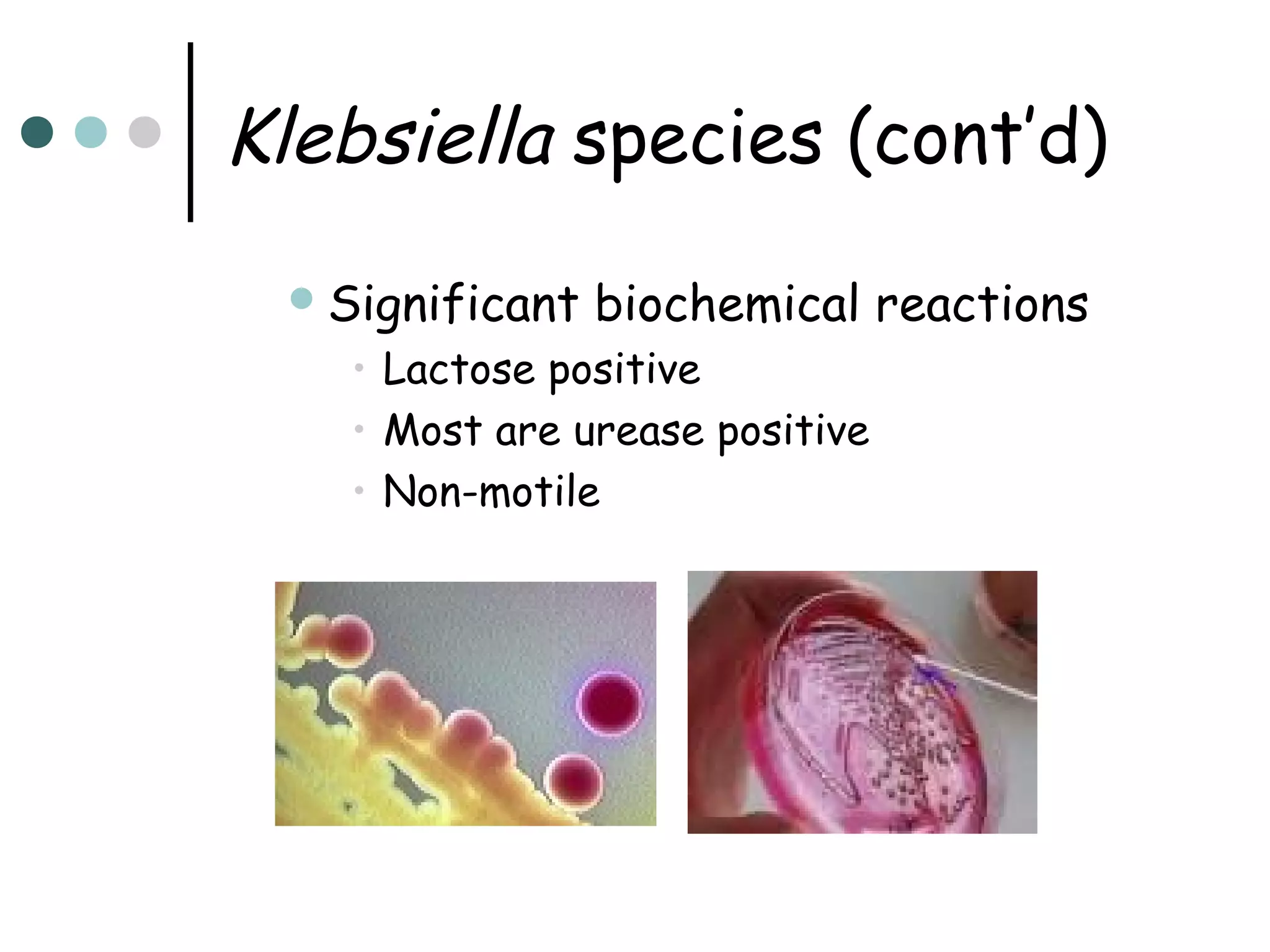
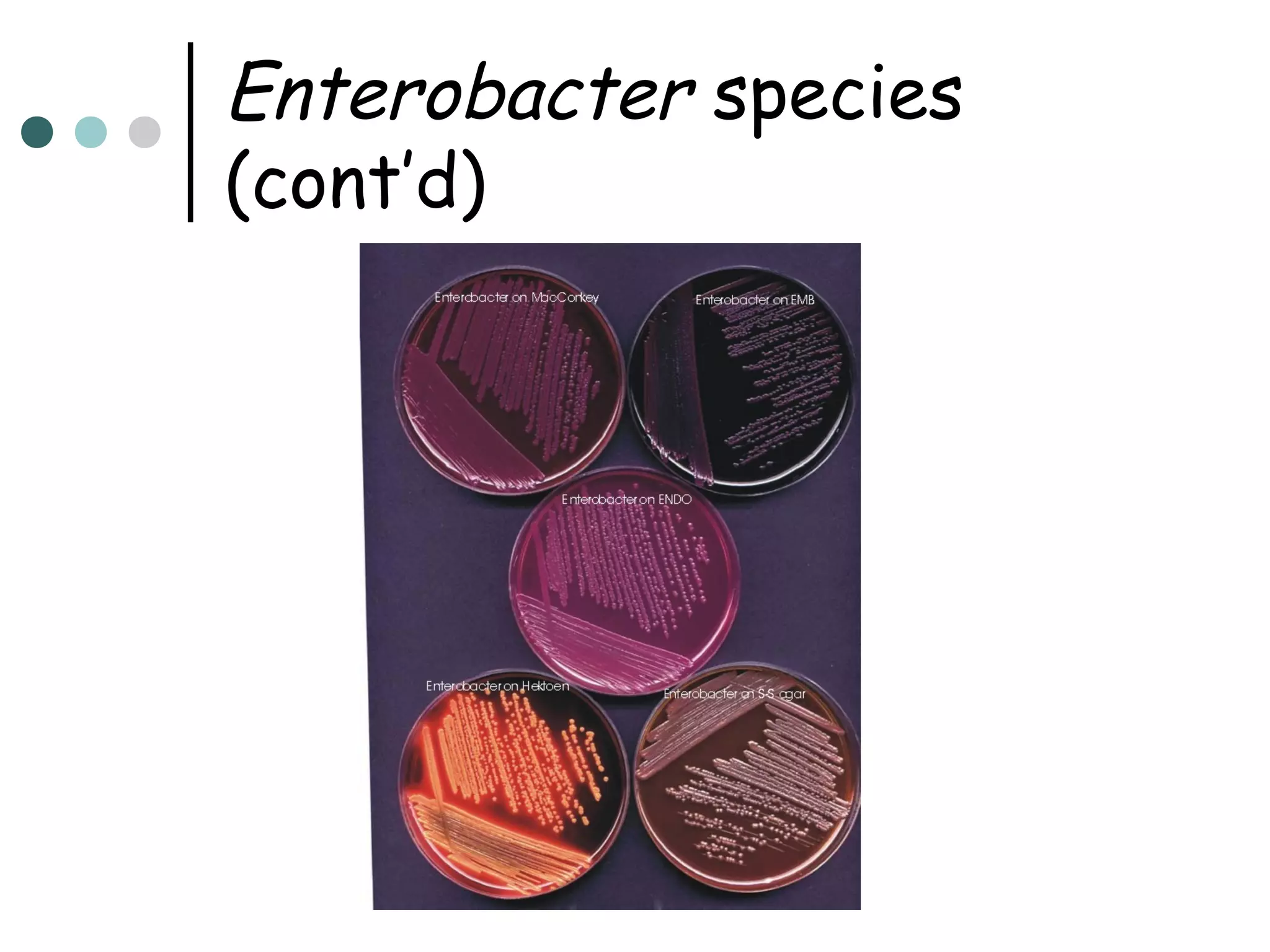
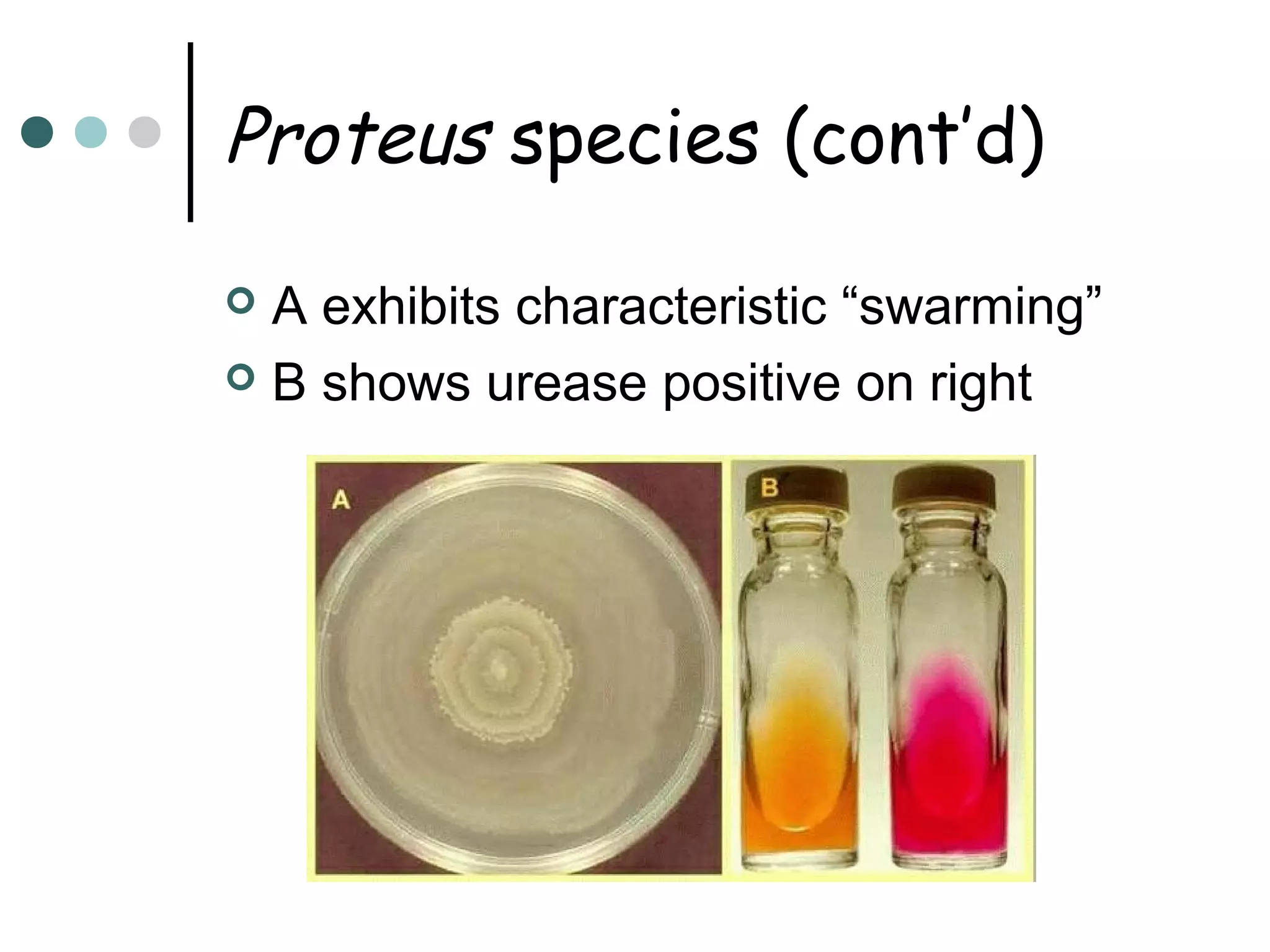
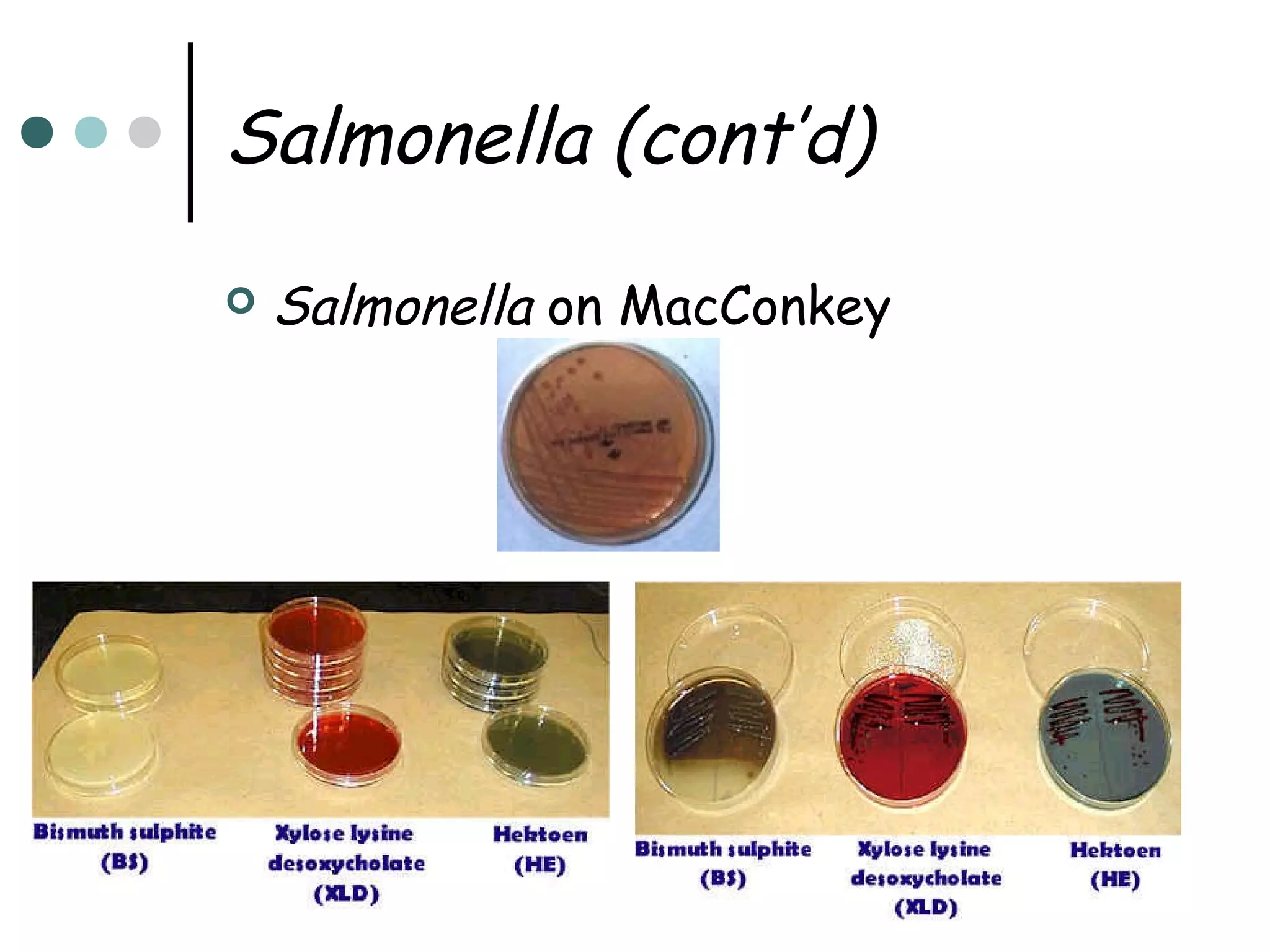
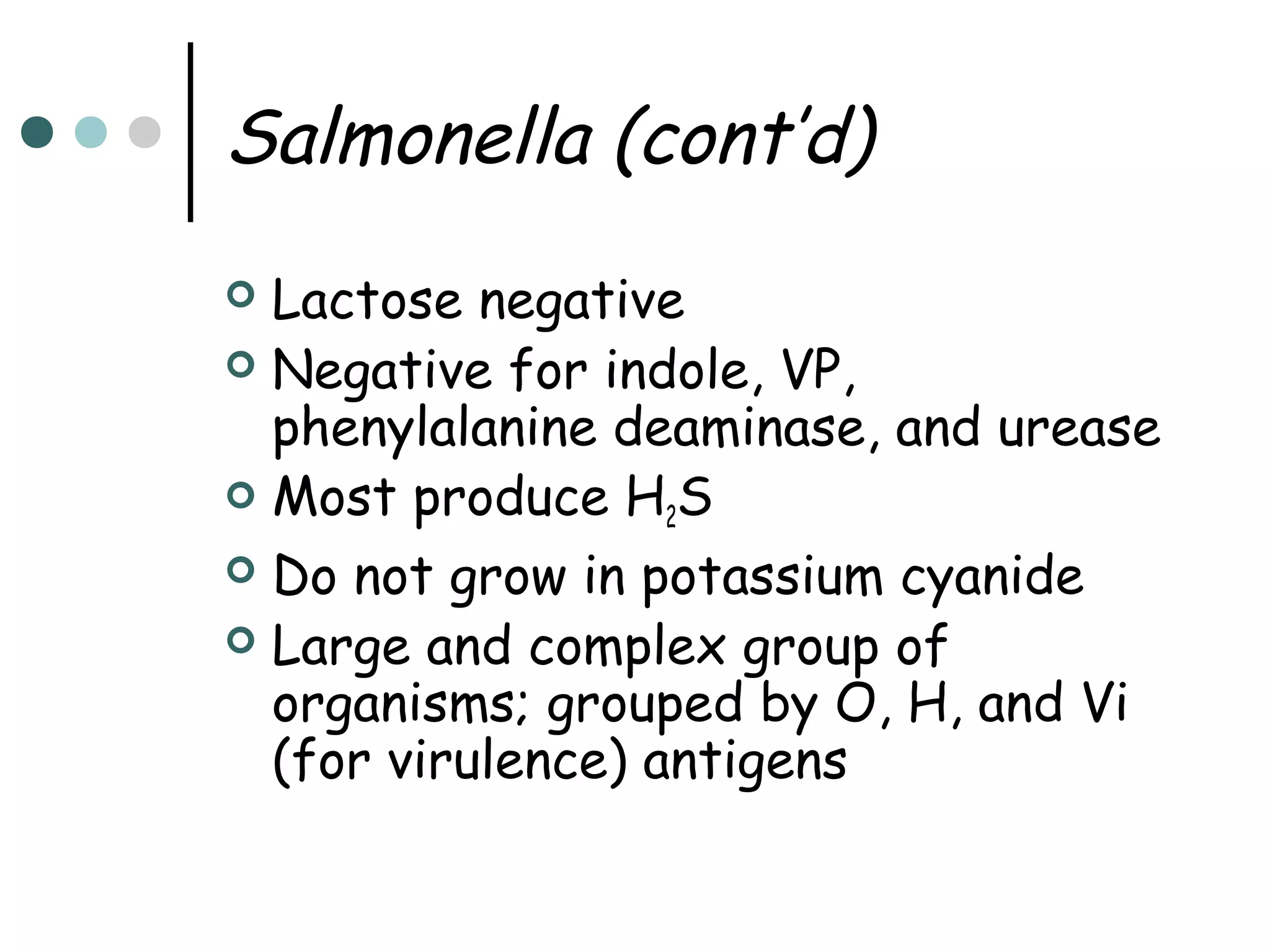
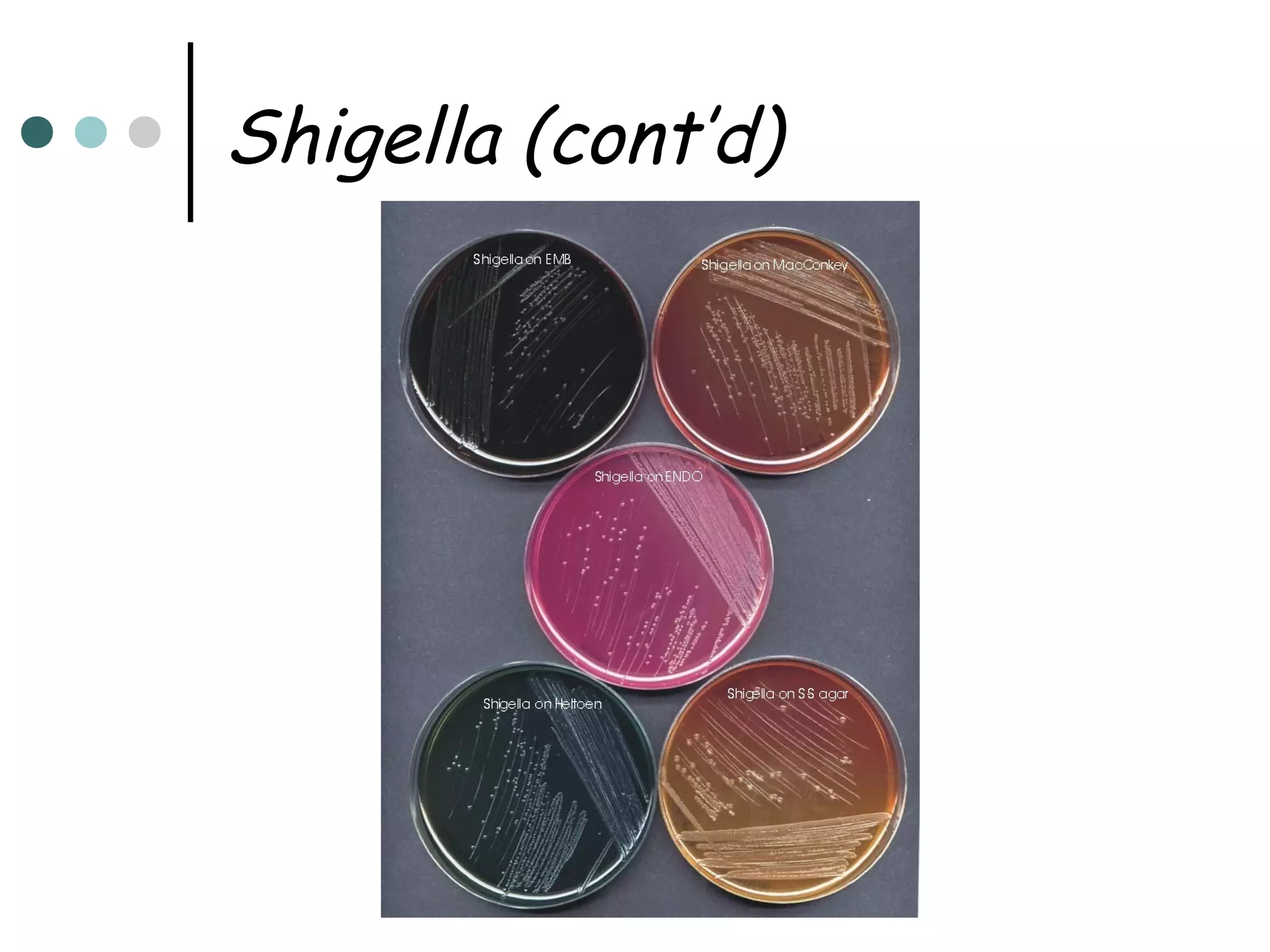
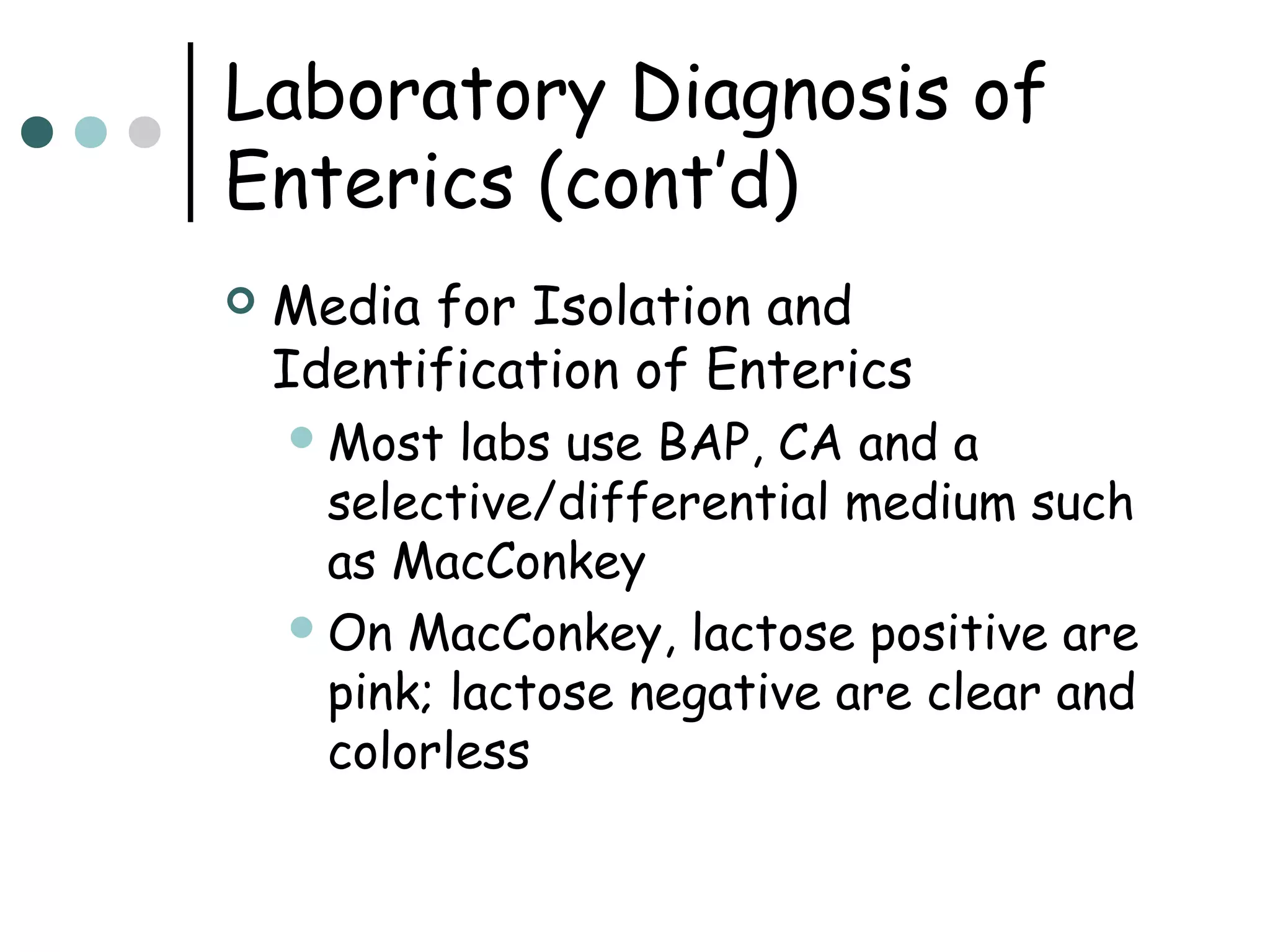
This document provides an overview of the Enterobacteriaceae family of bacteria, including their classification, characteristics, clinical significance, and important pathogenic species such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia. Key features of Enterobacteriaceae include being Gram-negative, non-spore forming bacilli that are oxidase-negative, reduce nitrates to nitrites, and ferment glucose. They can cause a variety of opportunistic infections and some are primary intestinal pathogens. The document describes the microbiological properties and diseases associated with major pathogenic genera.