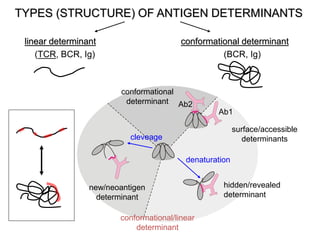
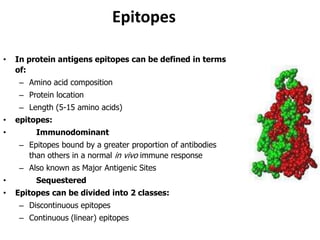
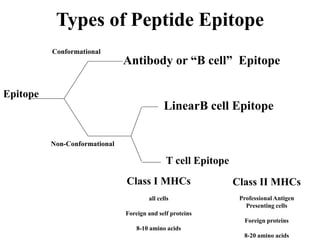
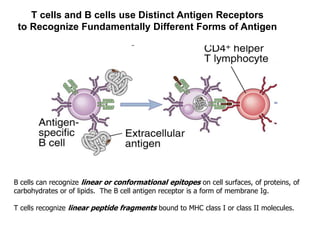
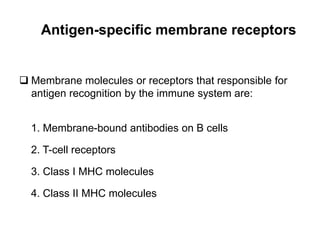
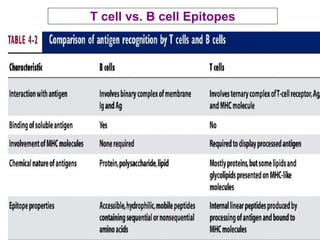
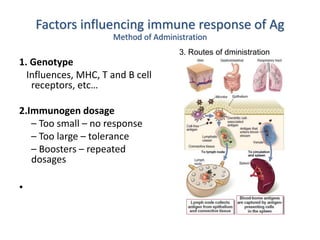
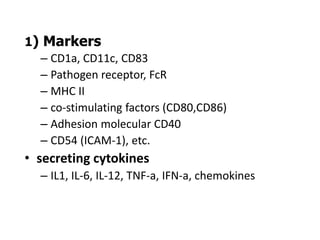
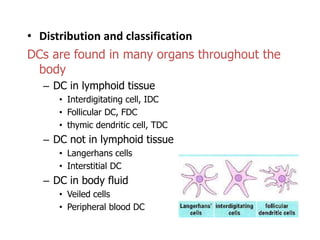
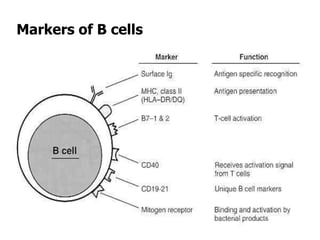
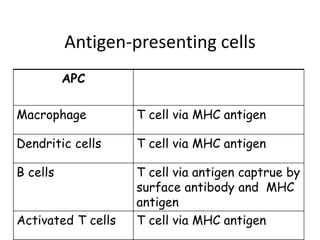
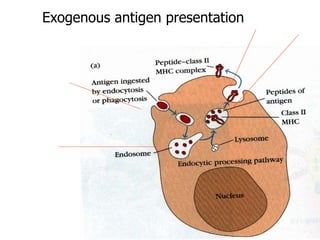
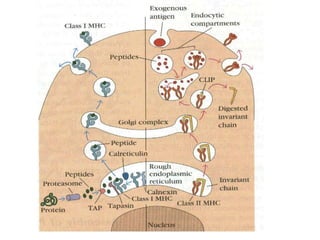
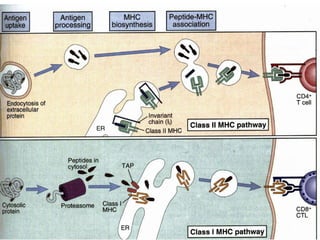
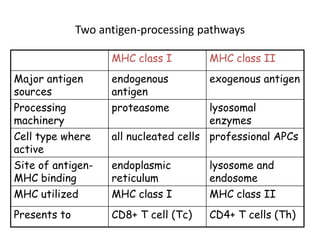
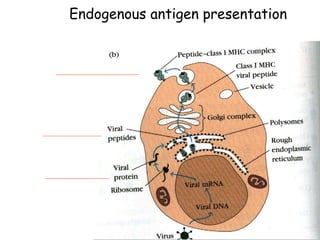
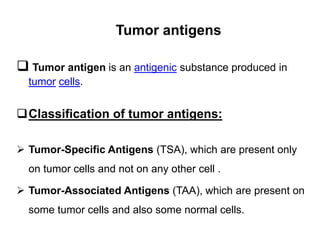
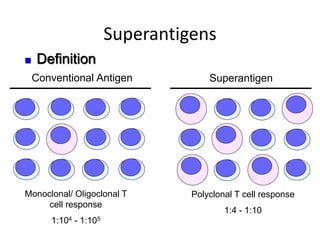
This document details the characteristics and classifications of antigens, including their definitions, subtypes, and mechanisms of immune response. It explains the roles of haptens, epitopes, and antigen-presenting cells, highlighting the distinctions between T-cell dependent and independent antigens and the properties influencing immune responses. Additionally, it discusses the significance of superantigens and the processing pathways for endogenous and exogenous antigens.