This document provides an overview of emotions, including:
1) It discusses the history of studying emotions from Aristotle to Hippocrates.
2) It defines emotions as complex feeling states involving physiological, cognitive, and behavioral components. Basic emotions include happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise, and disgust.
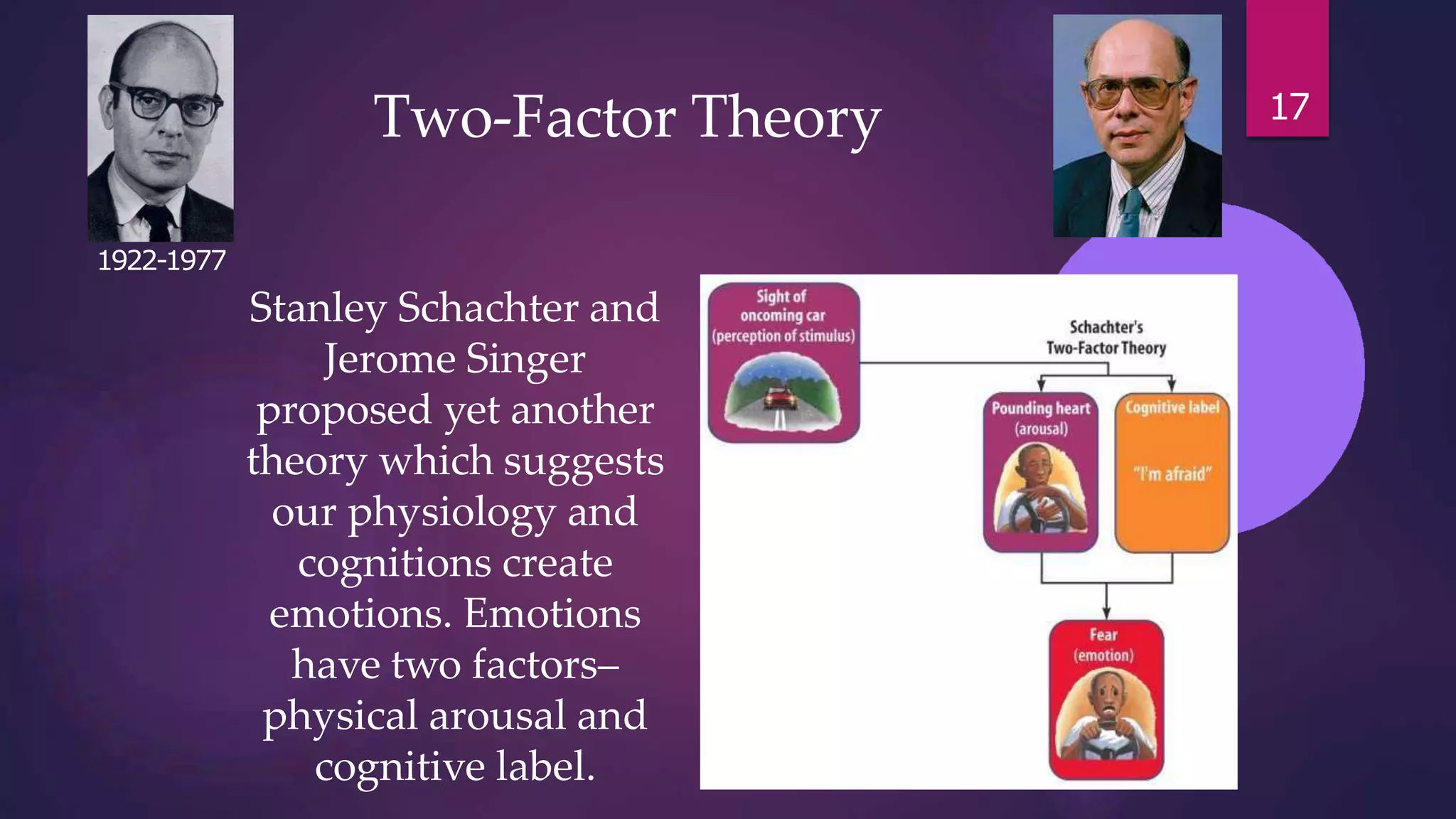
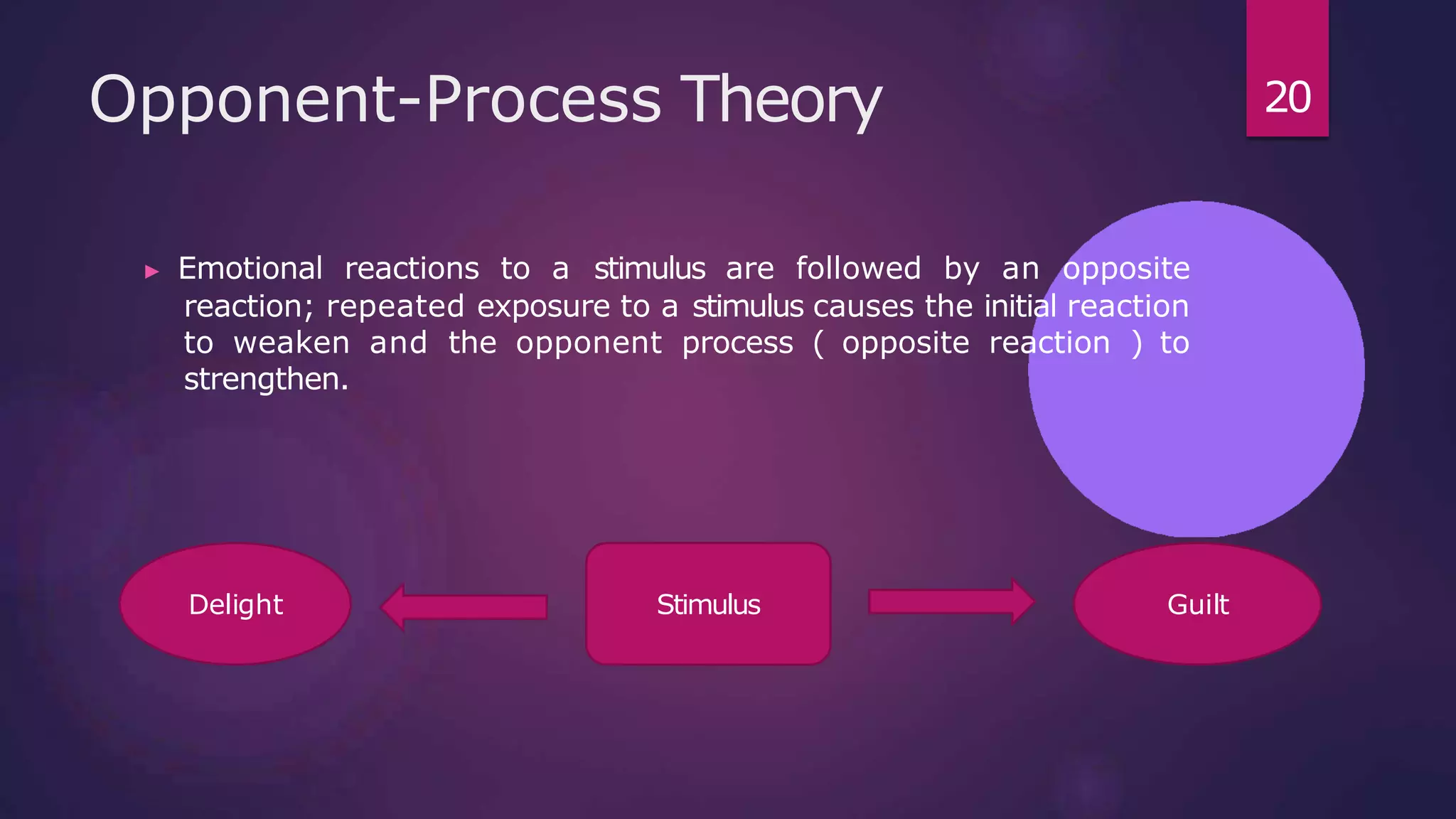
3) Emotions are associated with mood, temperament, personality, disposition, and motivation. Theories of emotion include the Cannon-Bard theory, James-Lange theory, Two-Factor theory, and Facial Feedback Hypothesis.
4) Factors that affect emotions include genetics, cognition, memory, external stimuli, health, and circadian rhythm. Emotions can