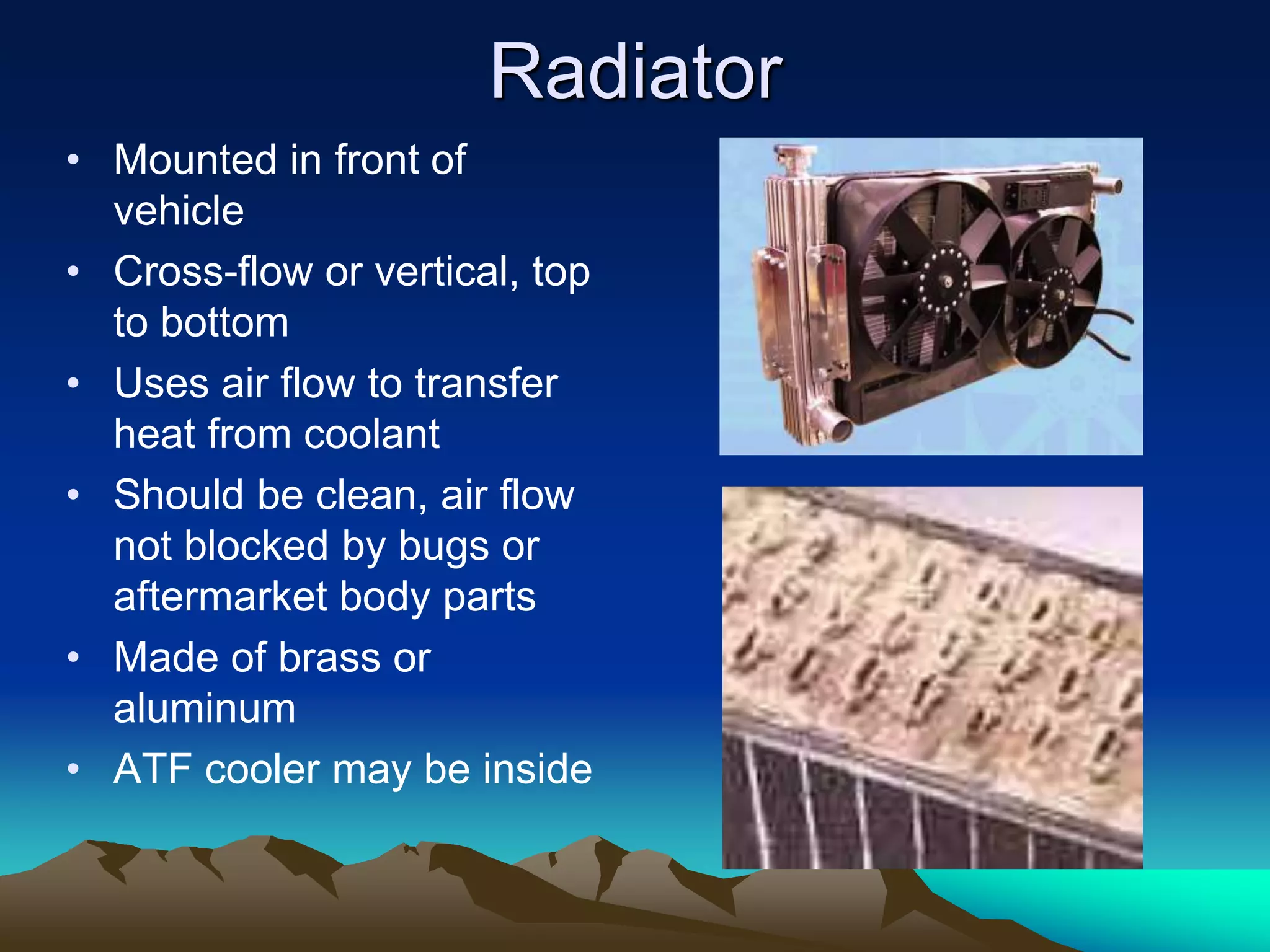
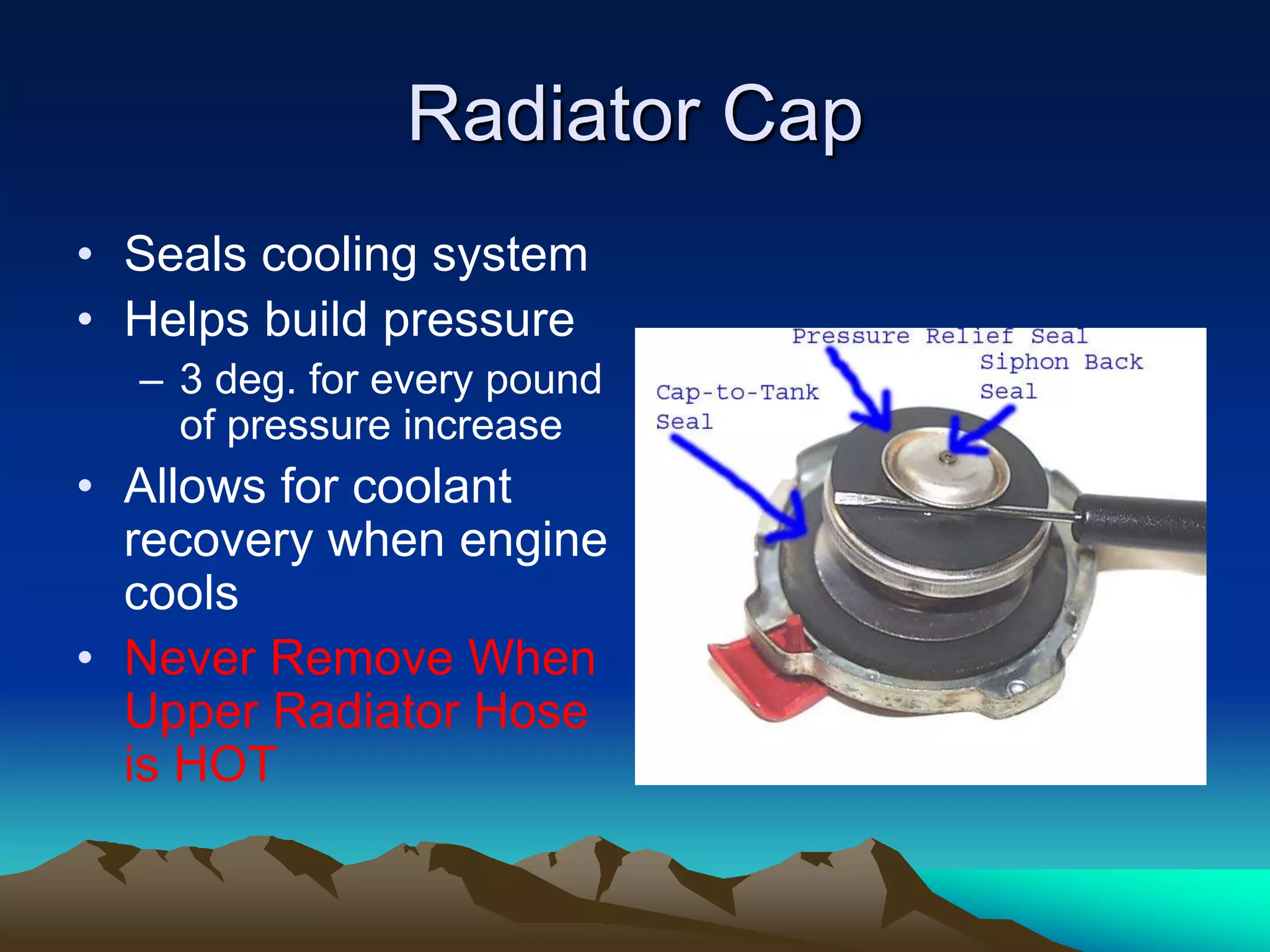
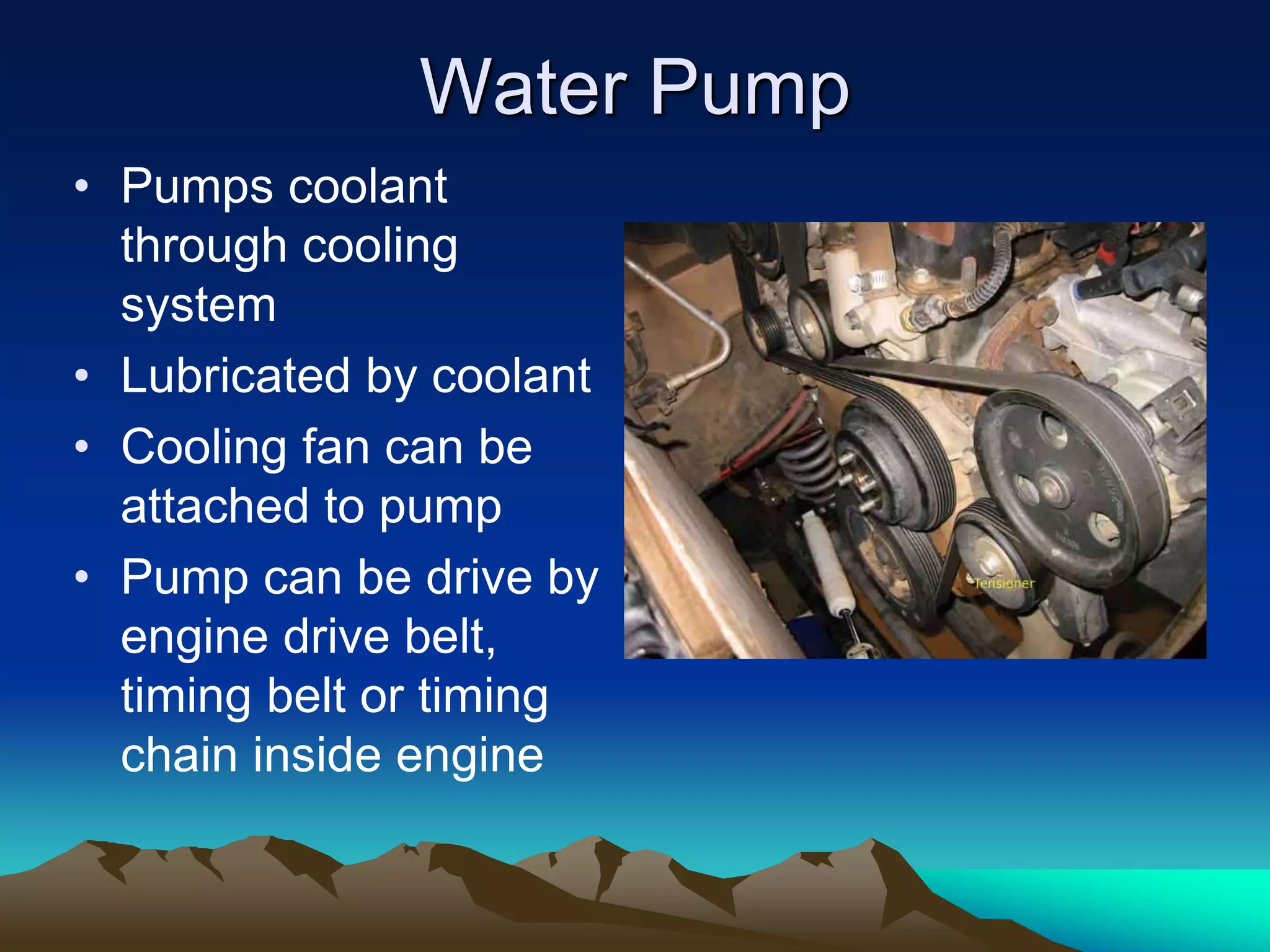
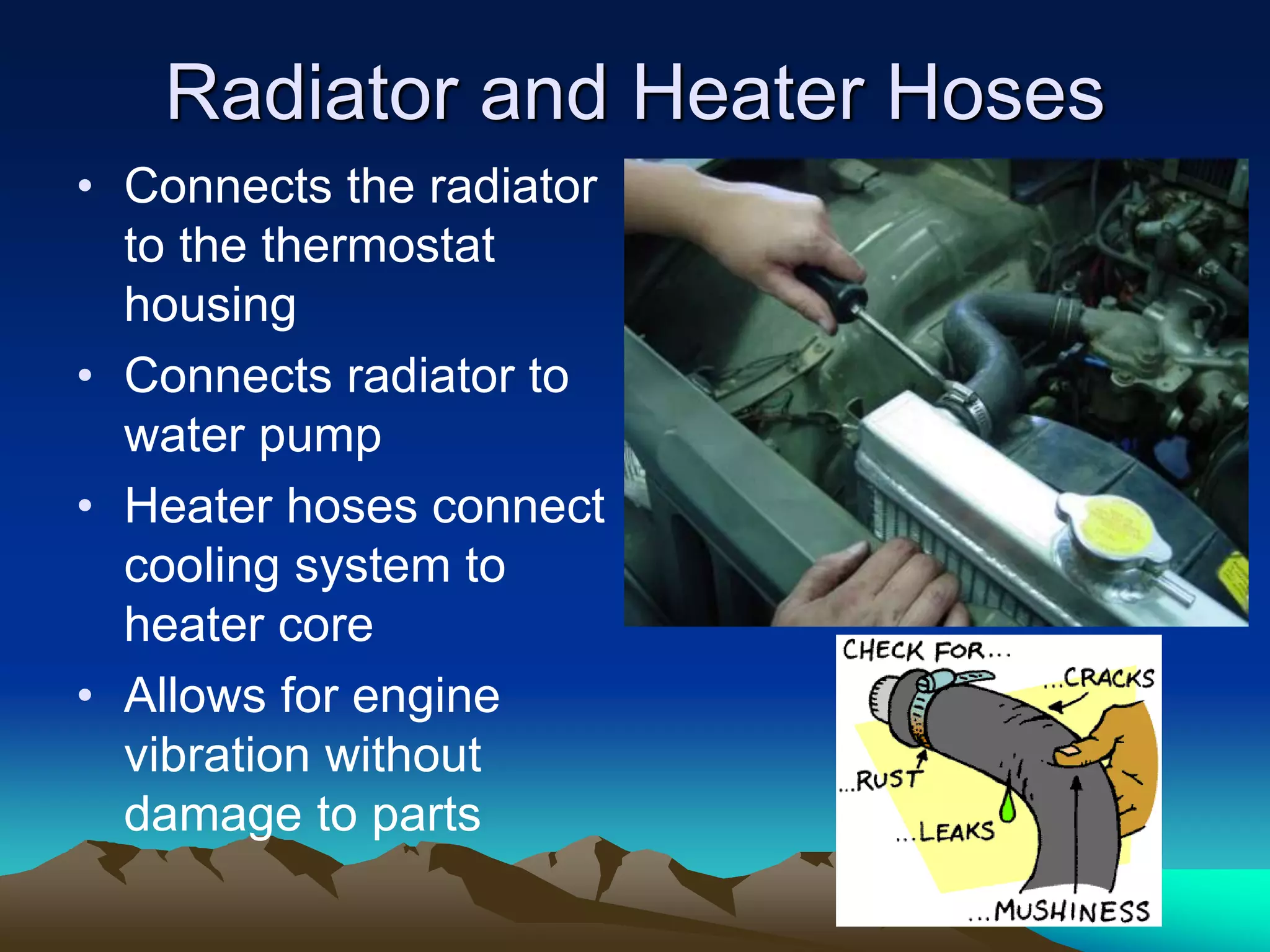
The document summarizes the main components of an automotive cooling system, including coolant, radiator, heater core, radiator cap, water pump, thermostat, hoses, overflow bottle, and cooling fan. It describes the purpose and function of each component in transferring heat from the engine to the radiator and maintaining the engine's optimal operating temperature. The document also provides guidelines for diagnosing cooling system issues through pressure testing, checking for leaks with fluorescent dye, and inspecting other components like the radiator cap and antifreeze concentration.