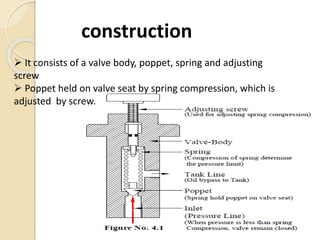
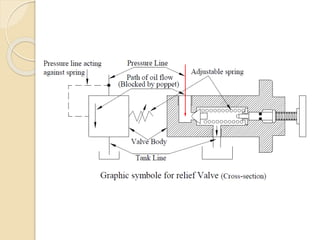
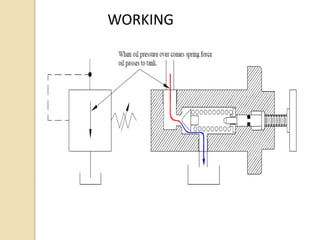
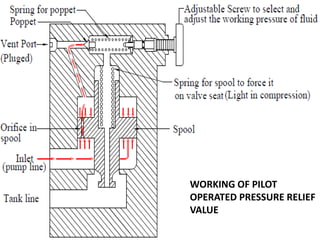
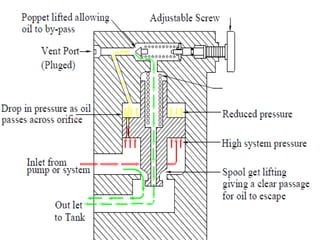
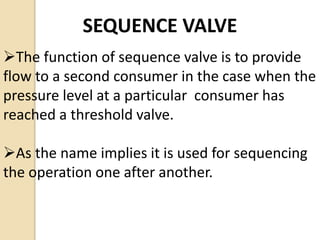
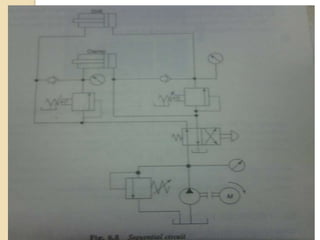
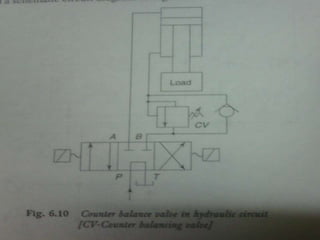
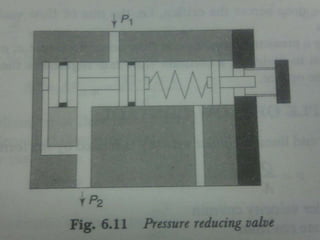
This document discusses different types of hydraulic pressure control valves. It describes pressure relief valves, pilot operated relief valves, sequence control valves, and other types. Pressure relief valves limit pressure by diverting fluid to the reservoir when pressure reaches a set point. Pilot operated relief valves use a piston or spool controlled by a pilot valve. Sequence valves provide flow to a second actuator after the first reaches a threshold pressure. The document also provides examples of applications for different valve types.