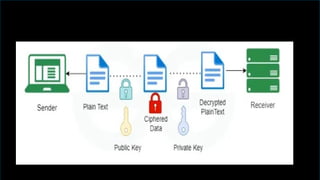
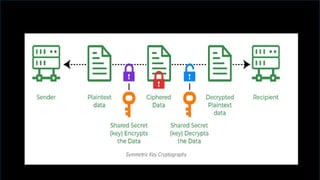
The document discusses network security, emphasizing the importance of protecting computer networks from unauthorized access and threats. It covers various types of security devices, threat categories, and cryptographic techniques, including symmetric (AES, DES) and asymmetric (RSA) cryptography. Additionally, it details the workings of digital signatures and their significance in ensuring secure communication.









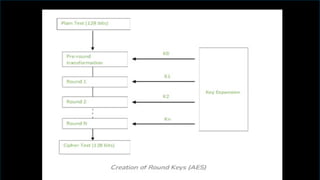
![• AES considers each block as a 16-byte (4 byte x 4 byte = 128 ) grid in a
column-major arrangement.
• [ b0 | b4 | b8 | b12 |
• | b1 | b5 | b9 | b13 |
• | b2 | b6 | b10| b14 |
• | b3 | b7 | b11| b15 ]
• Each round comprises of 4 steps :
• SubBytes
• ShiftRows
• MixColumns
• Add Round Key
Working of AES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nswebinar-250209135900-feb690c9/85/Introduction-to-Network-Security-presentation-12-320.jpg)