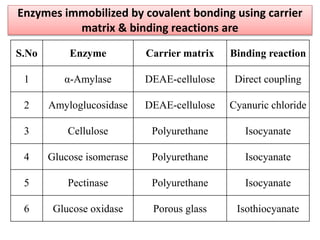
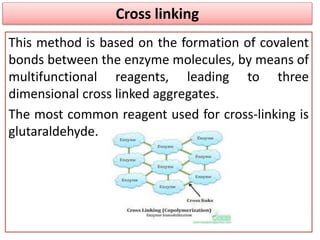
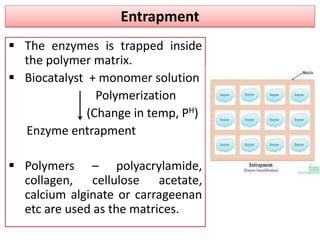
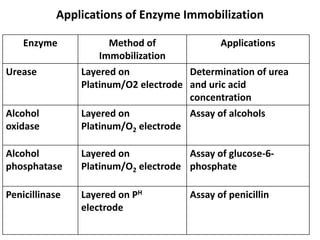
Enzyme immobilization involves restricting the movement of enzymes by confining them to a solid support. This allows for repeated use of enzymes, enhanced stability, and easy separation of products. Common immobilization methods include physical adsorption, covalent bonding, cross-linking, and entrapment. Immobilized enzymes have various applications, such as isomerization of glucose to fructose using immobilized glucose isomerase, and use of immobilized urease in compact artificial kidneys. Immobilization provides benefits like recyclability and cost-efficiency compared to free enzymes.