This document provides an introduction to engine terminology by defining key terms:
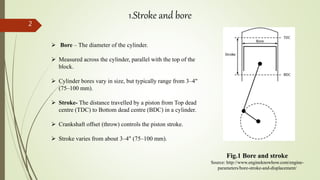
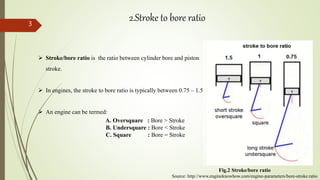
- Bore is the diameter of the cylinder, while stroke is the distance the piston travels. The stroke-to-bore ratio affects engine characteristics.
- Cylinder displacement is the volume displaced by the piston from bottom to top dead center. Total engine displacement is the sum of the displacements of all cylinders.
- Other terms defined include compression ratio, air-fuel ratio, torque, power, volumetric efficiency, thermal efficiency, mean effective pressure, indicated horsepower, and brake horsepower. Factors that influence various engine parameters are also discussed.