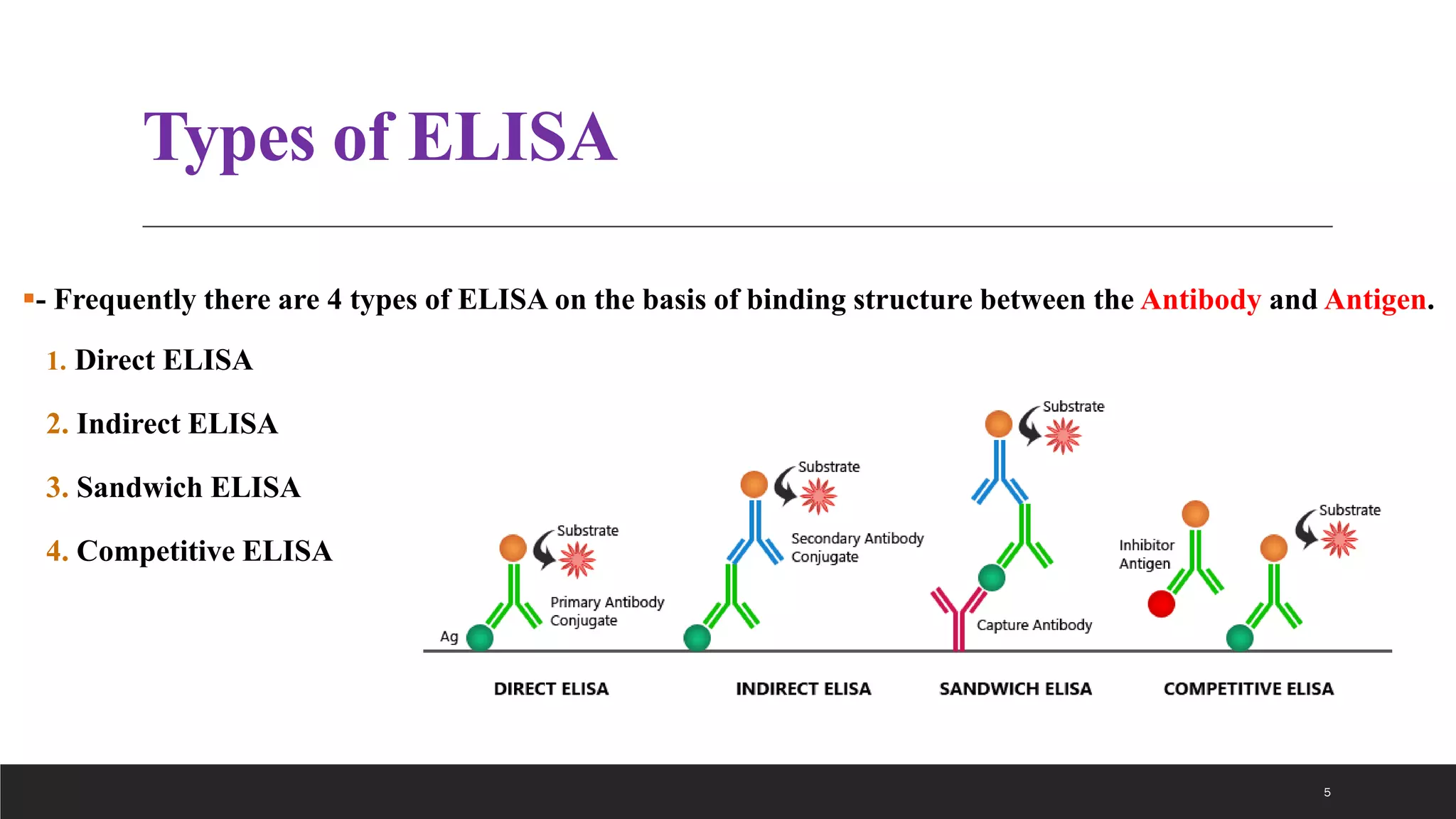
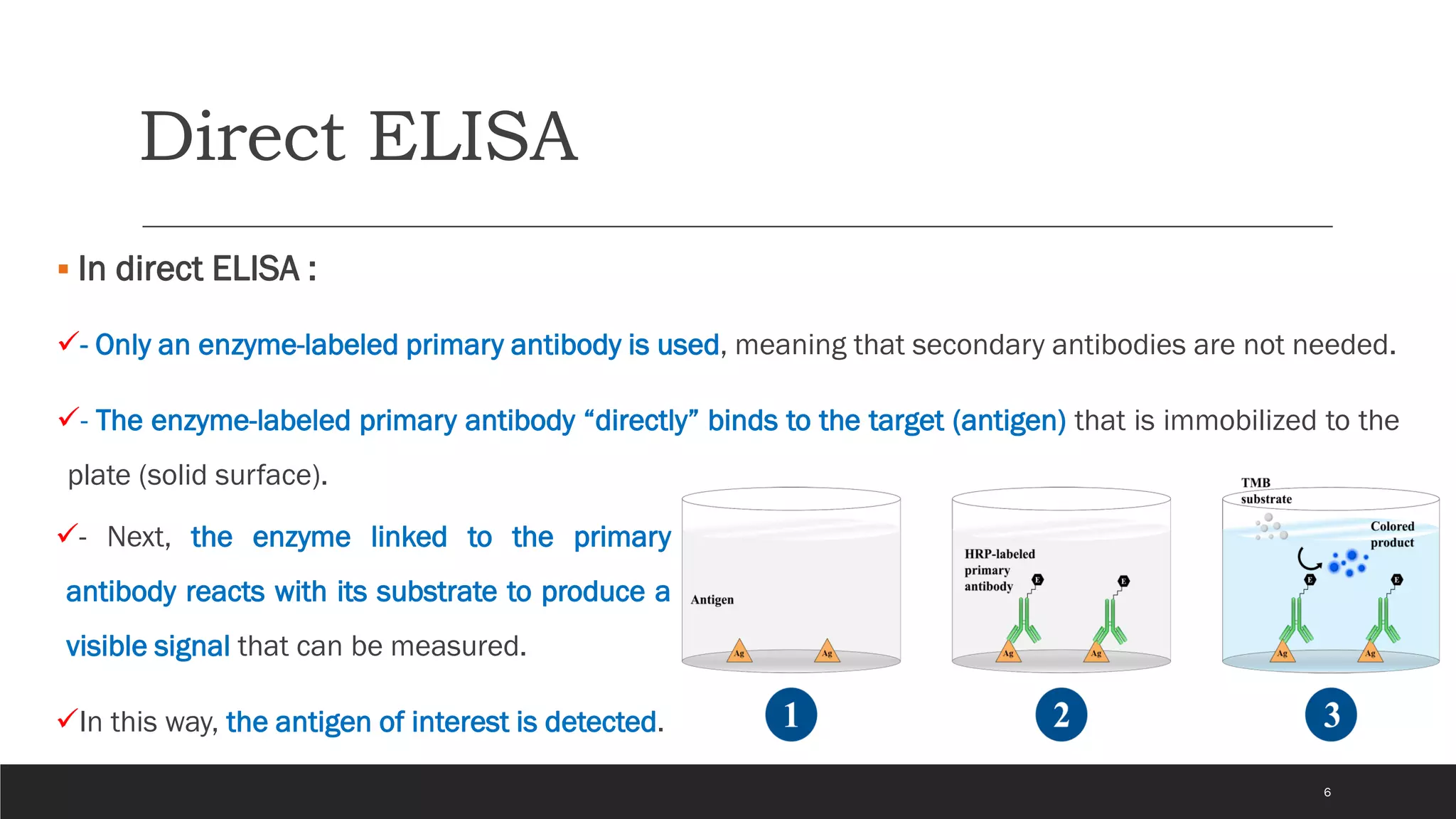
The document explains the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), a common laboratory technique used to measure antibodies or antigens in the blood. It outlines the principle, types (direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive), and application of ELISA in areas such as viral contamination screening, hormone level measurement, and infection detection. Equipment required for the test and the process of detecting bound antibodies or antigens using color intensity are also discussed.