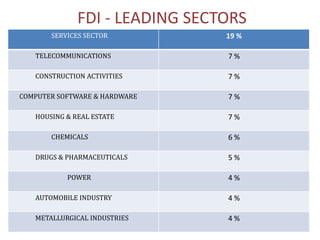
Foreign direct investment (FDI) occurs when a firm in one country acquires assets in another country to manage them. FDI provides ownership advantages like special knowledge or economies of scale. Location advantages and internalization advantages also influence FDI decisions. Firms invest abroad to reduce costs, increase sales volumes, promote knowledge sharing, and retain domestic customers. Common FDI strategies include wholly owned subsidiaries, joint ventures, mergers, and acquisitions. While FDI supplements capital and resources, some argue it can displace competition and exploit host country resources. India's top FDI investors are Mauritius, Singapore, and the UK, while its leading sectors are services, telecommunications, and construction.