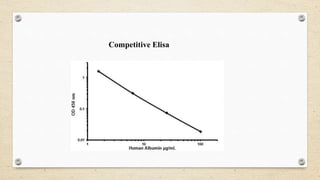
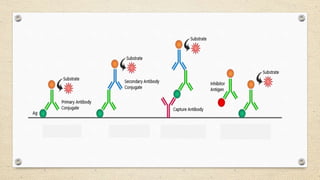
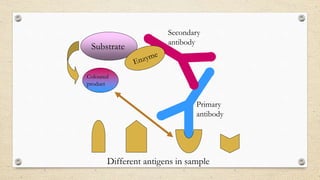
The document provides a detailed overview of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), including its definition, historical context, and various formats such as direct, indirect, sandwich, and competition ELISA. It describes the advantages of each type, such as increased sensitivity and specificity, and explains the underlying principles and procedures for conducting the test. Additionally, it highlights the common reagents and chromogenic substrates used in ELISA, notably the popularity of certain substrates for enhancing sensitivity.