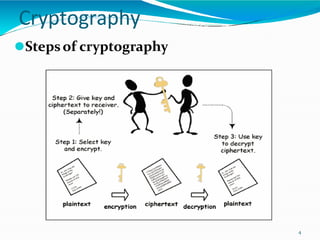
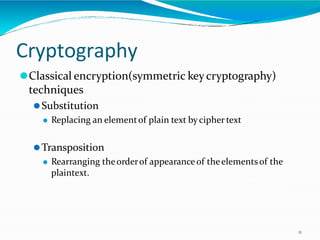
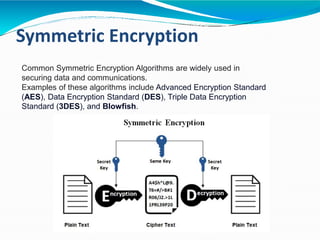
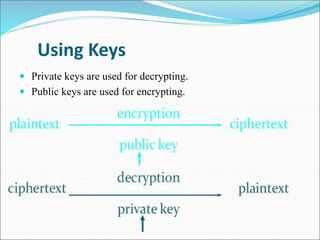
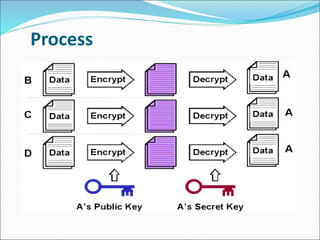
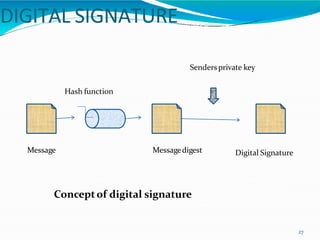
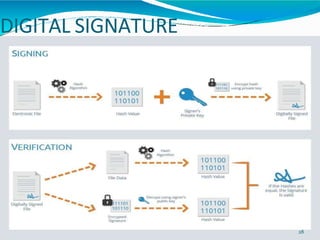
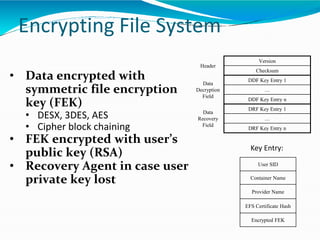
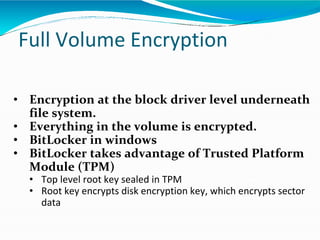
This document provides an overview of cryptography. It defines cryptography as the art and science of writing in secret codes, and explains its purpose is to achieve security through encrypting messages. The key topics covered include symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms, hash functions, digital signatures, encrypting file systems, and full disk encryption using BitLocker. Application areas like secure communication, authentication, and e-commerce are also discussed.