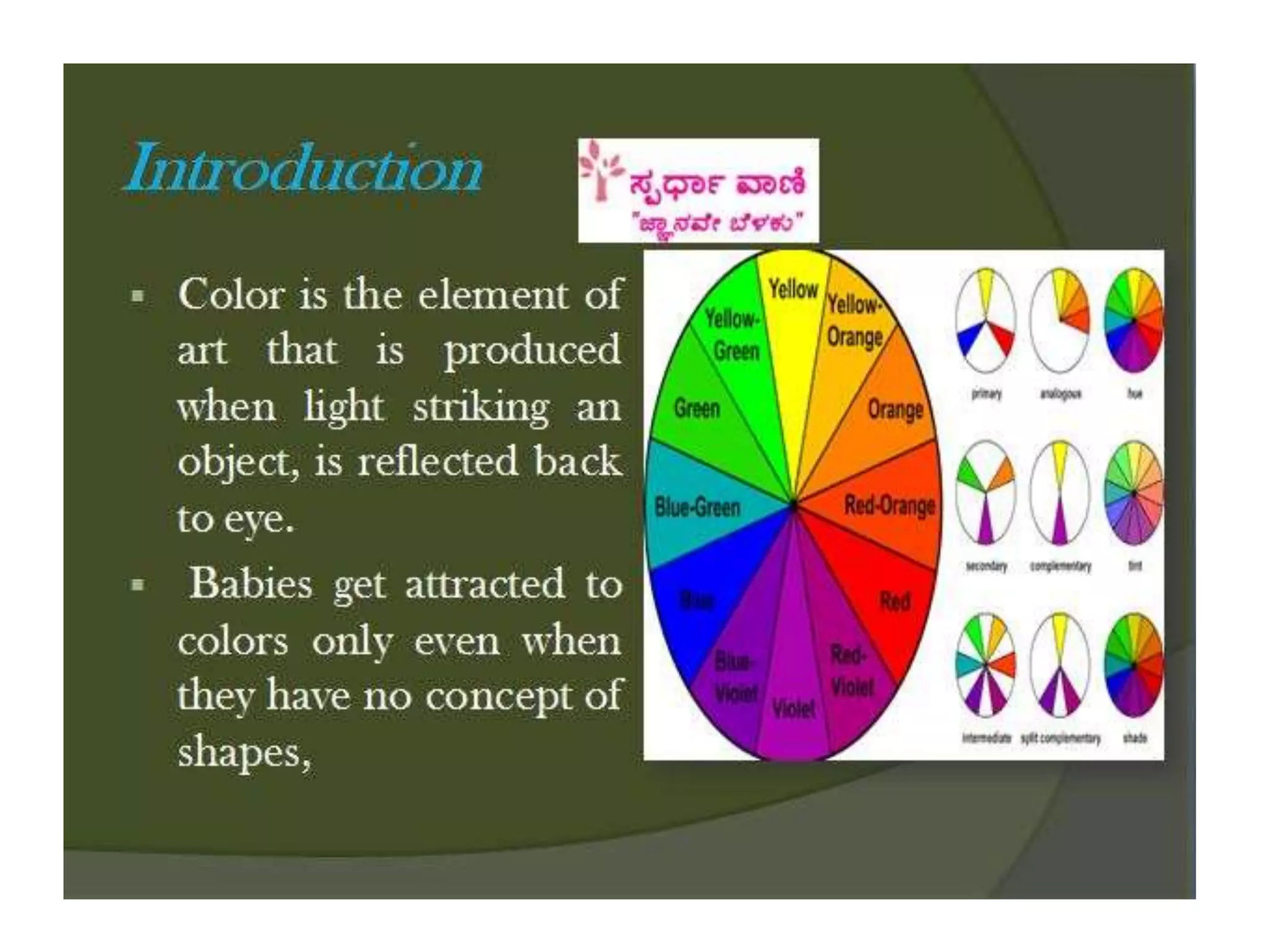
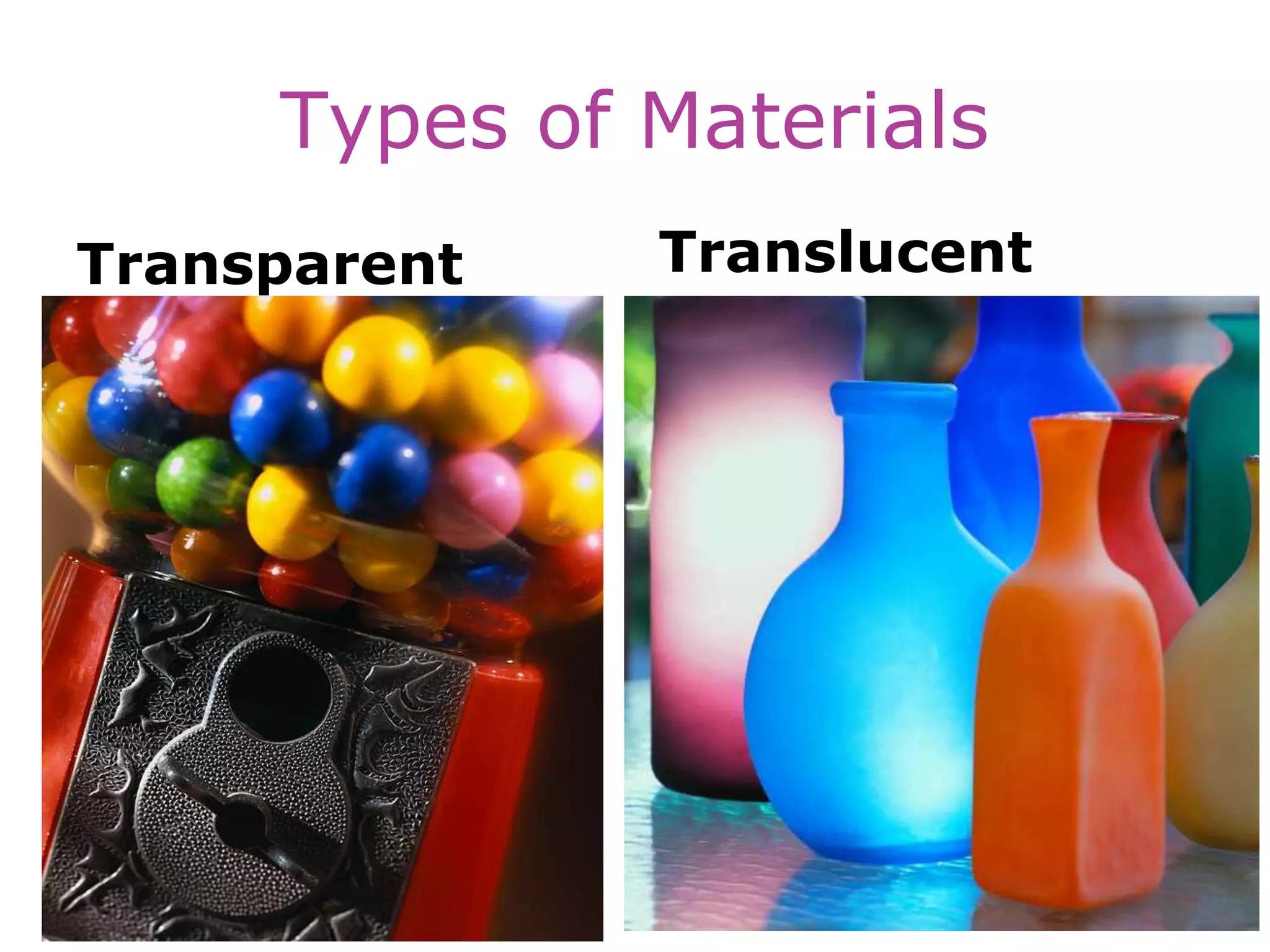
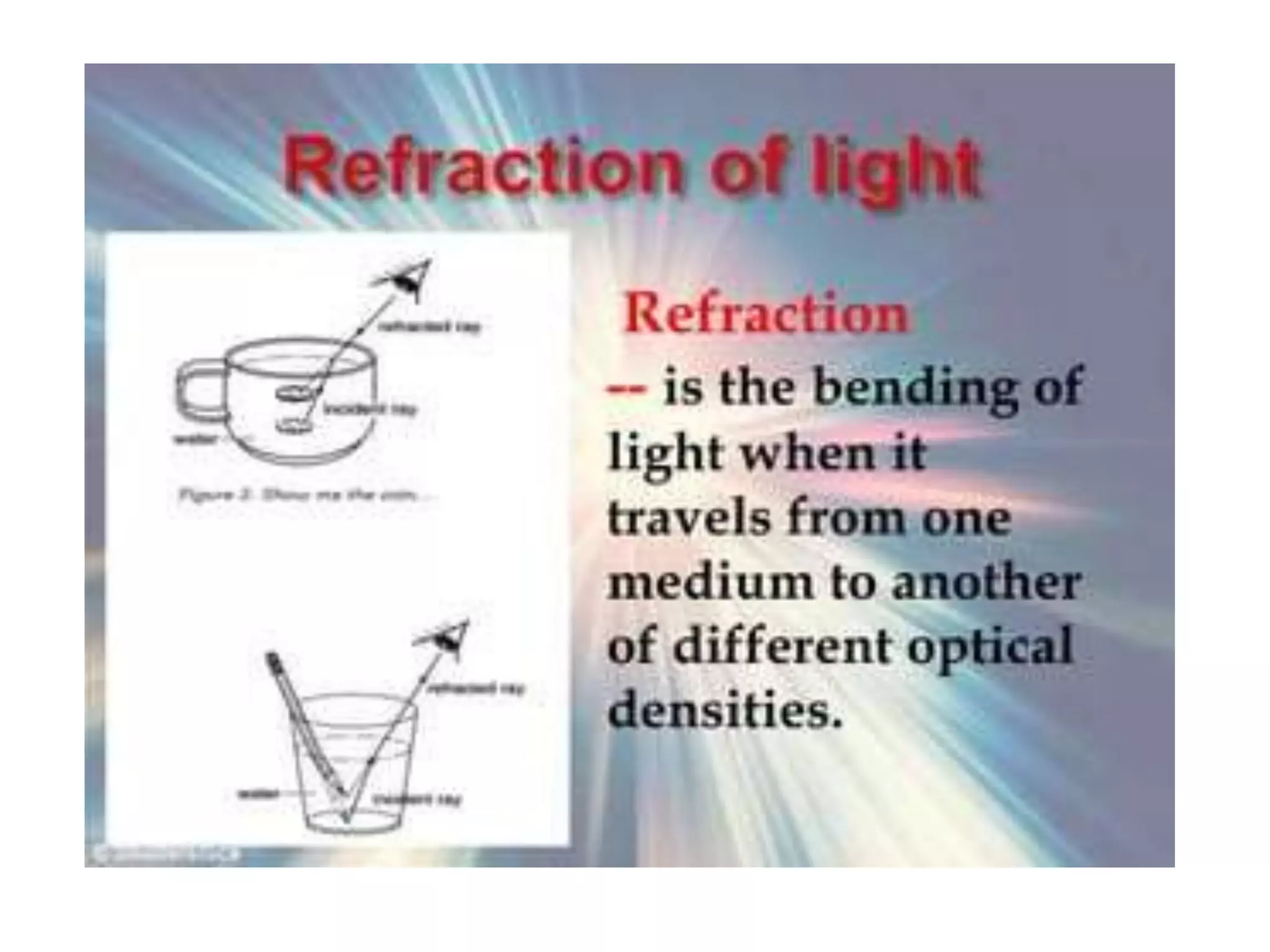
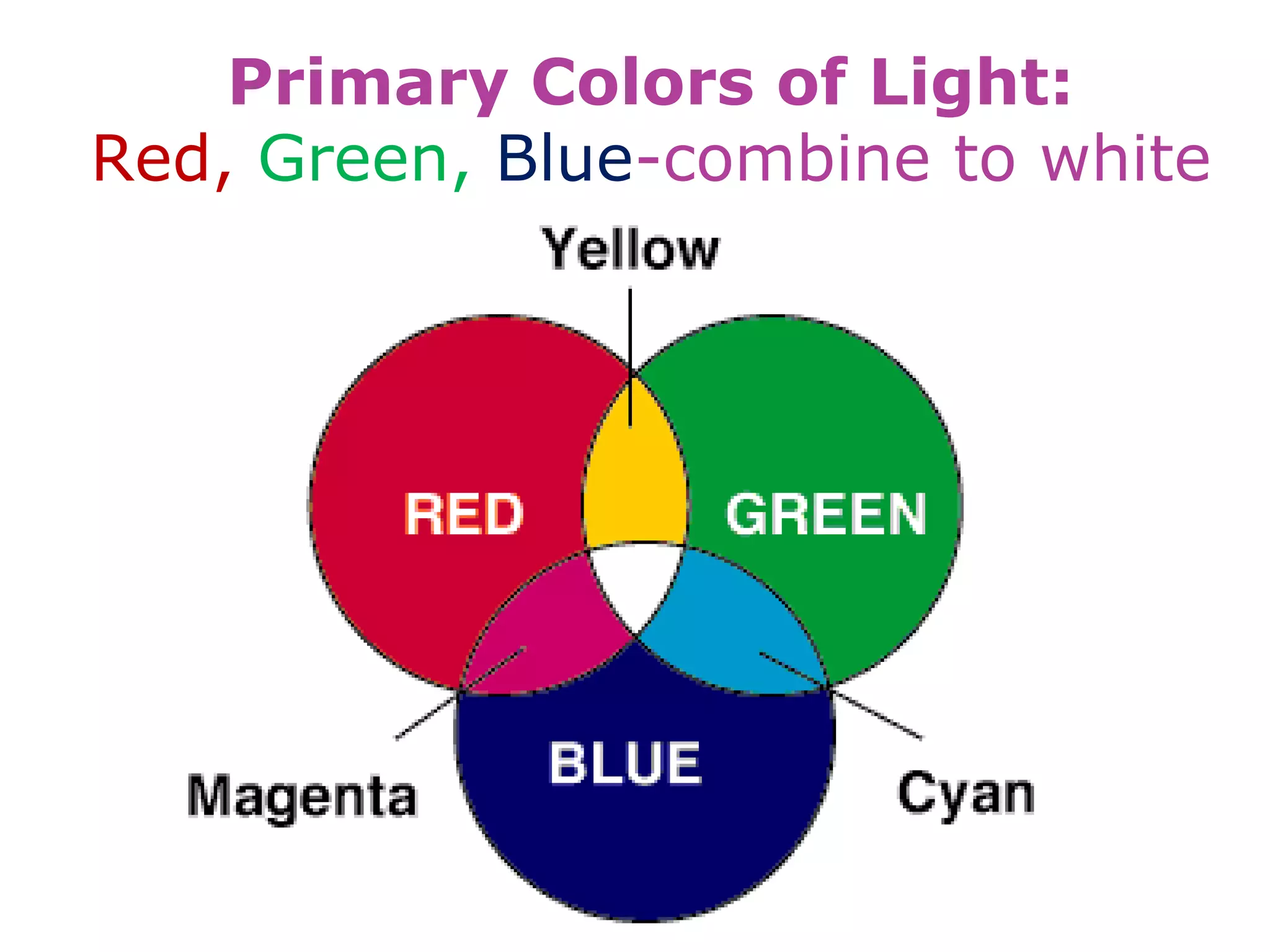
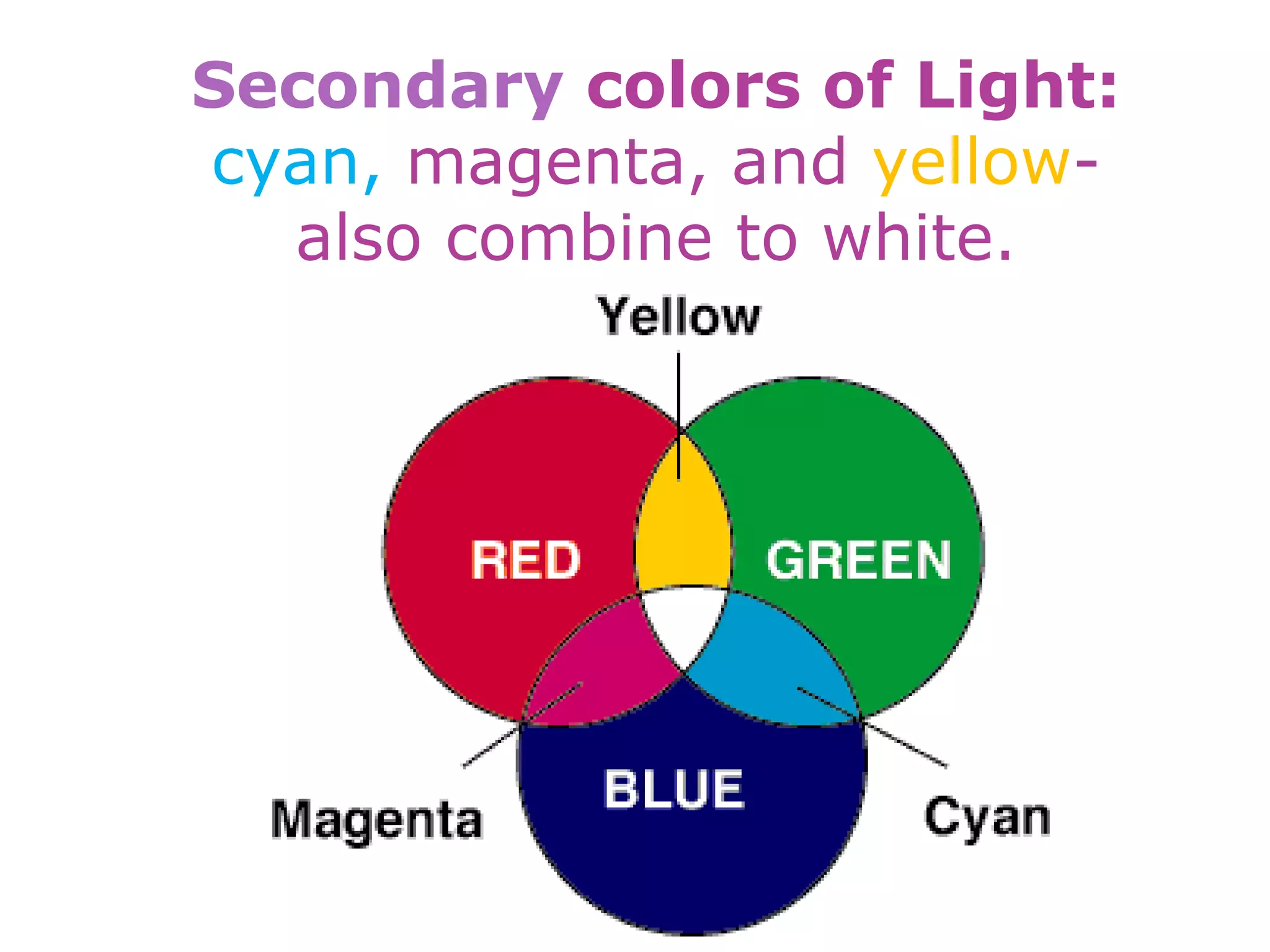
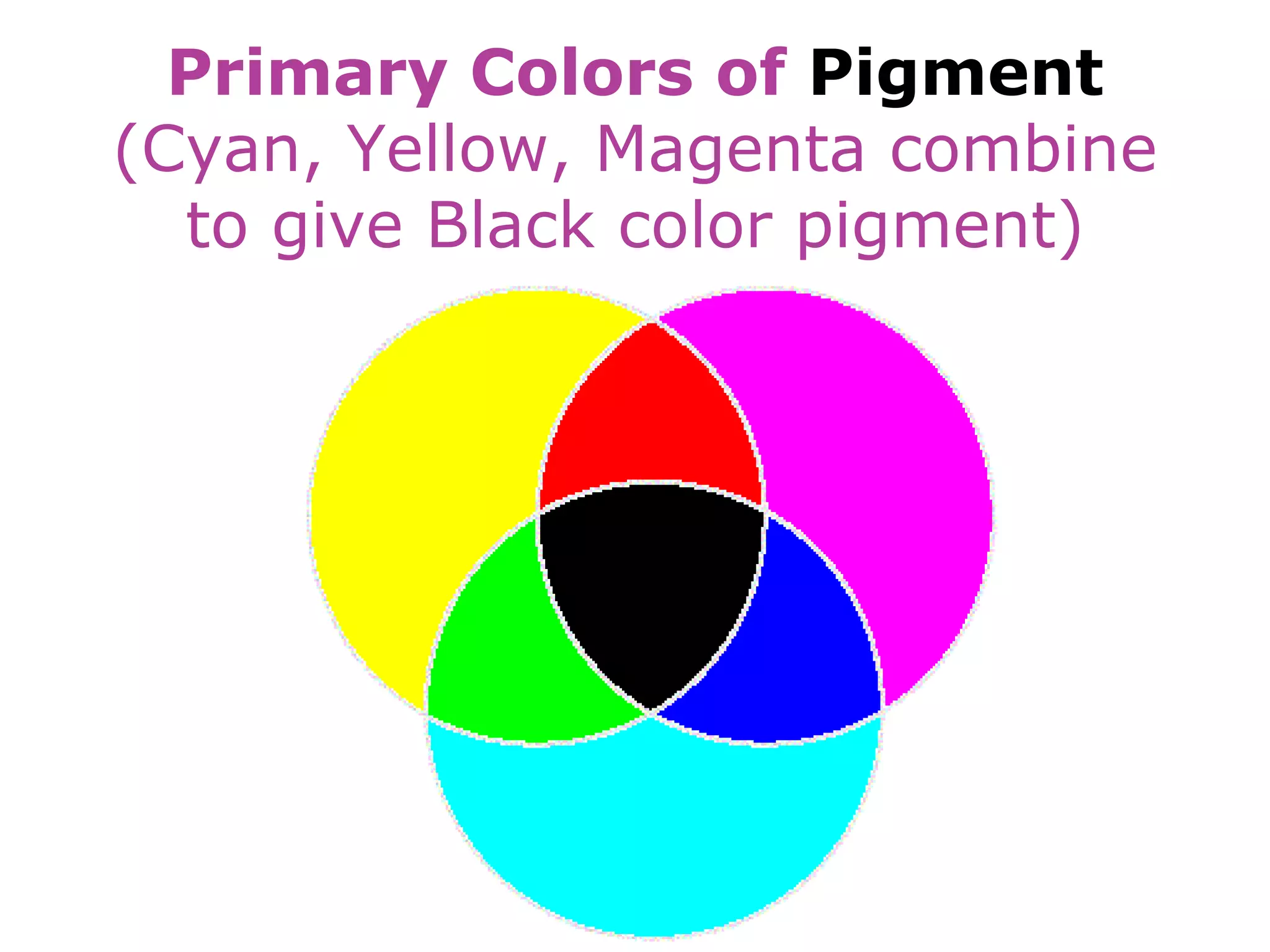
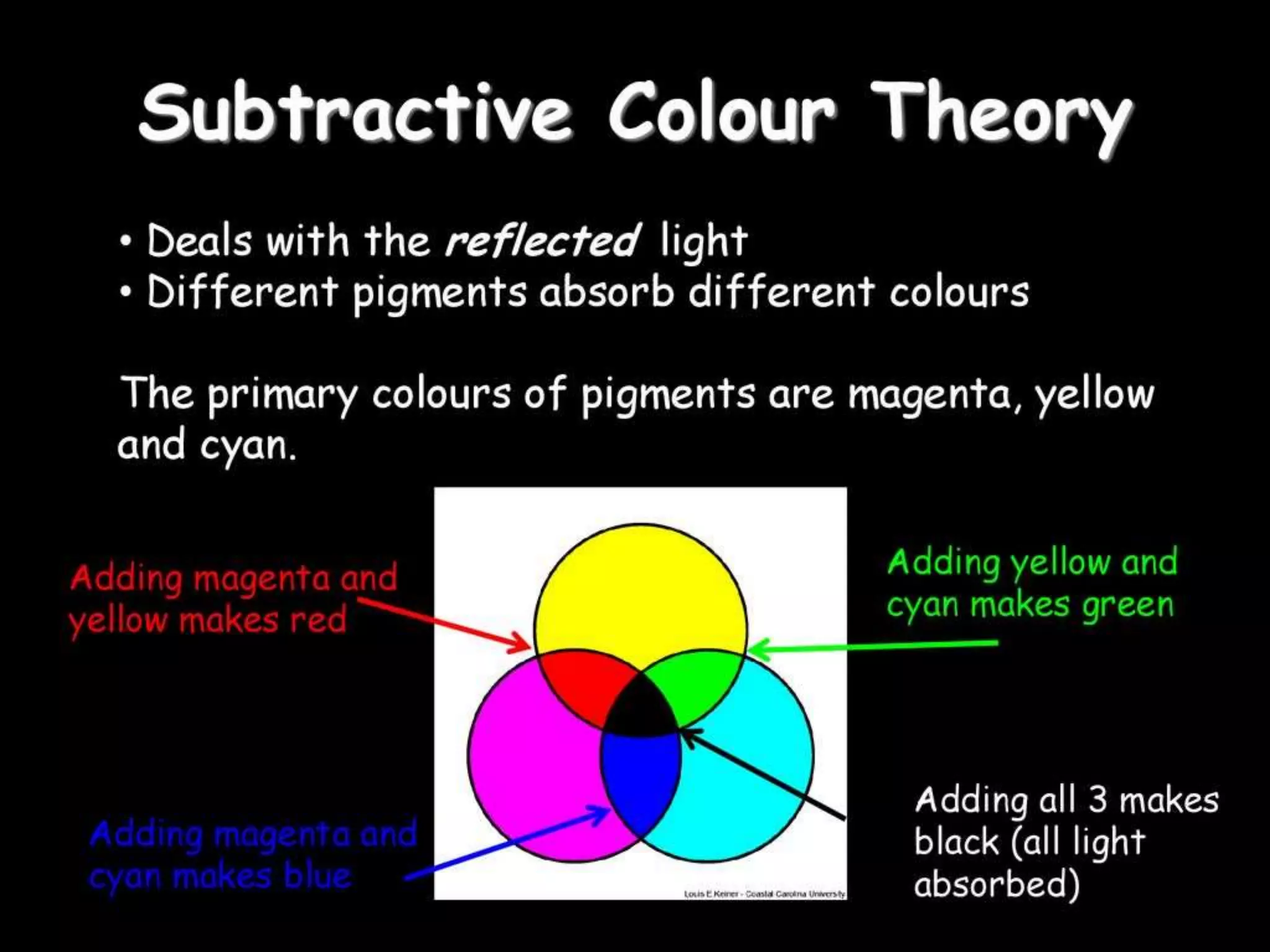
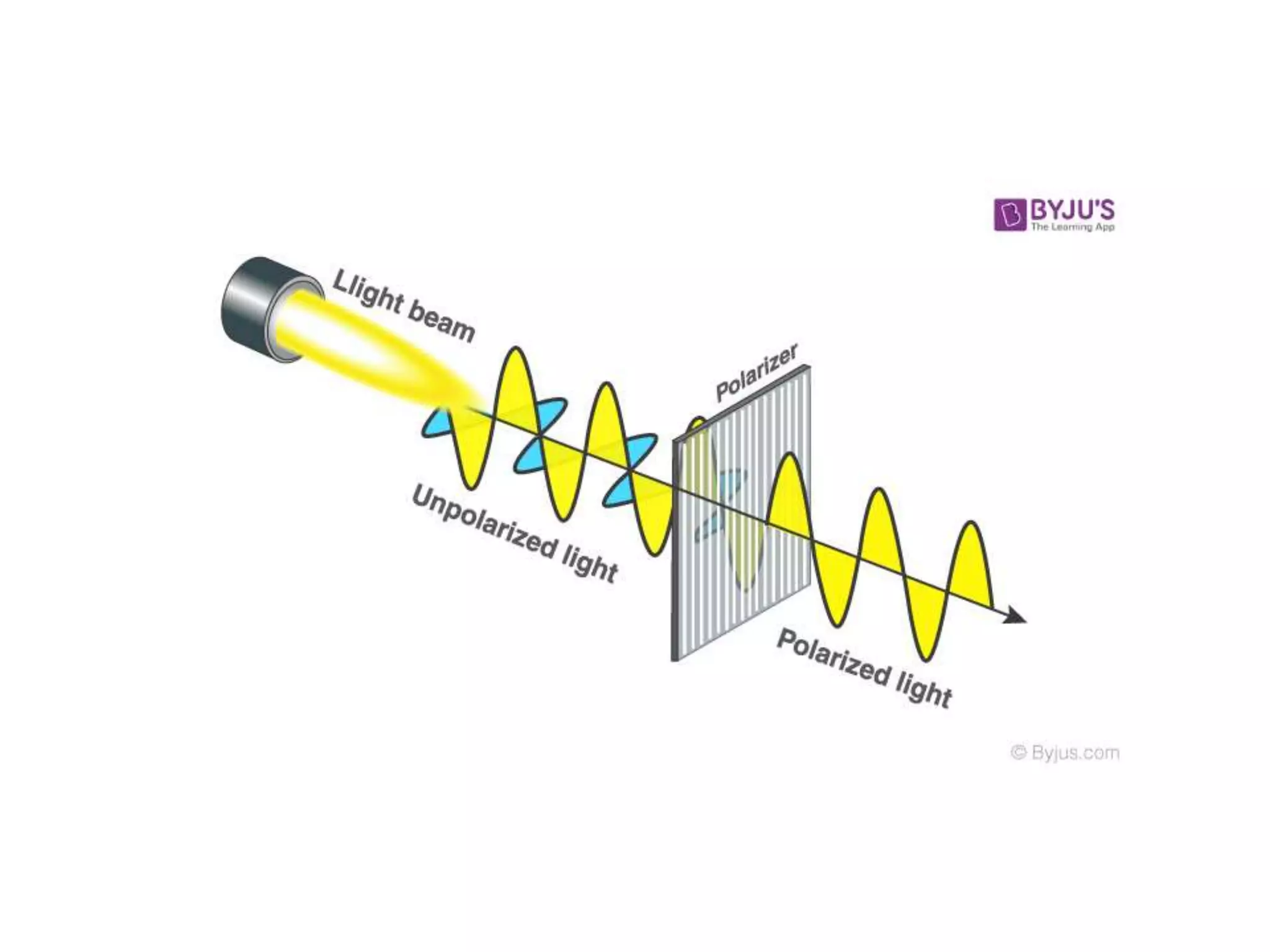
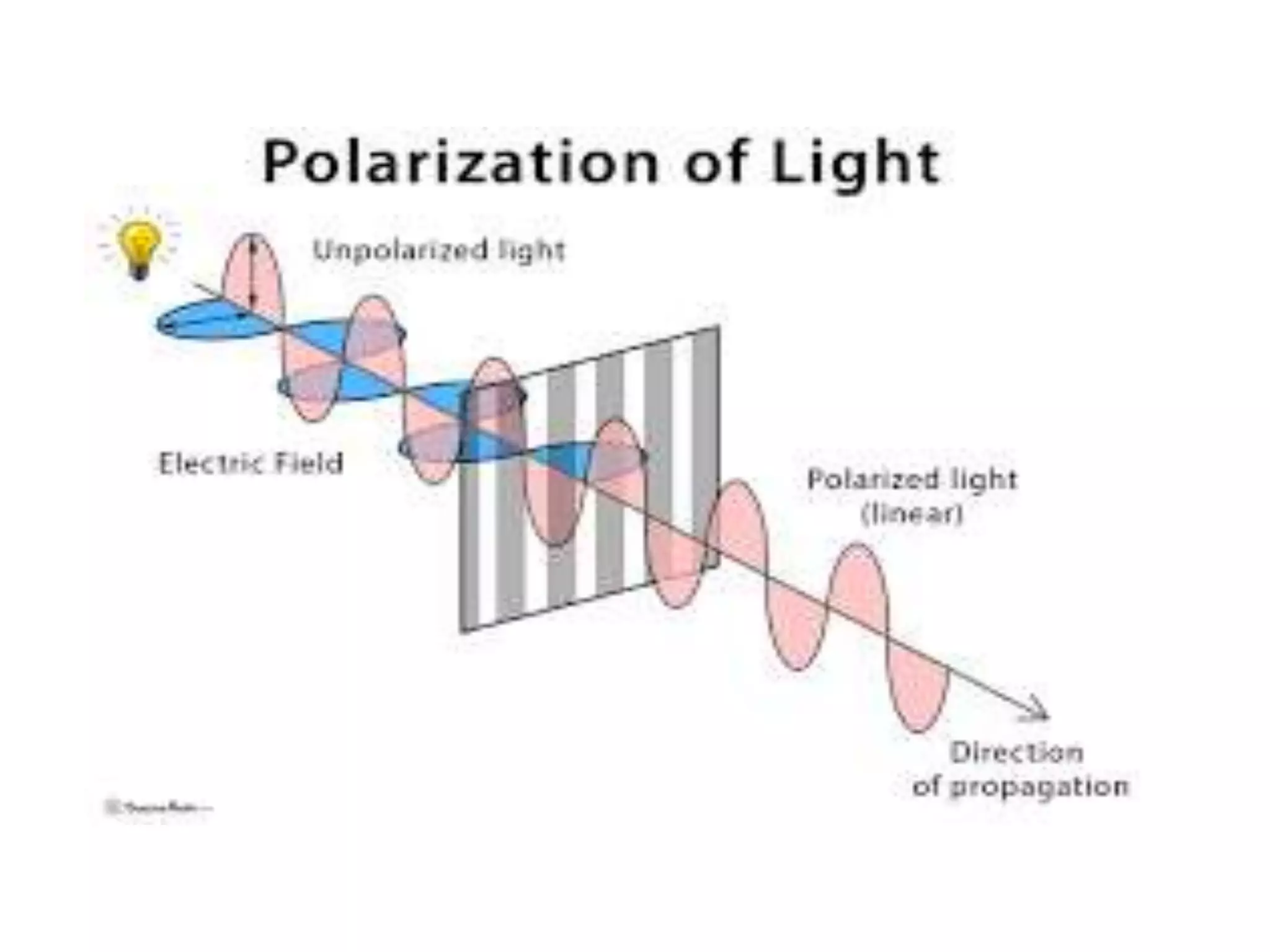
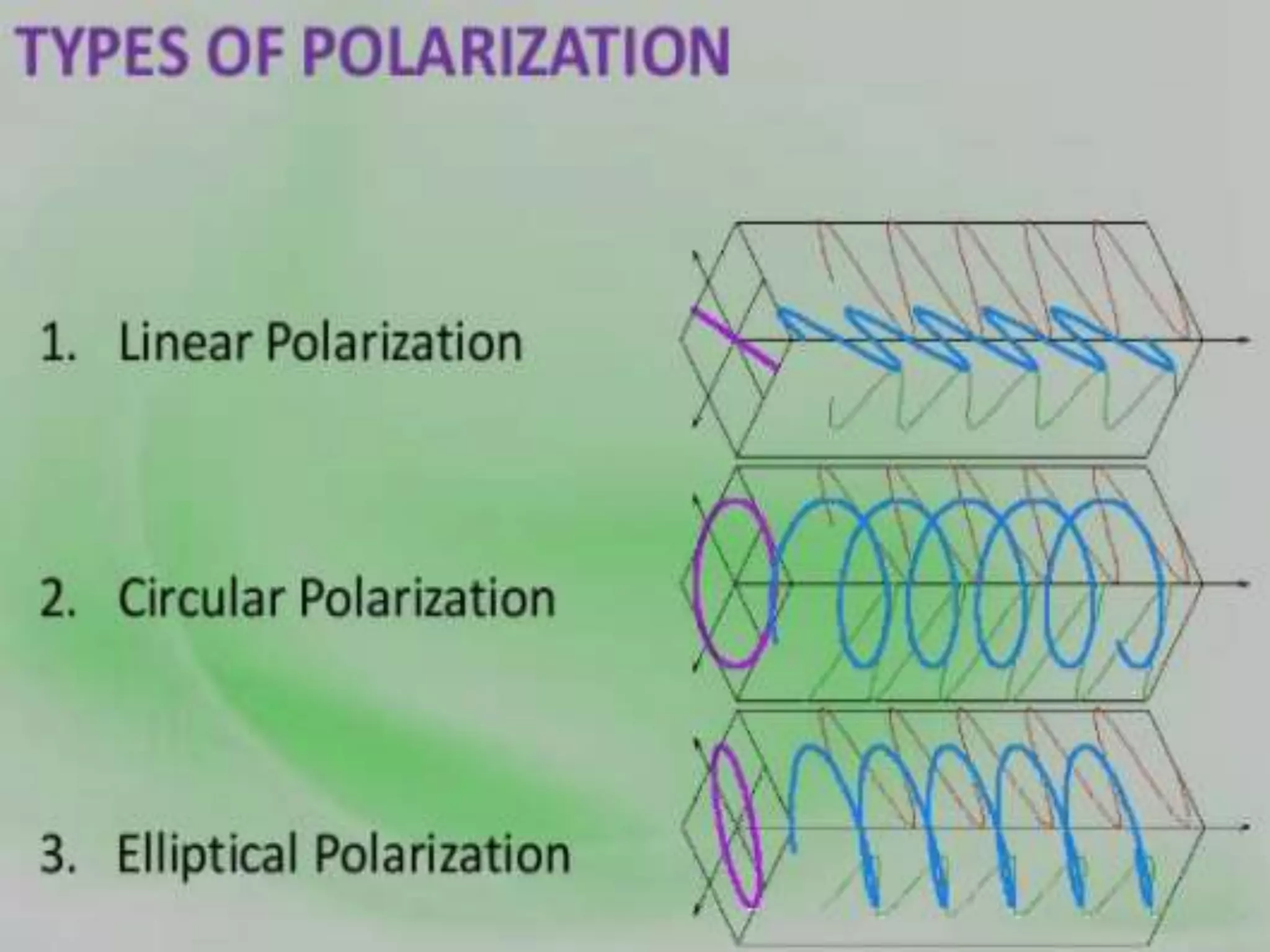
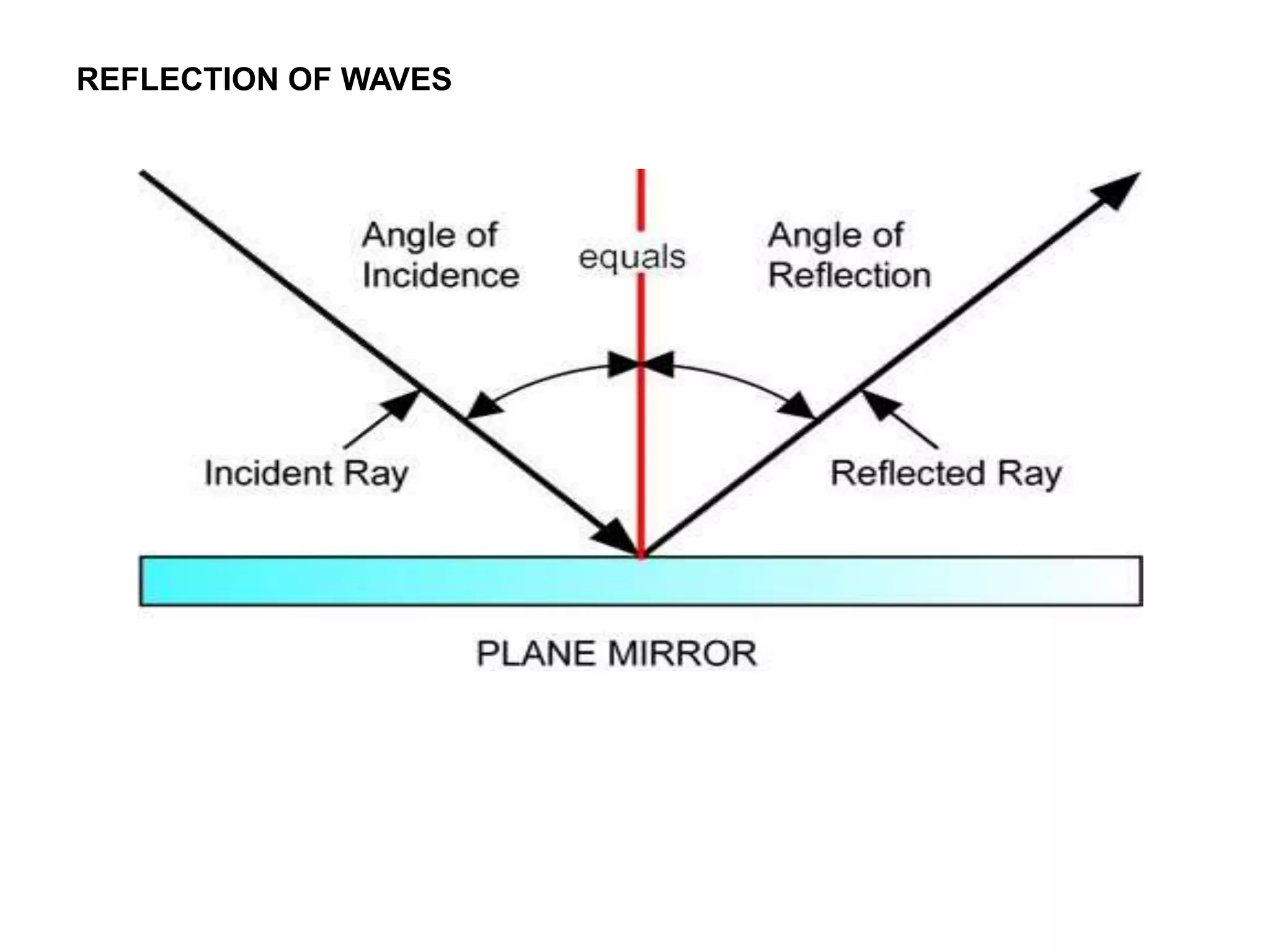
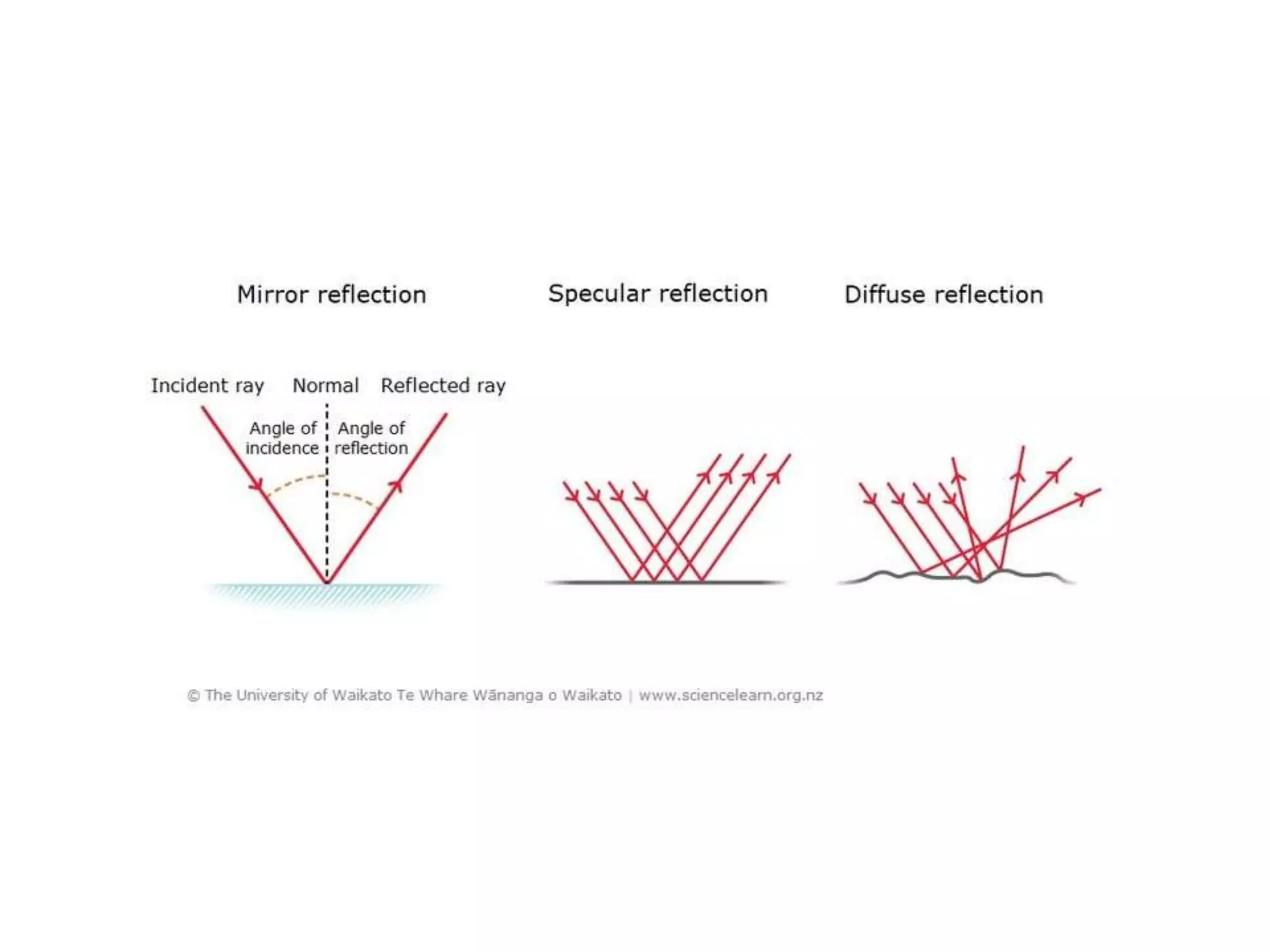
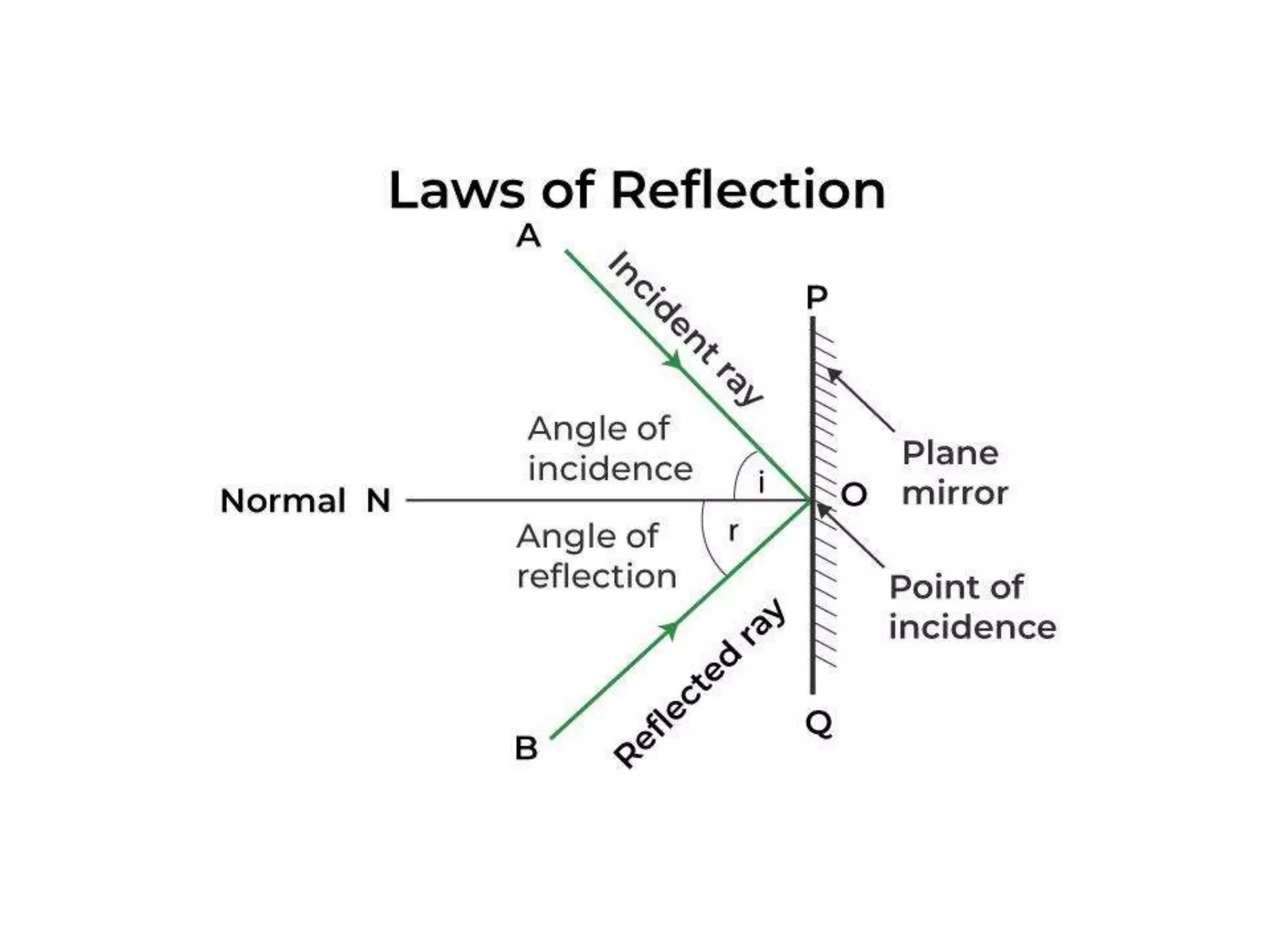
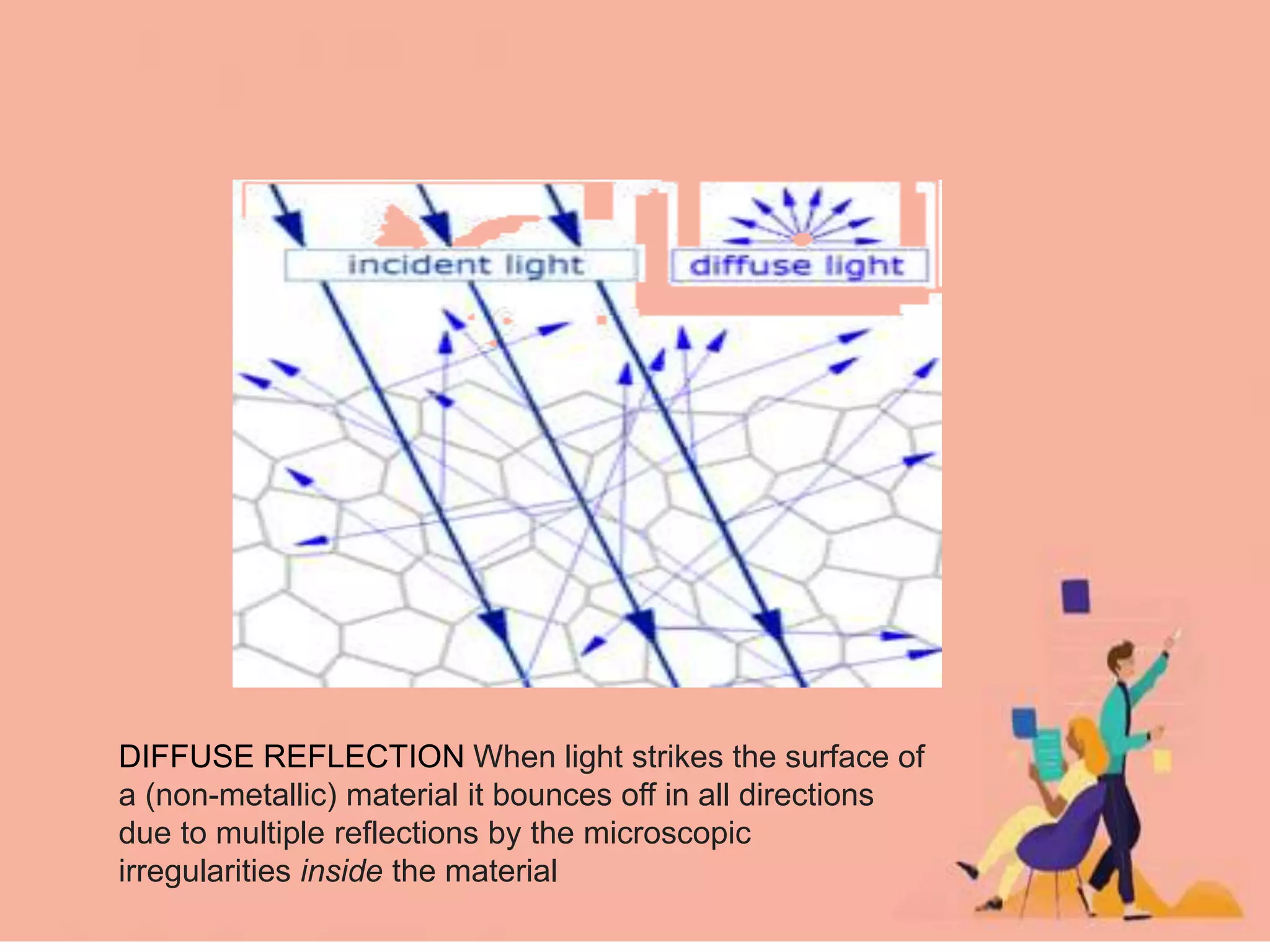
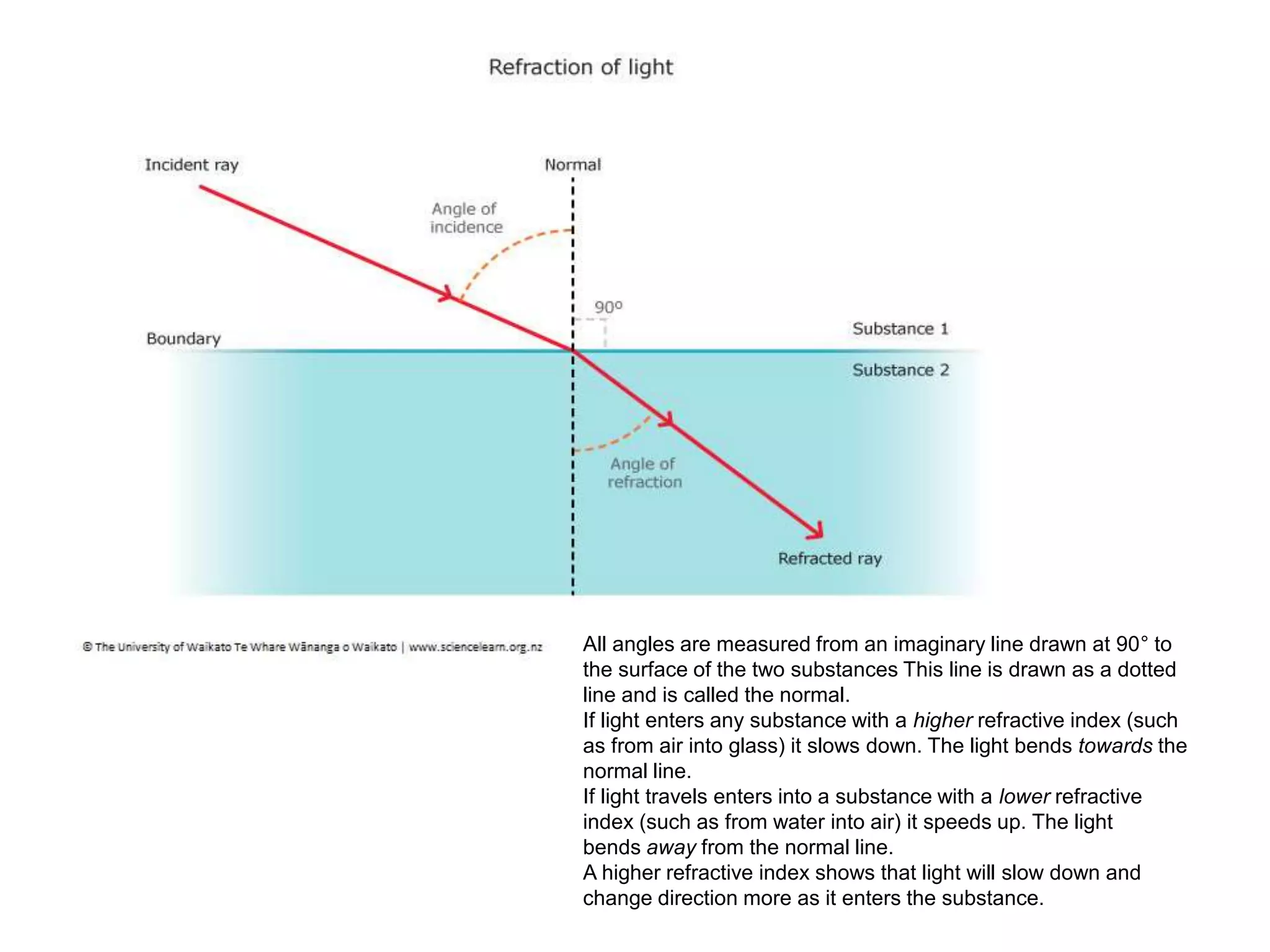
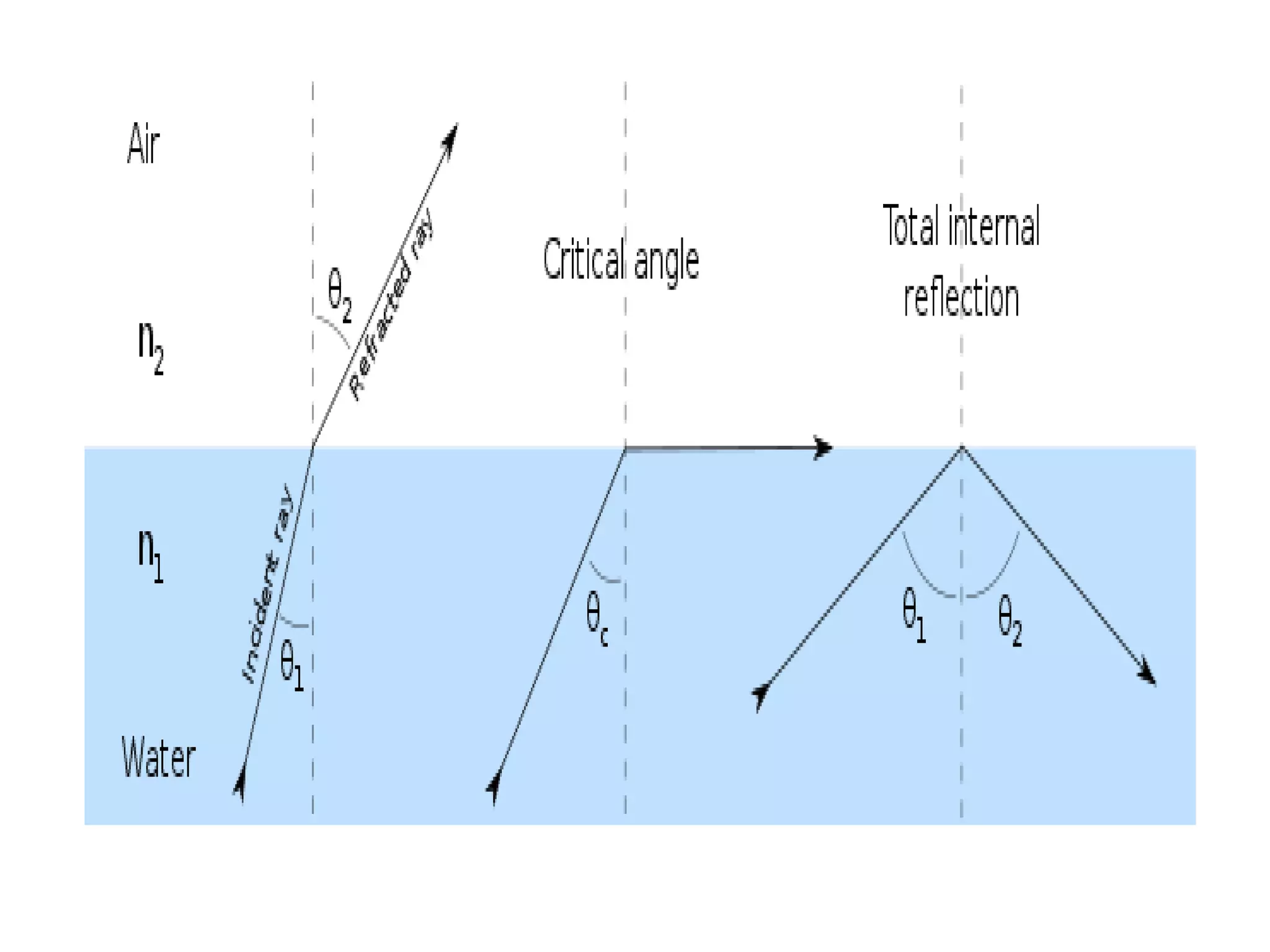
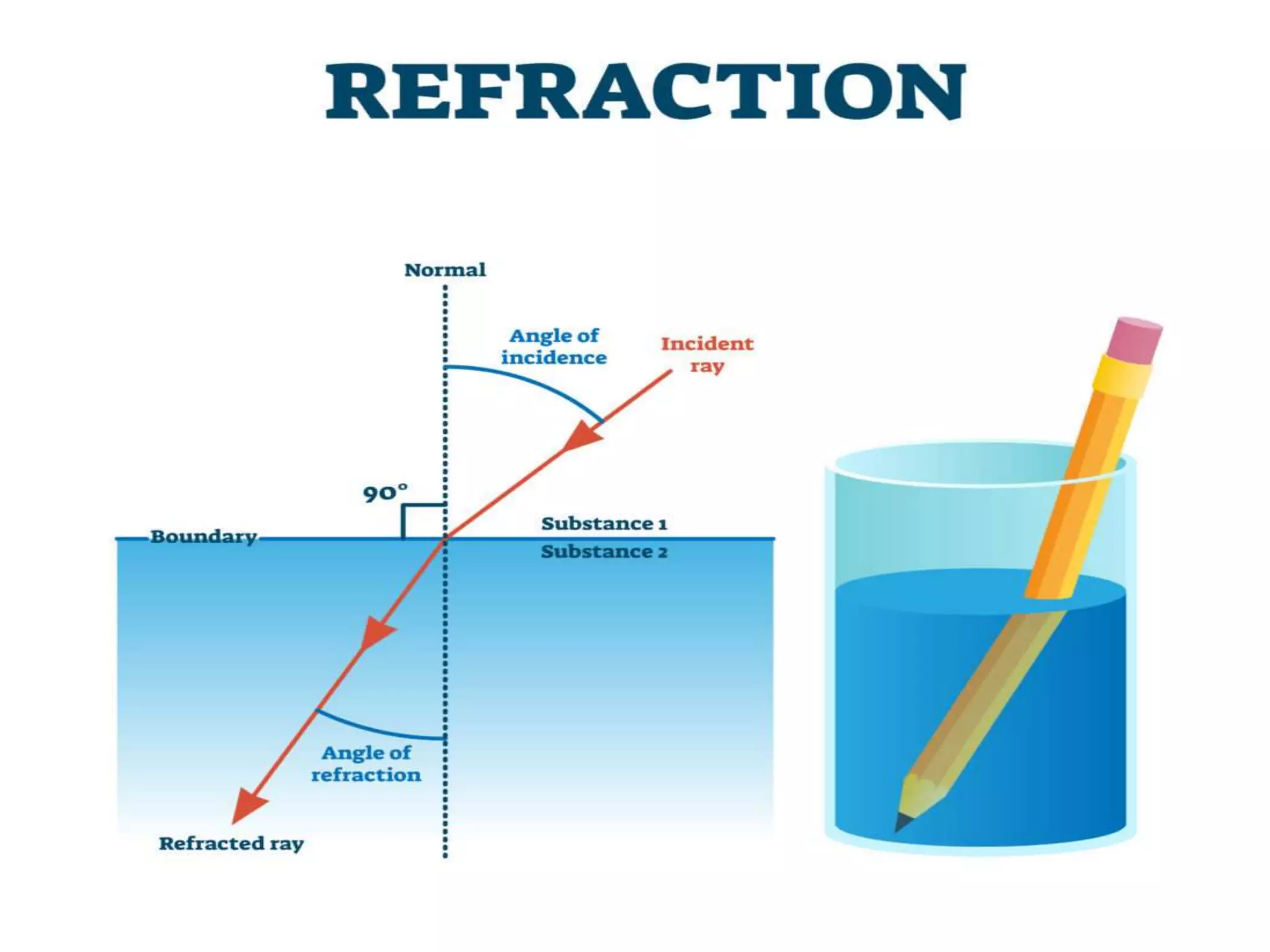
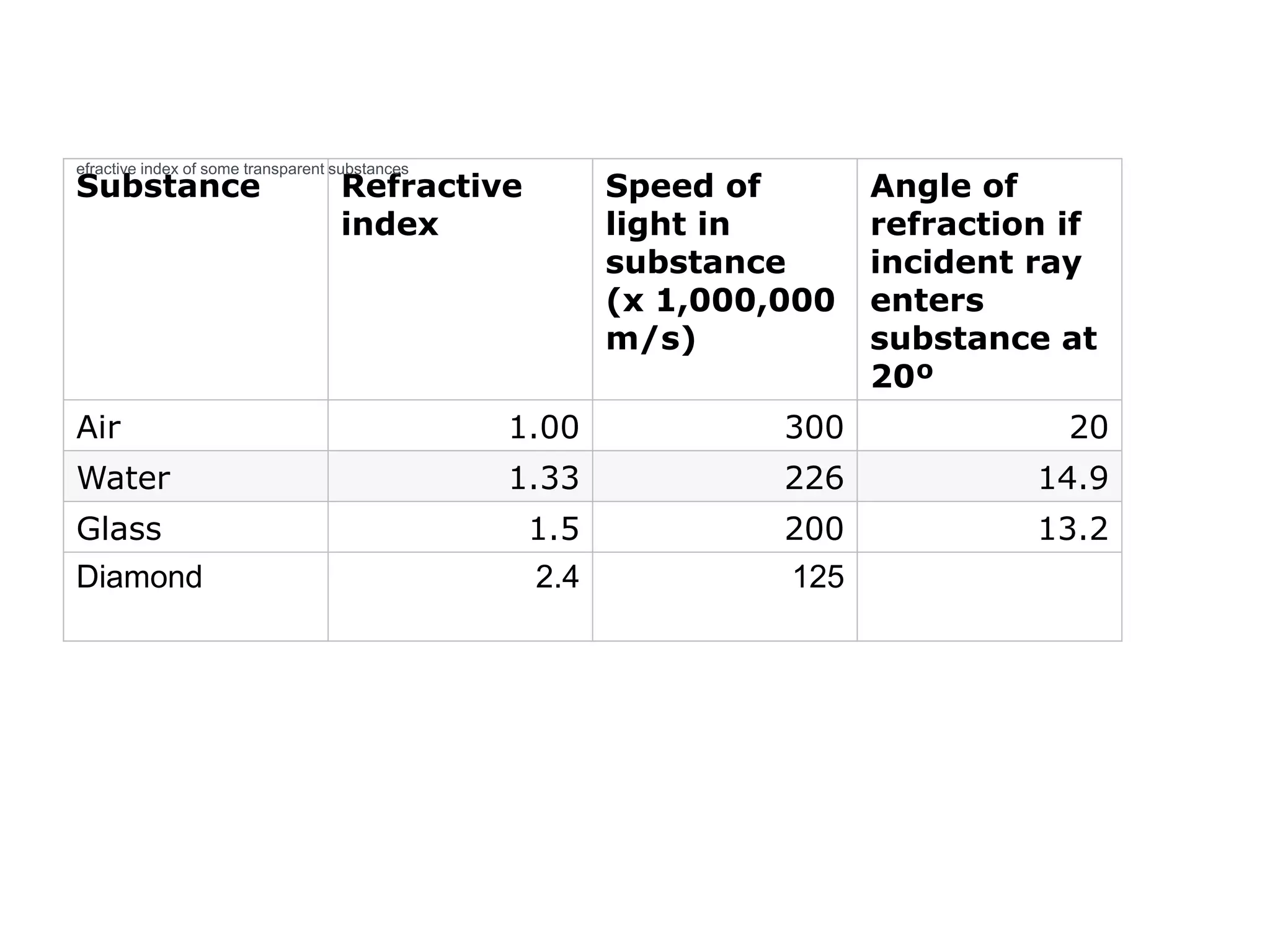
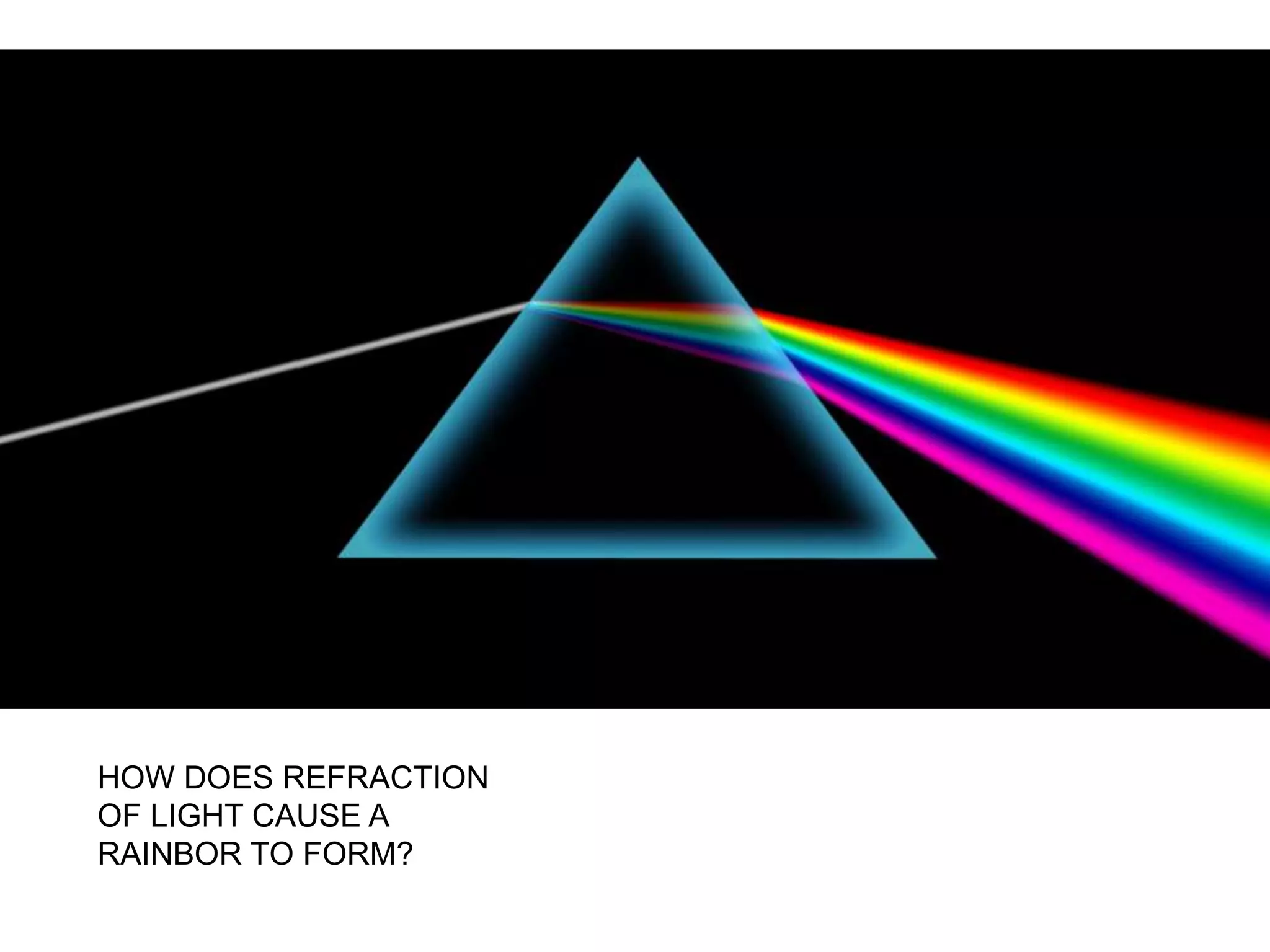
Electromagnetic waves interact with materials in several ways that determine the color perceived. Color arises from emission, reflection, transmission, interference, dispersion, and scattering of light waves interacting with objects. The primary colors of light are red, green and blue, which combine to make white light. The primary colors of pigment are cyan, yellow and magenta, which combine to make black. Reflection, refraction, polarization, and interference cause the wide variety of colors observed from different materials due to the interaction of light waves.