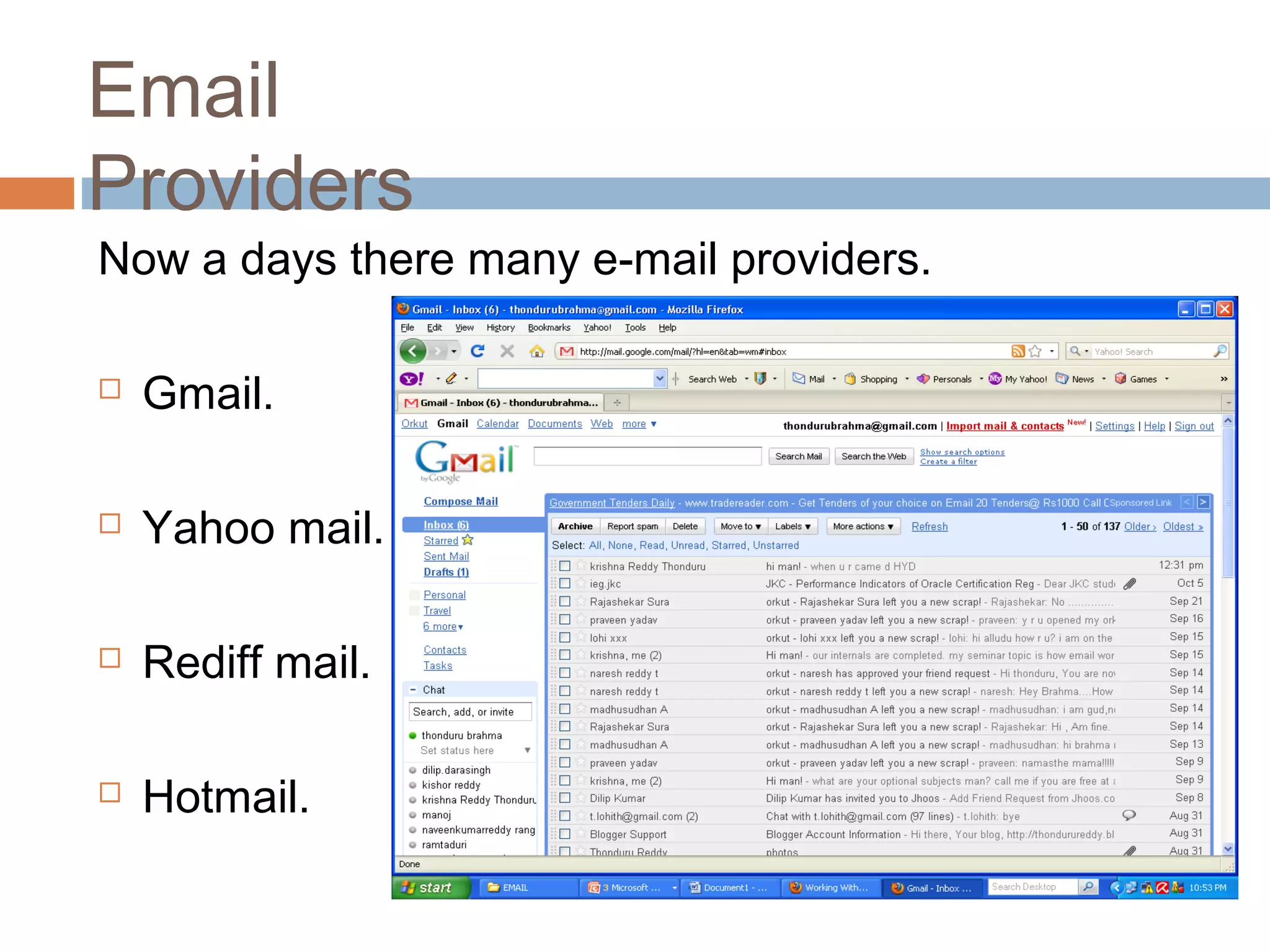
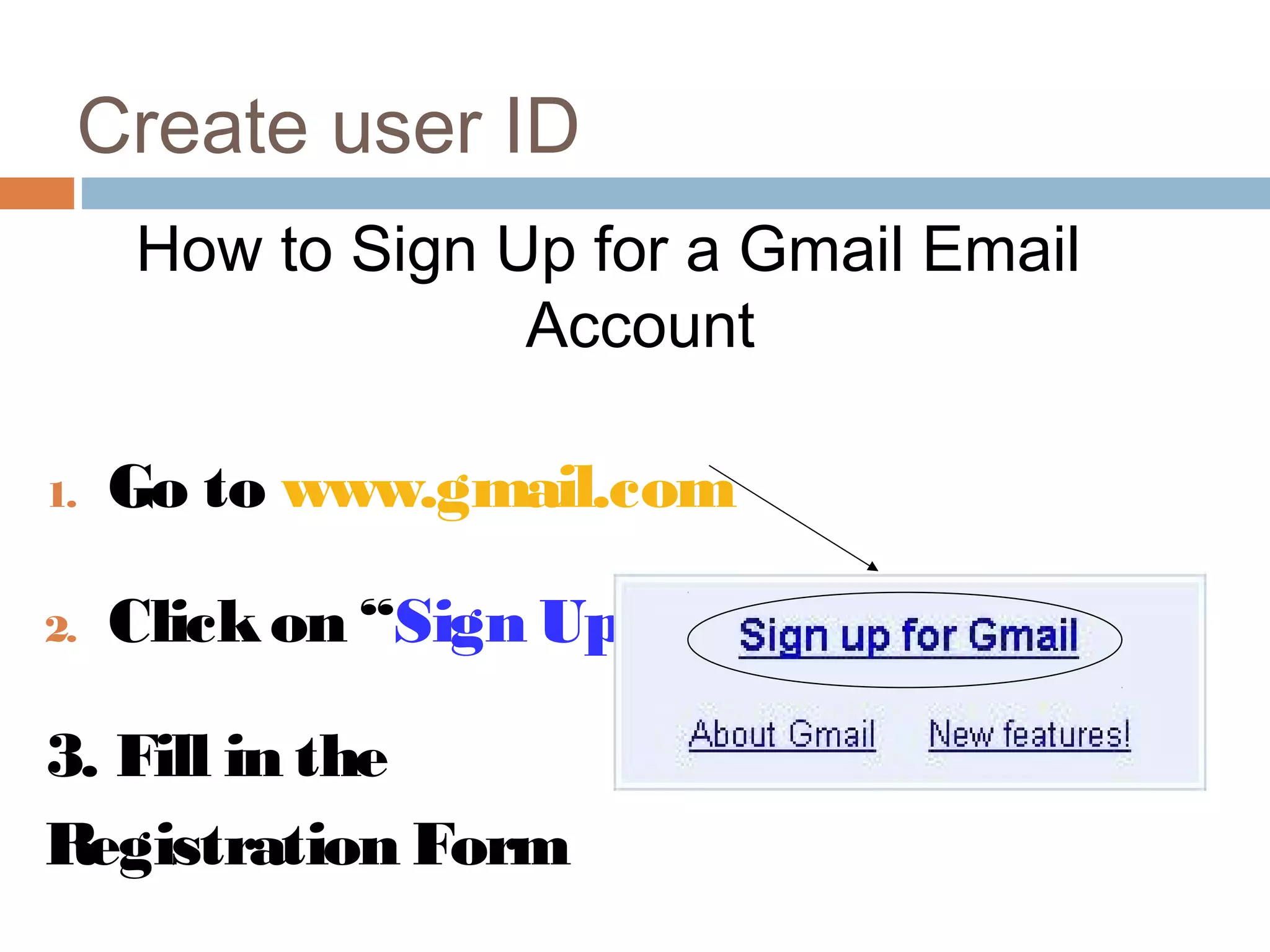
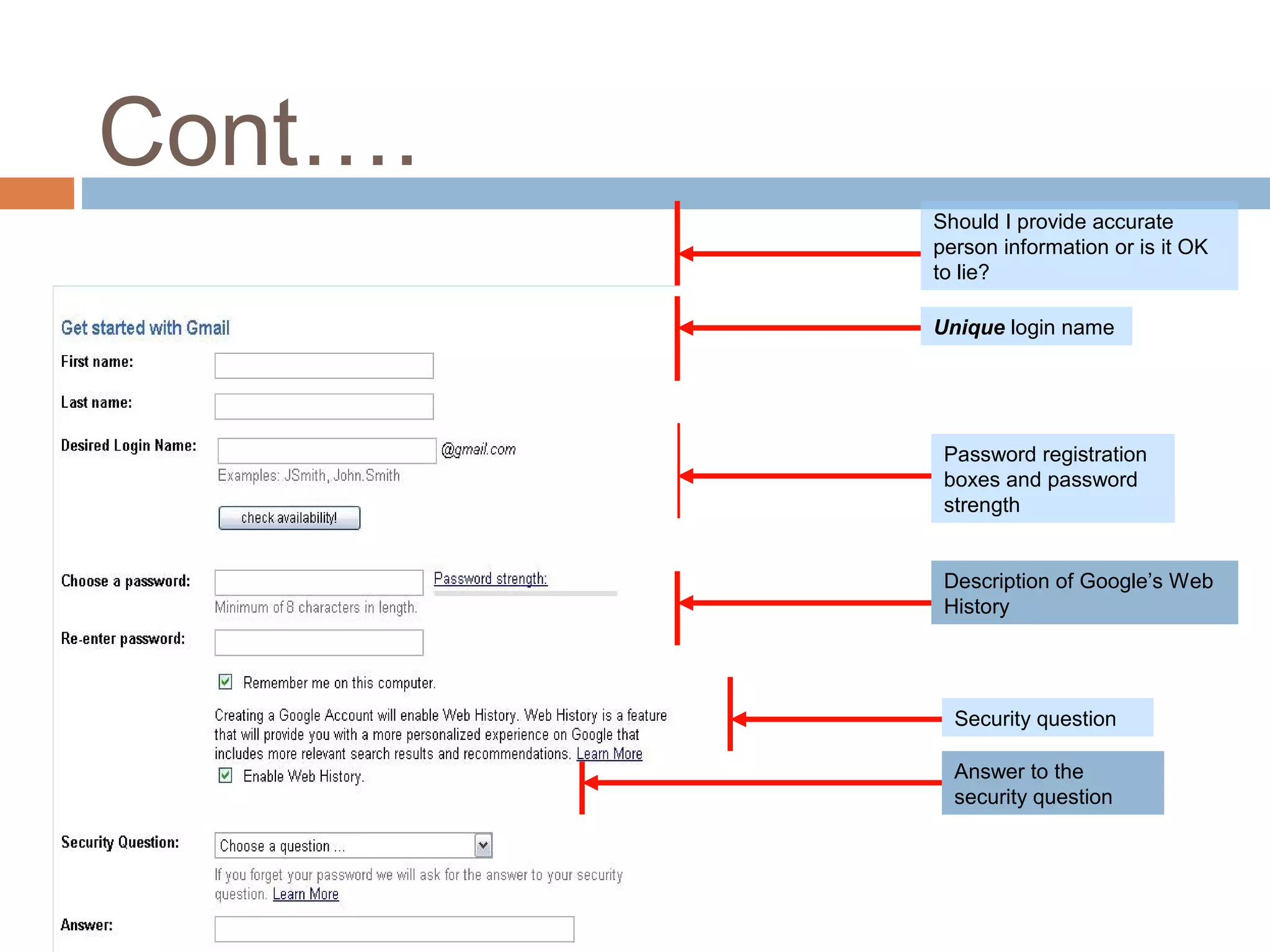
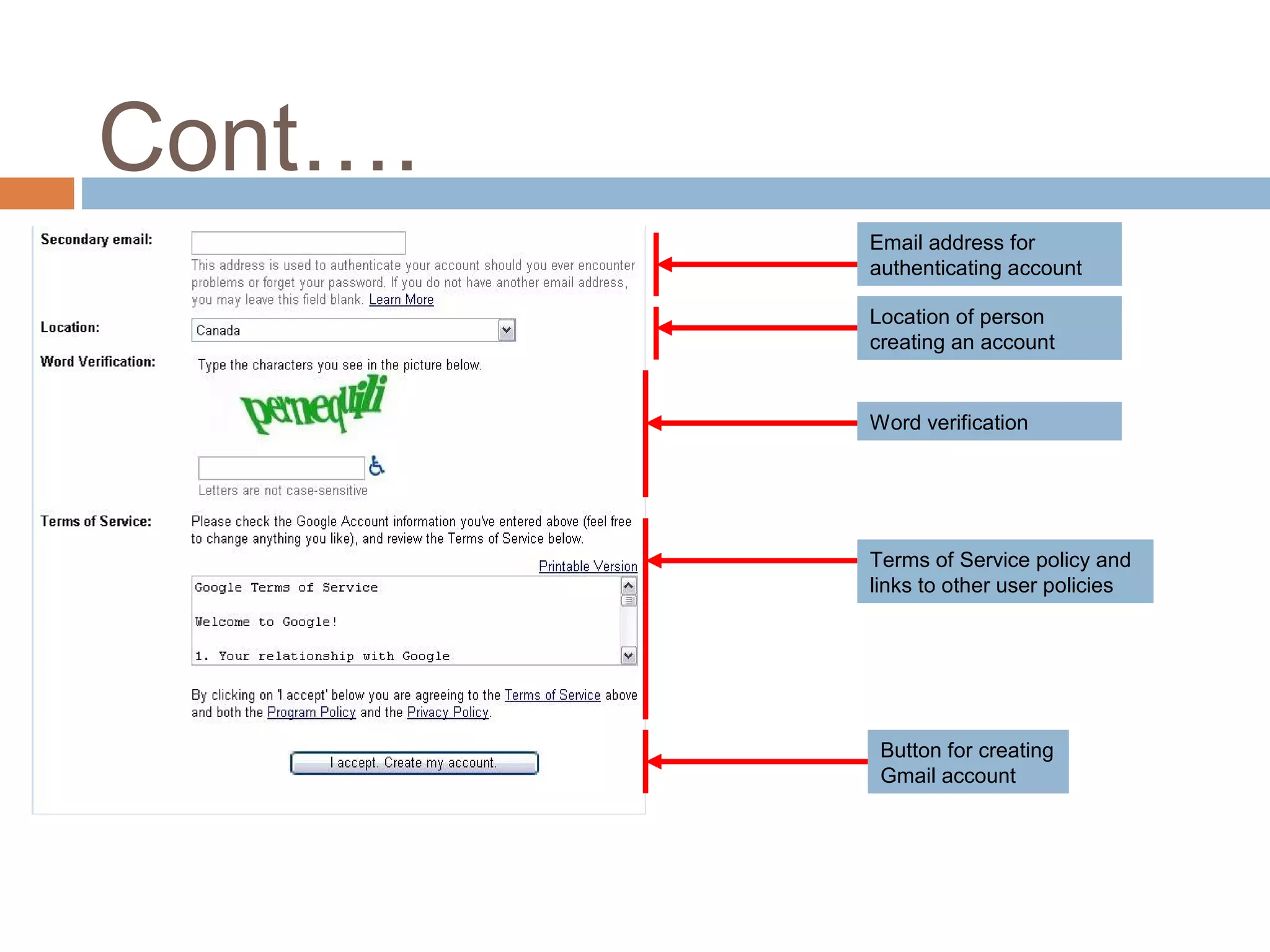
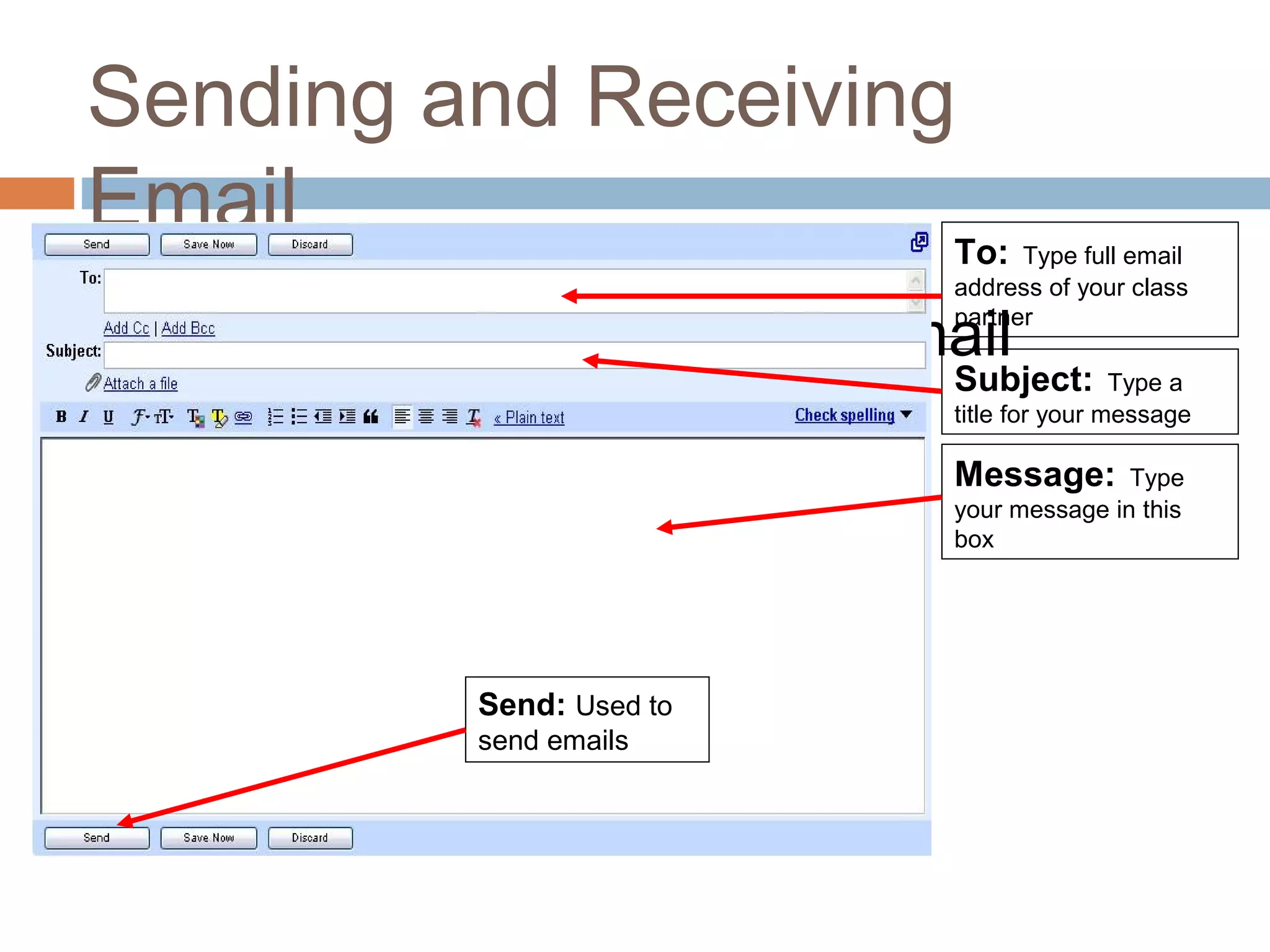
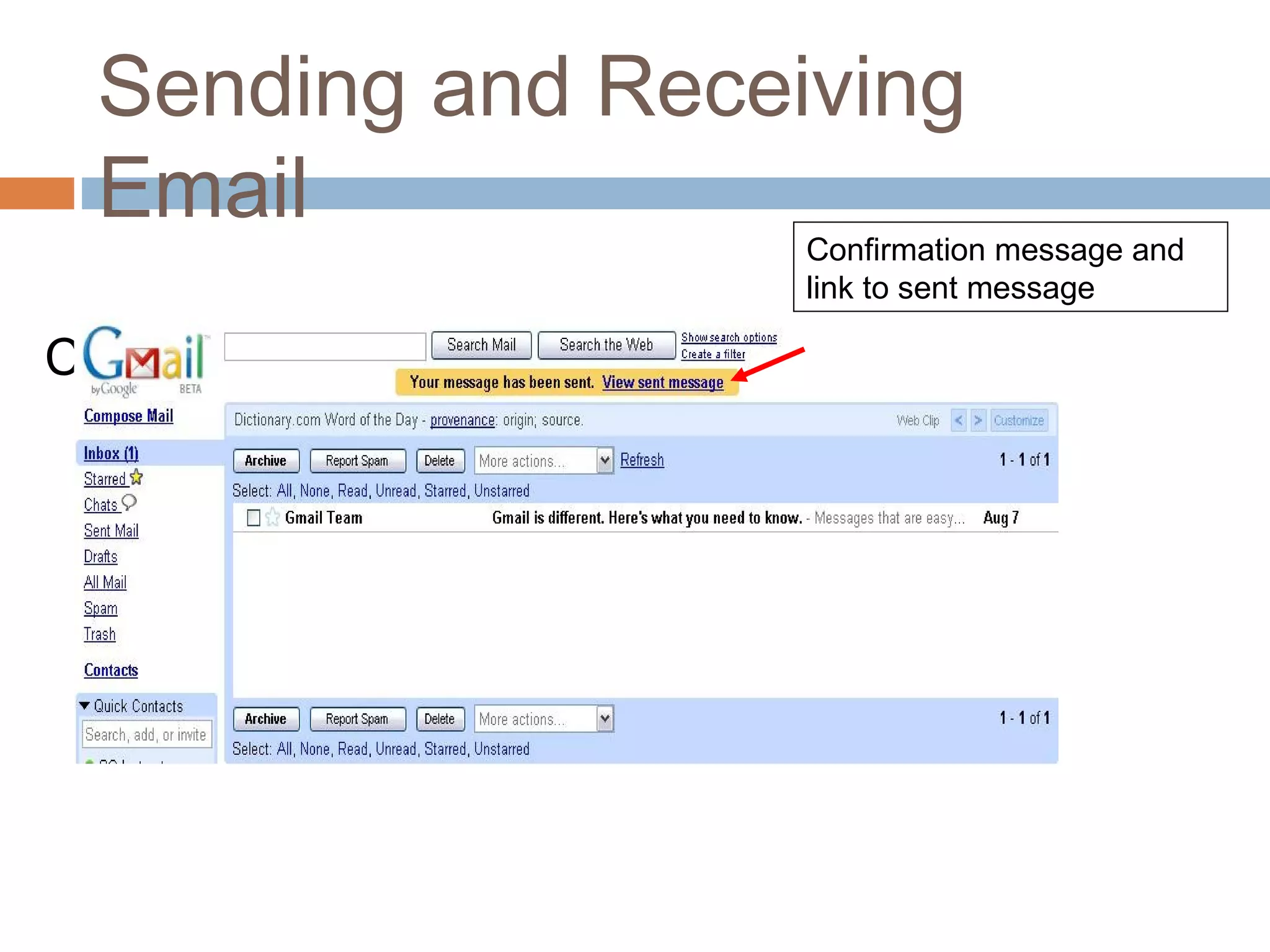
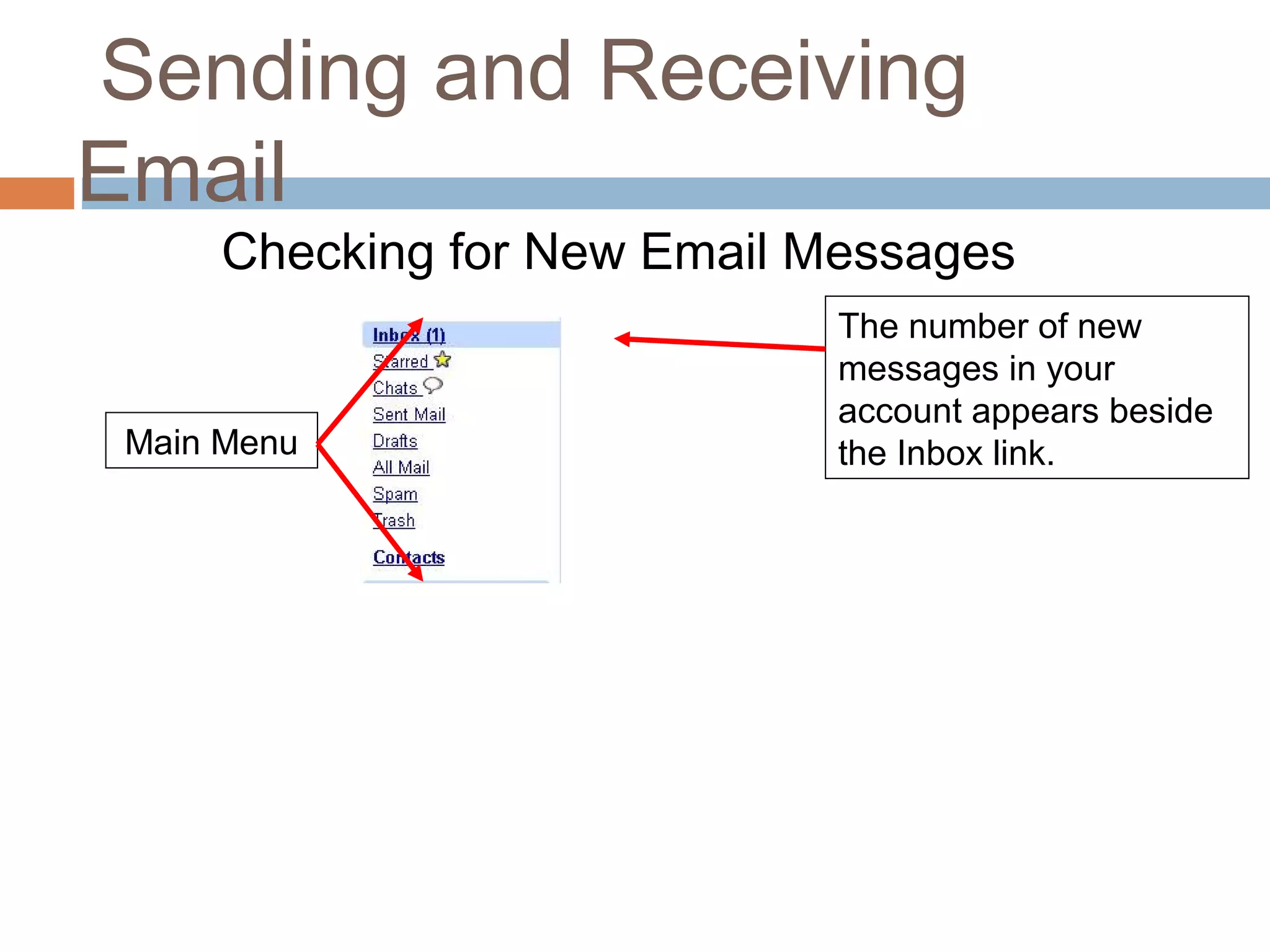
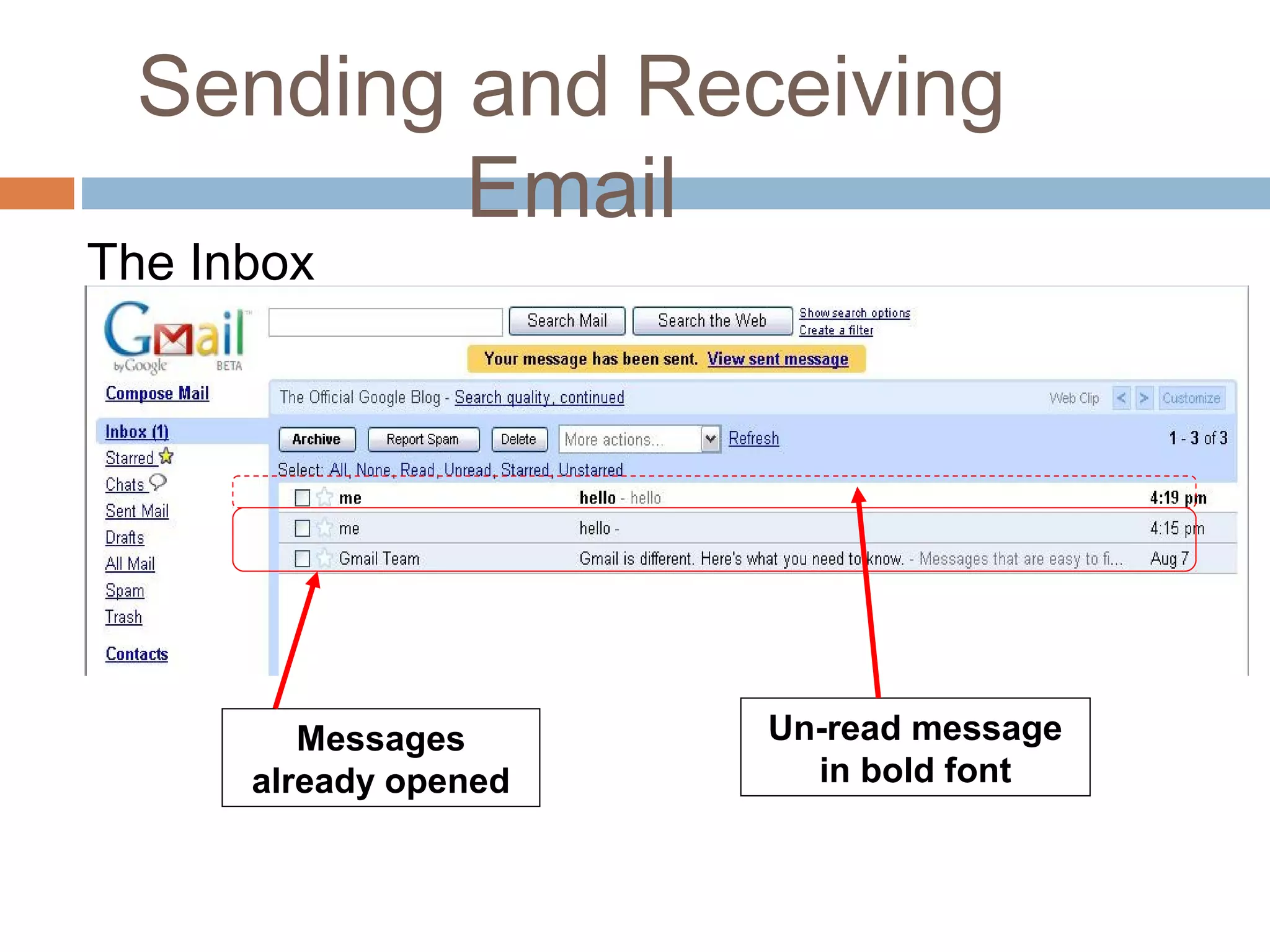
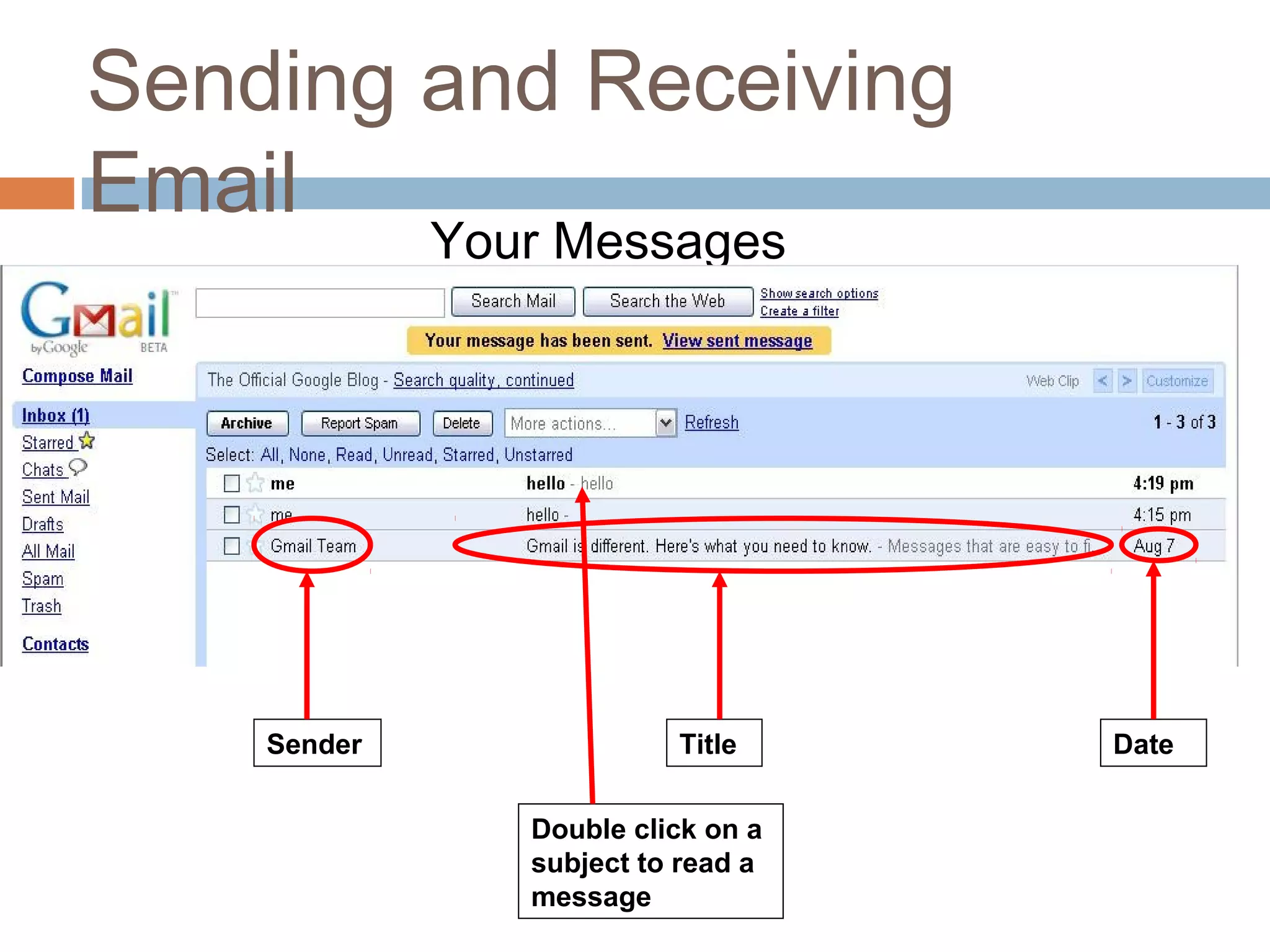
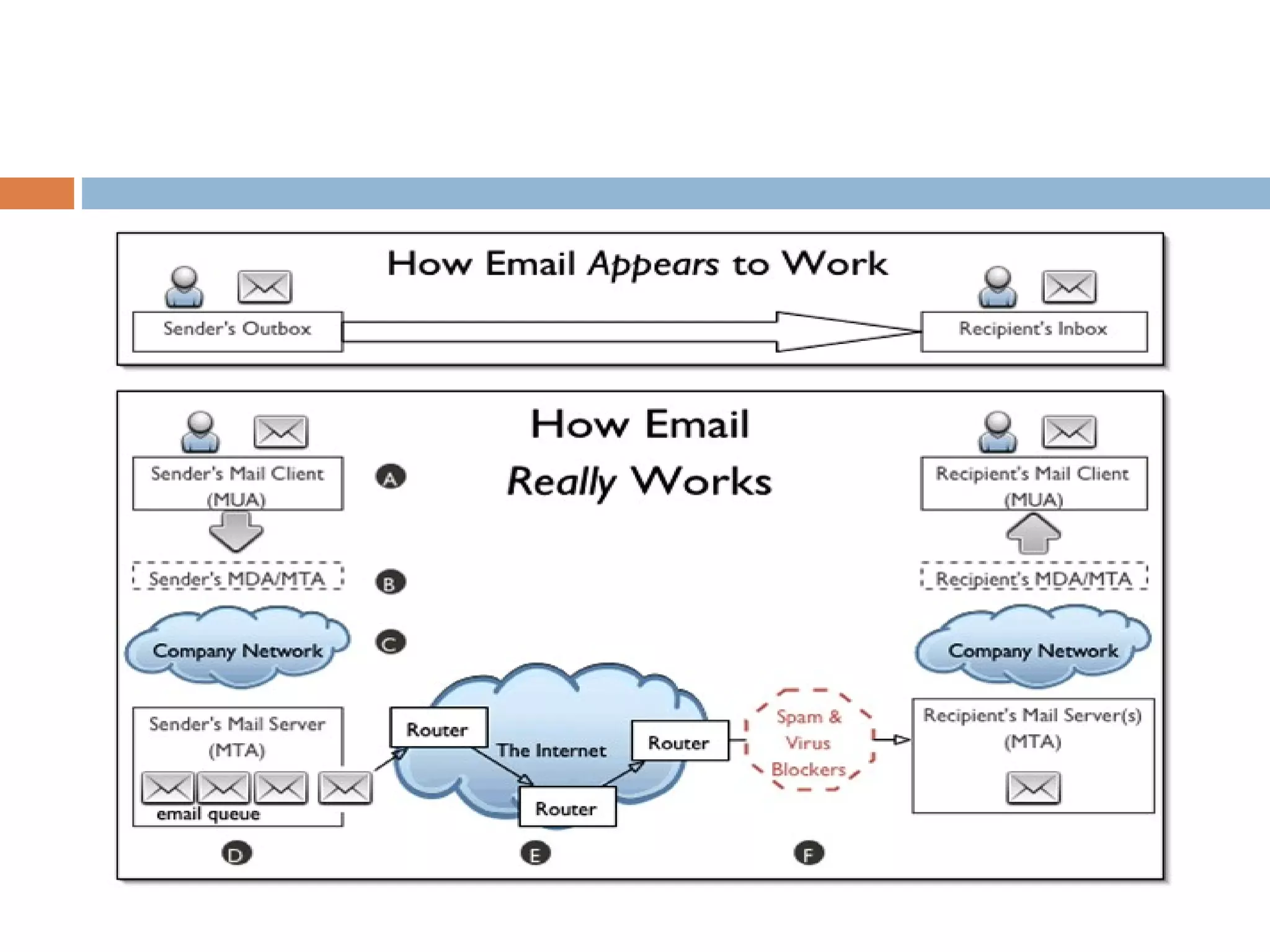
This document provides an overview of email, including its history, components, models, and threats. It discusses how email works using a client-server model and store-and-forward architecture. Common email providers and components like headers, bodies, and attachments are described. Reasons for email bouncing and threats like spoofing and bombing are covered, along with methods for overcoming threats like encryption.