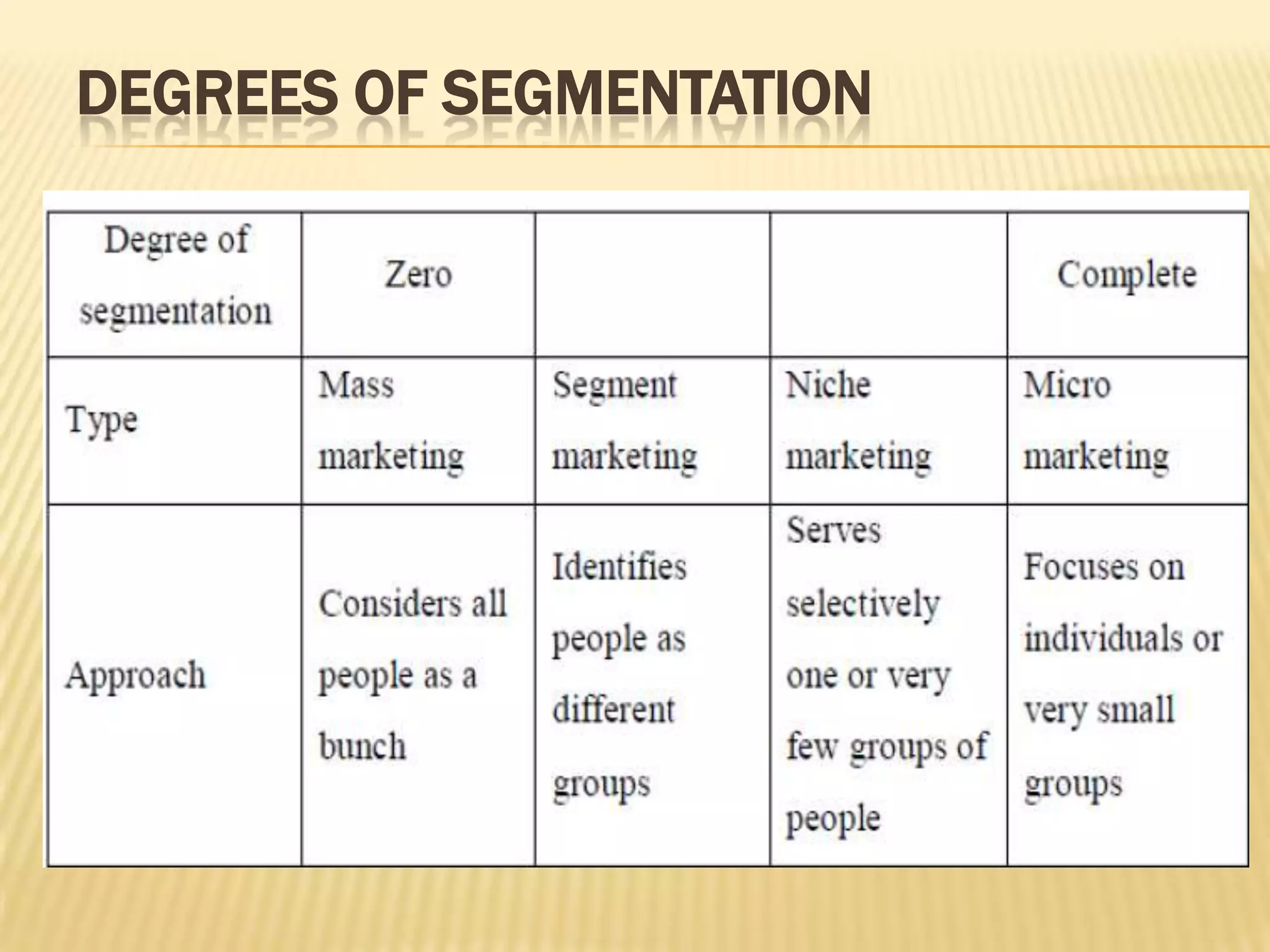
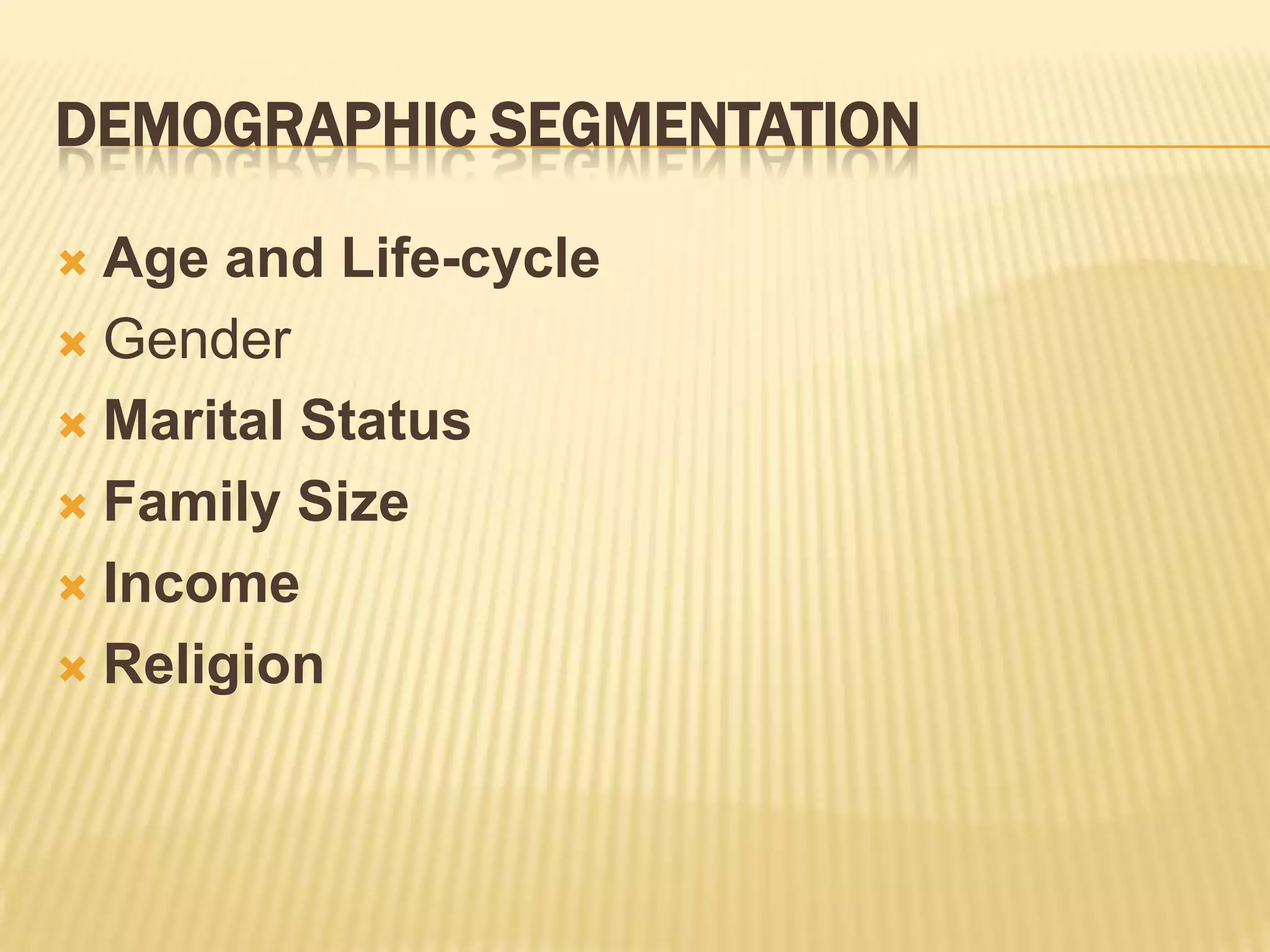
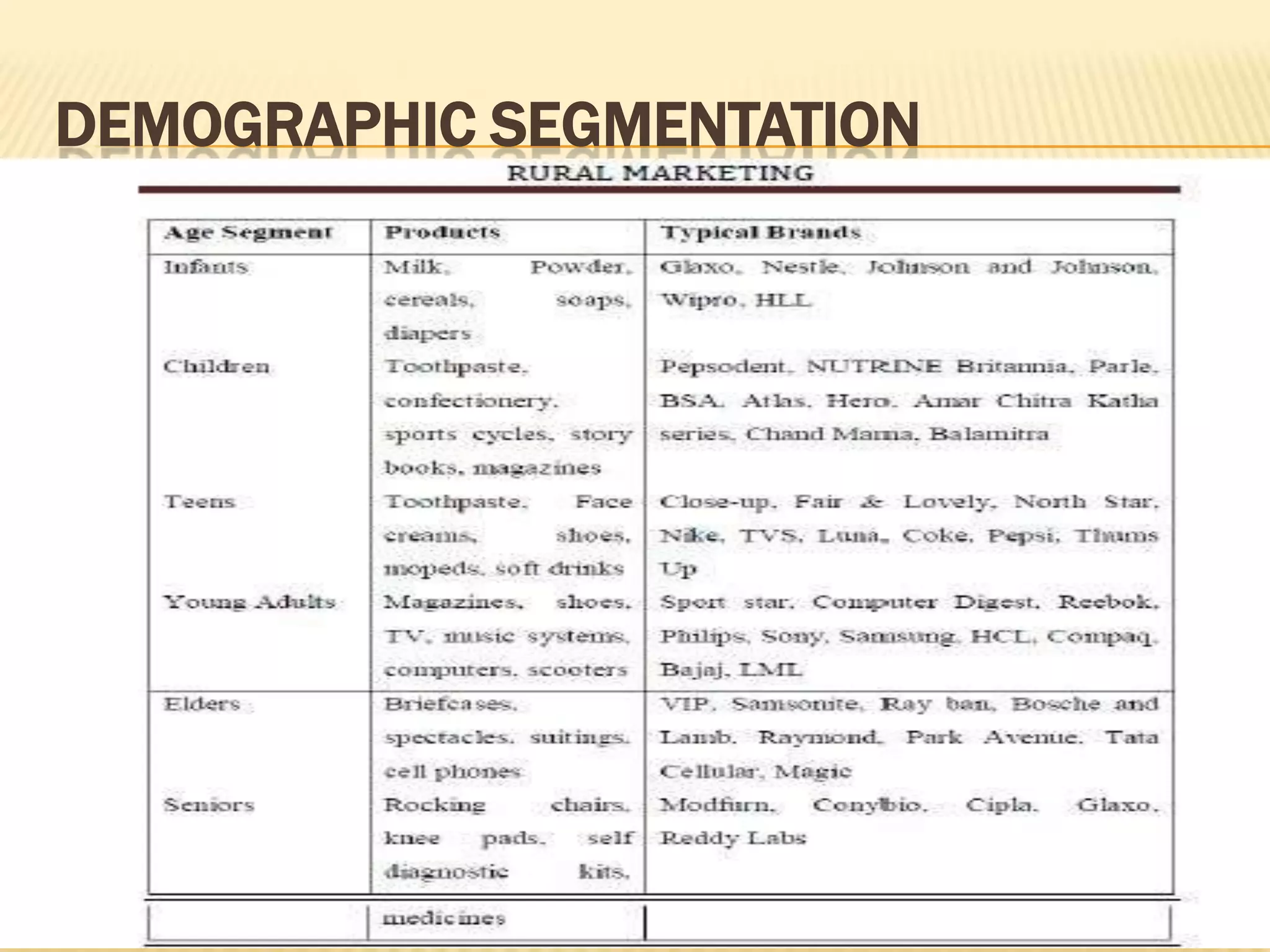
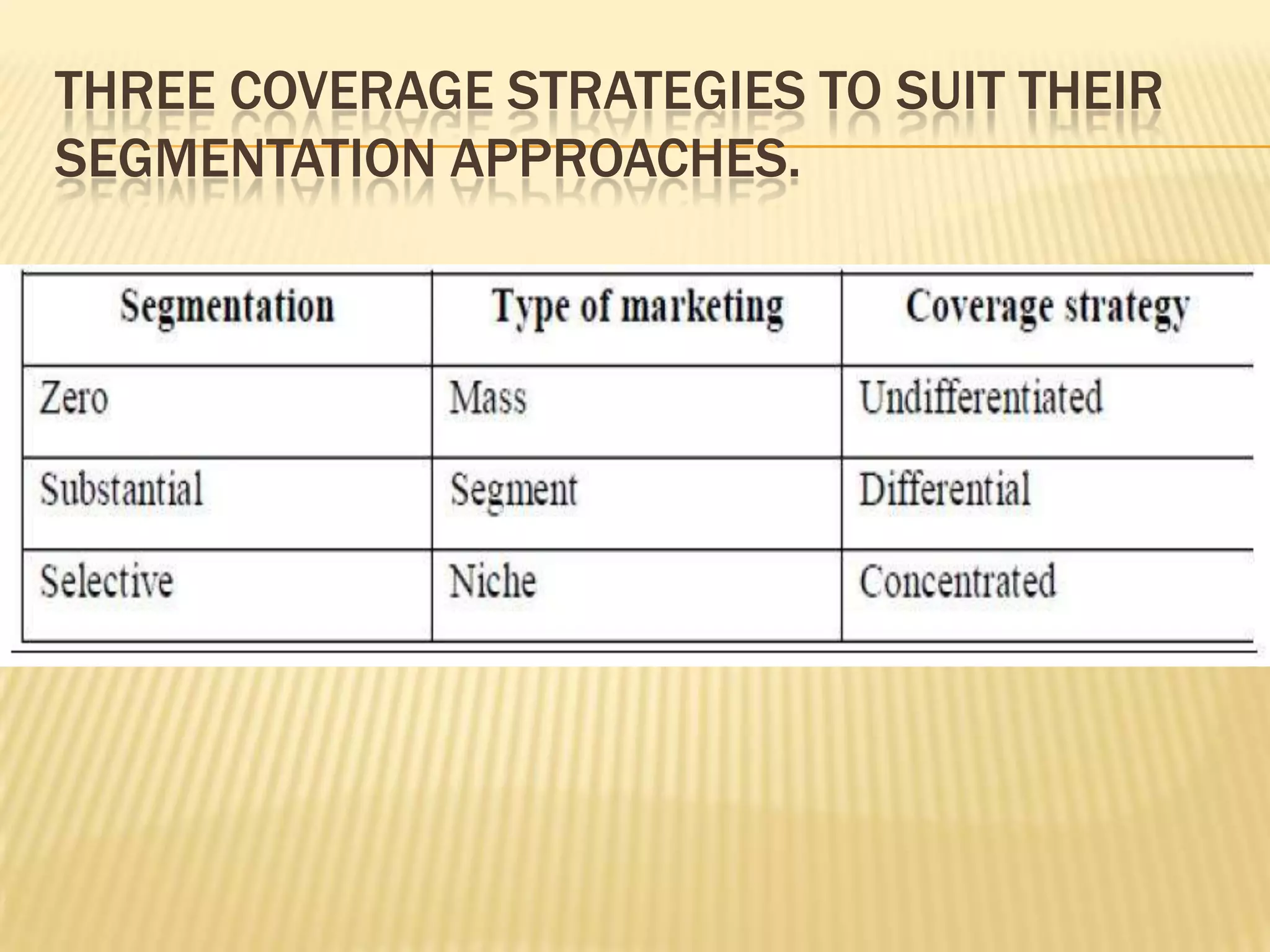
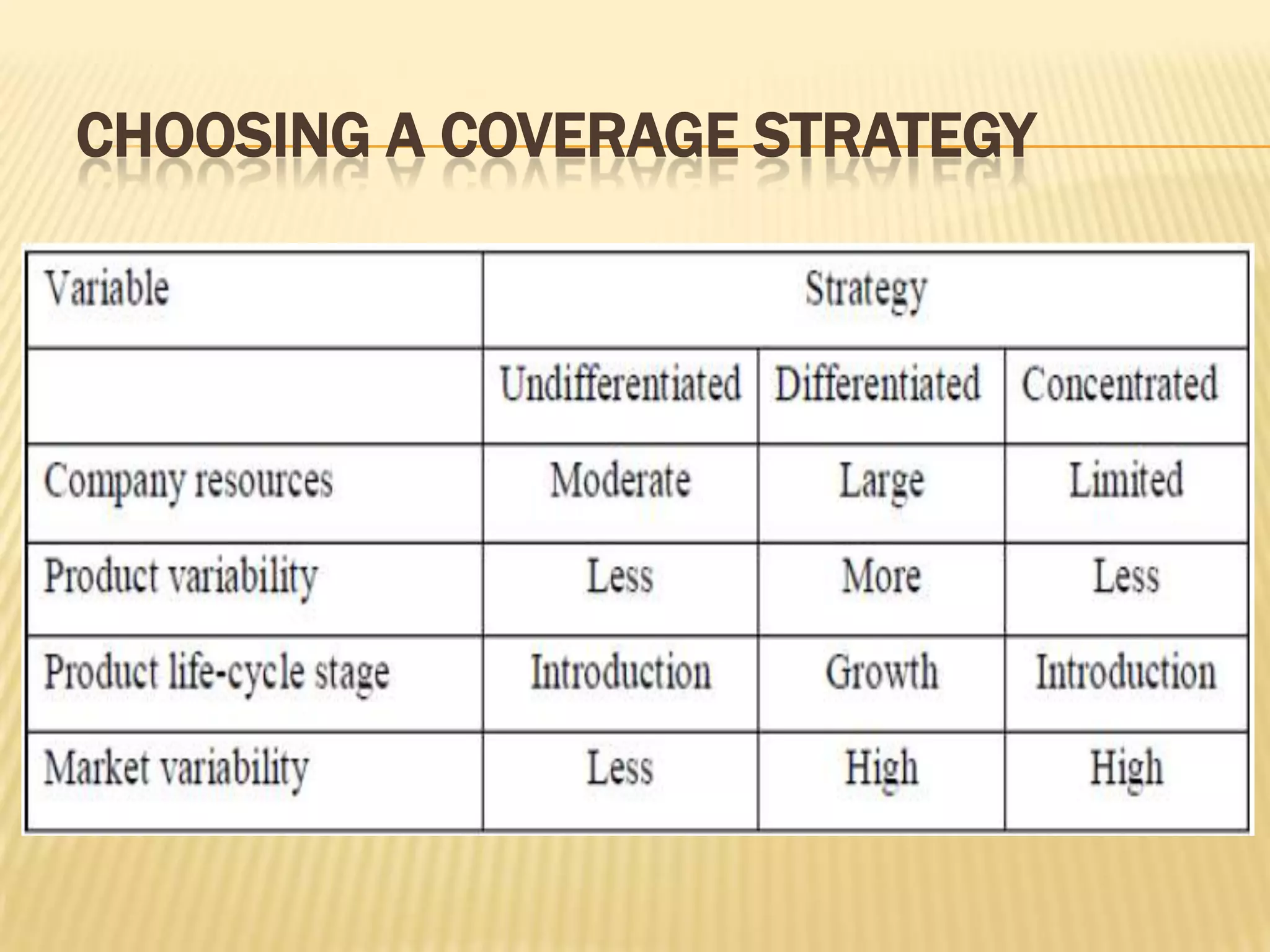
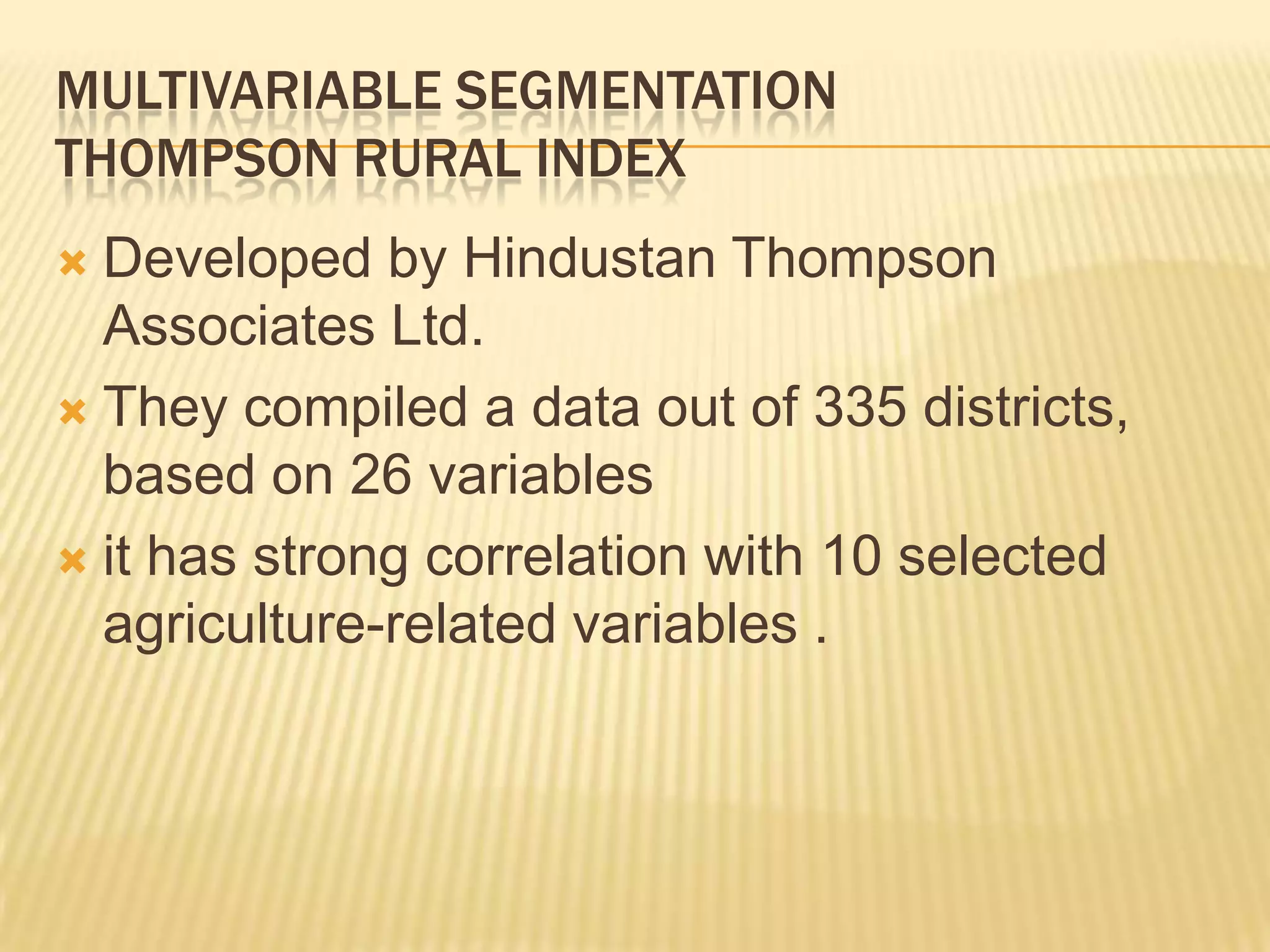
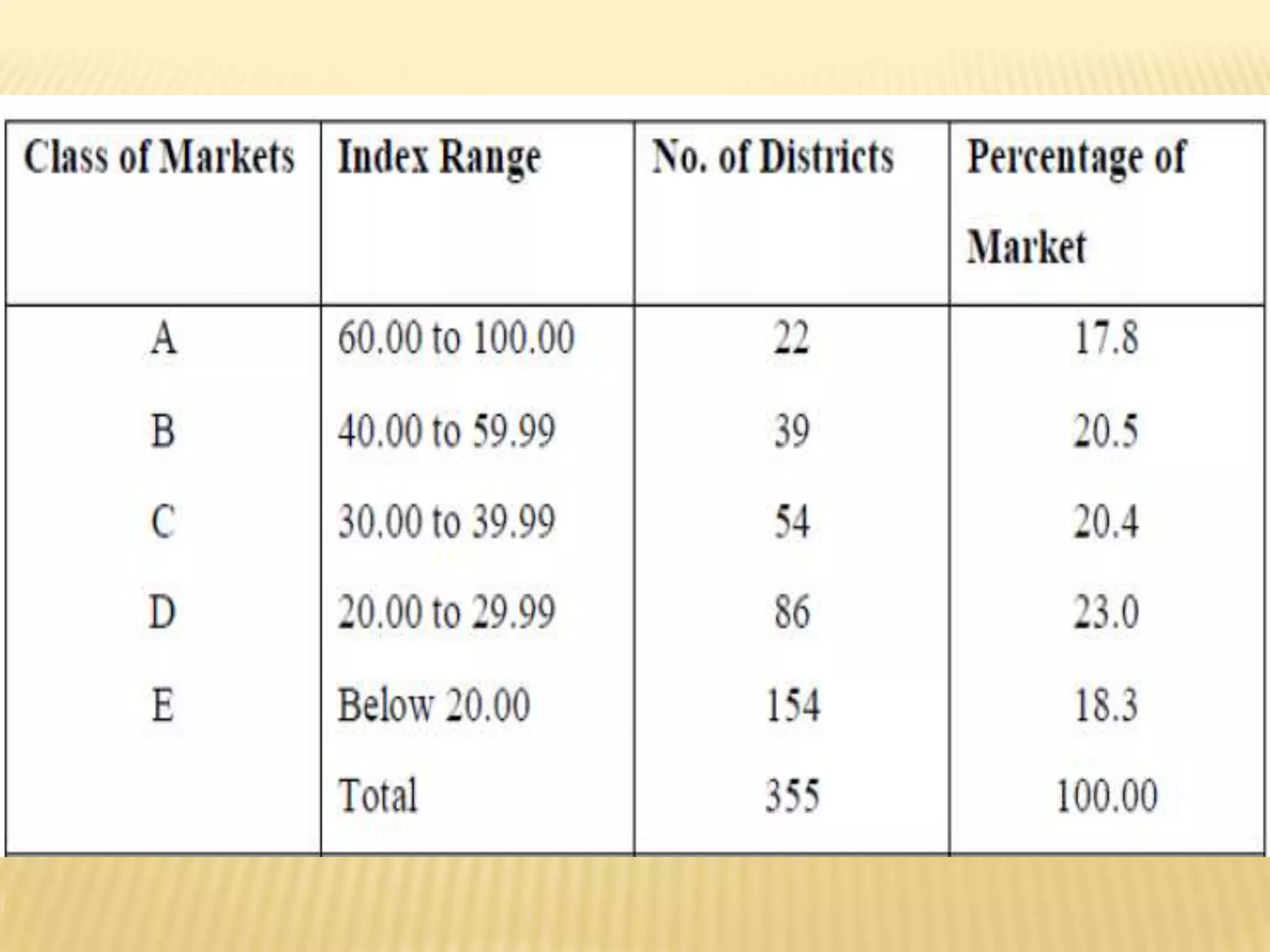
This document discusses strategies for rural market segmentation and targeting. It begins by classifying rural consumers into affluent, middle class, and poor groups. It then discusses why companies target rural markets due to increasing consumer durable penetration and the emergence of women customers. The document outlines the STP approach to selecting and attracting market segments - segmenting, targeting, and positioning. It then discusses degrees of segmentation from mass to niche to micro marketing. Various bases for segmentation like geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors are also presented.