This document provides an overview of emotions, including:
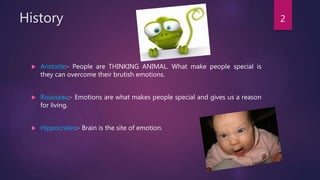
1) It discusses the history of how emotions have been viewed from Aristotle saying they should be overcome to Rousseau saying they make us human.
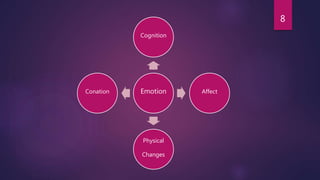
2) It defines emotions as intense feelings directed at something that involve physiological, behavioral, and cognitive components.
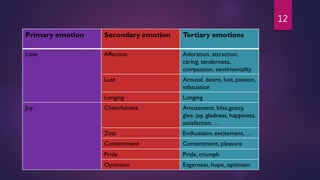
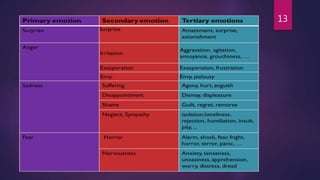
3) Basic emotions include happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise, and disgust, which can combine to form more complex emotions.
4) Theories of emotion are discussed, such as the James-Lange theory that physiological changes precede emotions and the Cannon-Bard theory that physiological arousal and emotions occur simultaneously.