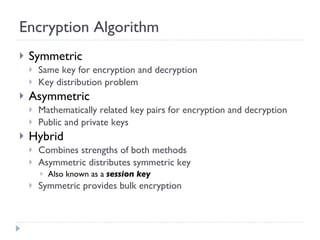
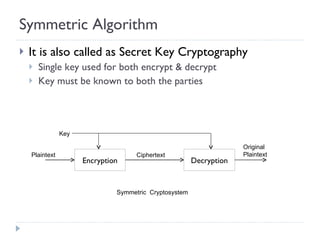
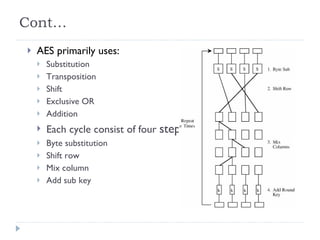
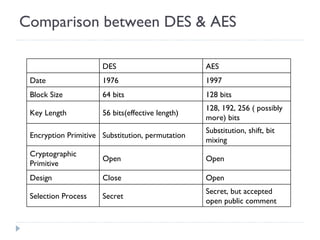
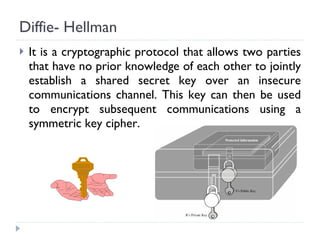
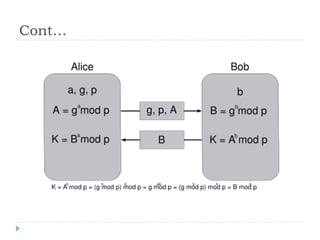
The document discusses the fundamentals of elementary cryptography, including definitions, encryption techniques, and the need for securing communication. It contrasts symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods, detailing algorithms such as DES, AES, and RSA, along with their applications and processes. Key concepts include the importance of confidentiality, integrity, and authentication through digital signatures and cryptographic hash functions.







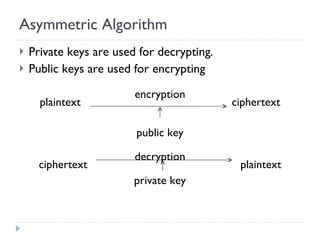
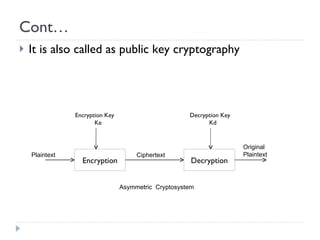
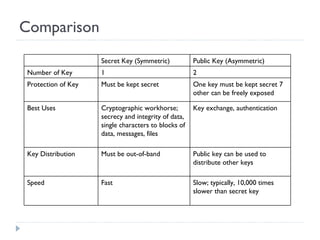

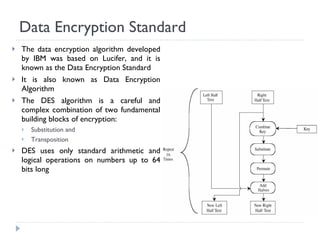








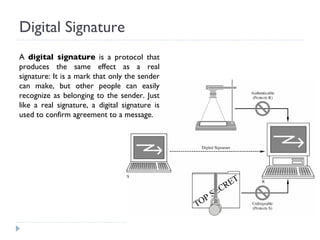
![Properties of Digital Signature A digital signature must meet two primary conditions: It must be unforgeable. If person P signs message M with signature S(P,M), it is impossible for anyone else to produce the pair [M, S(P,M)]. It must be authentic. If a person R receives the pair [M, S(P,M)] purportedly from P, R can check that the signature is really from P. Only P could have created this signature, and the signature is firmly attached to M. It is not alterable. After being transmitted, M cannot be changed by S, R, or an interceptor. It is not reusable. A previous message presented again will be instantly detected by R.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elementrycryptography1-12767370794013-phpapp01/85/Elementry-Cryptography-29-320.jpg)