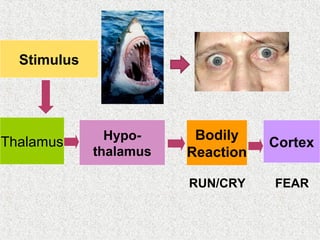
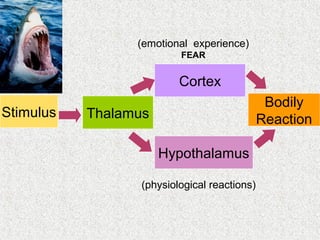
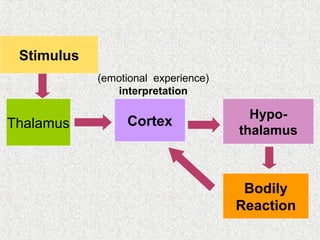
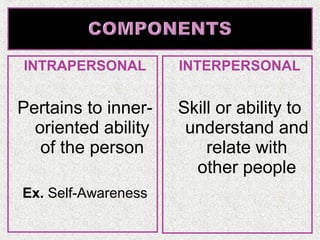
The document discusses emotions and various theories of emotion. It defines emotion as a spontaneous reaction to pleasurable or unpleasurable stimuli, accompanied by physiological changes and readiness to act. Theories covered include the James-Lange theory that emotions arise from physiological arousal, and the Cannon-Bard theory that arousal is non-specific. The document also outlines characteristics of emotions, basic emotion types, steps for managing emotions, and defines emotional intelligence.