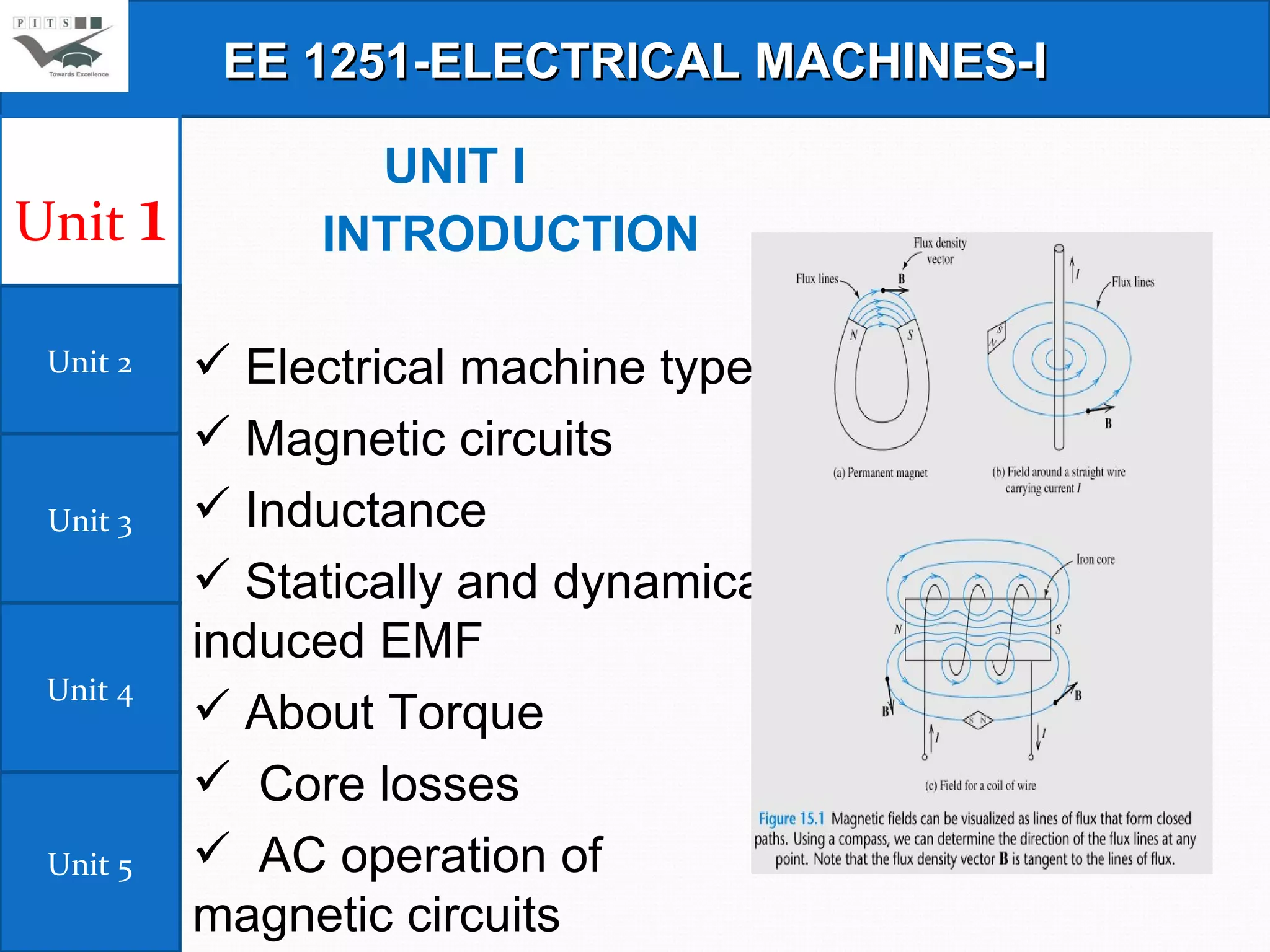
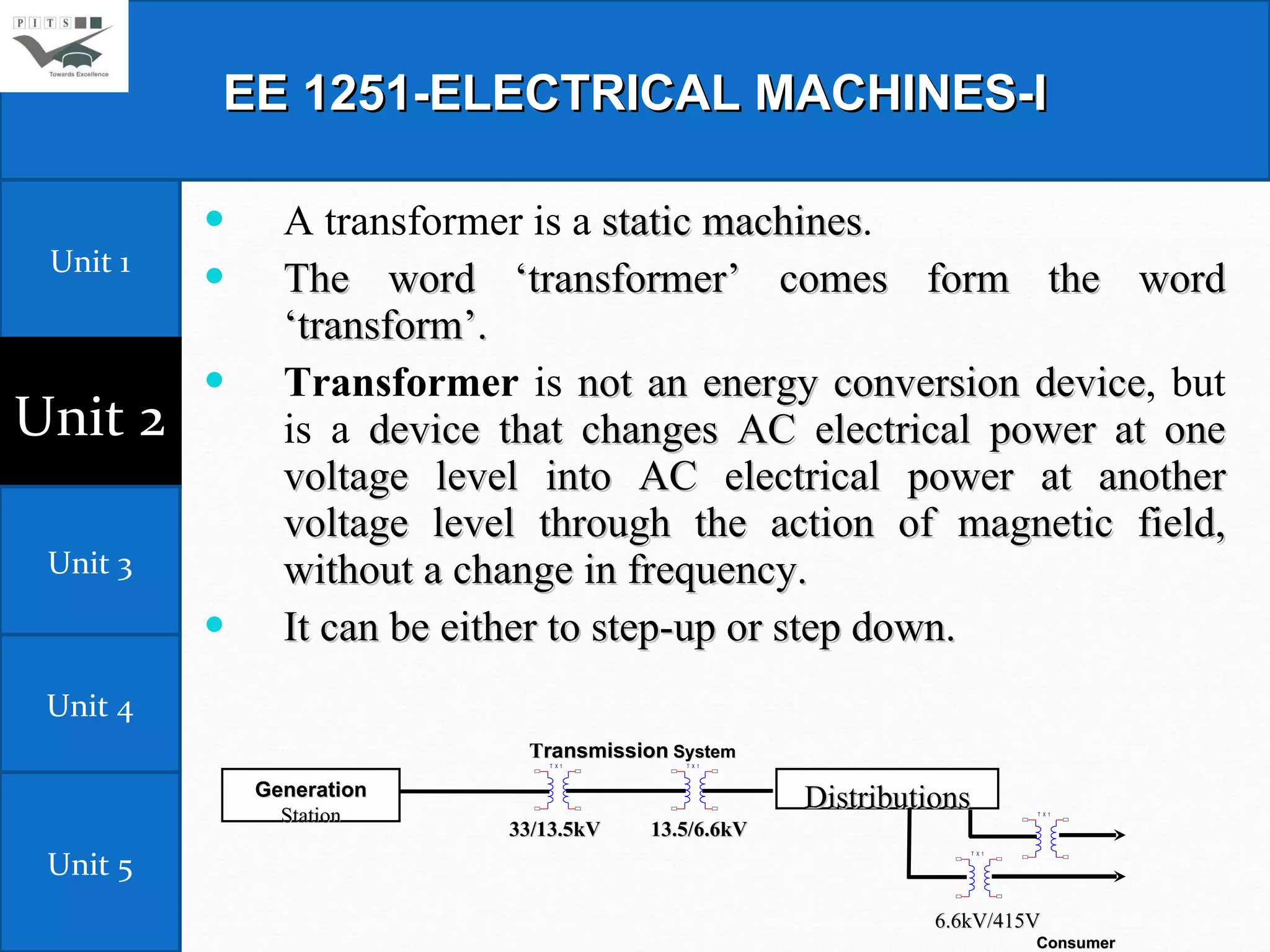
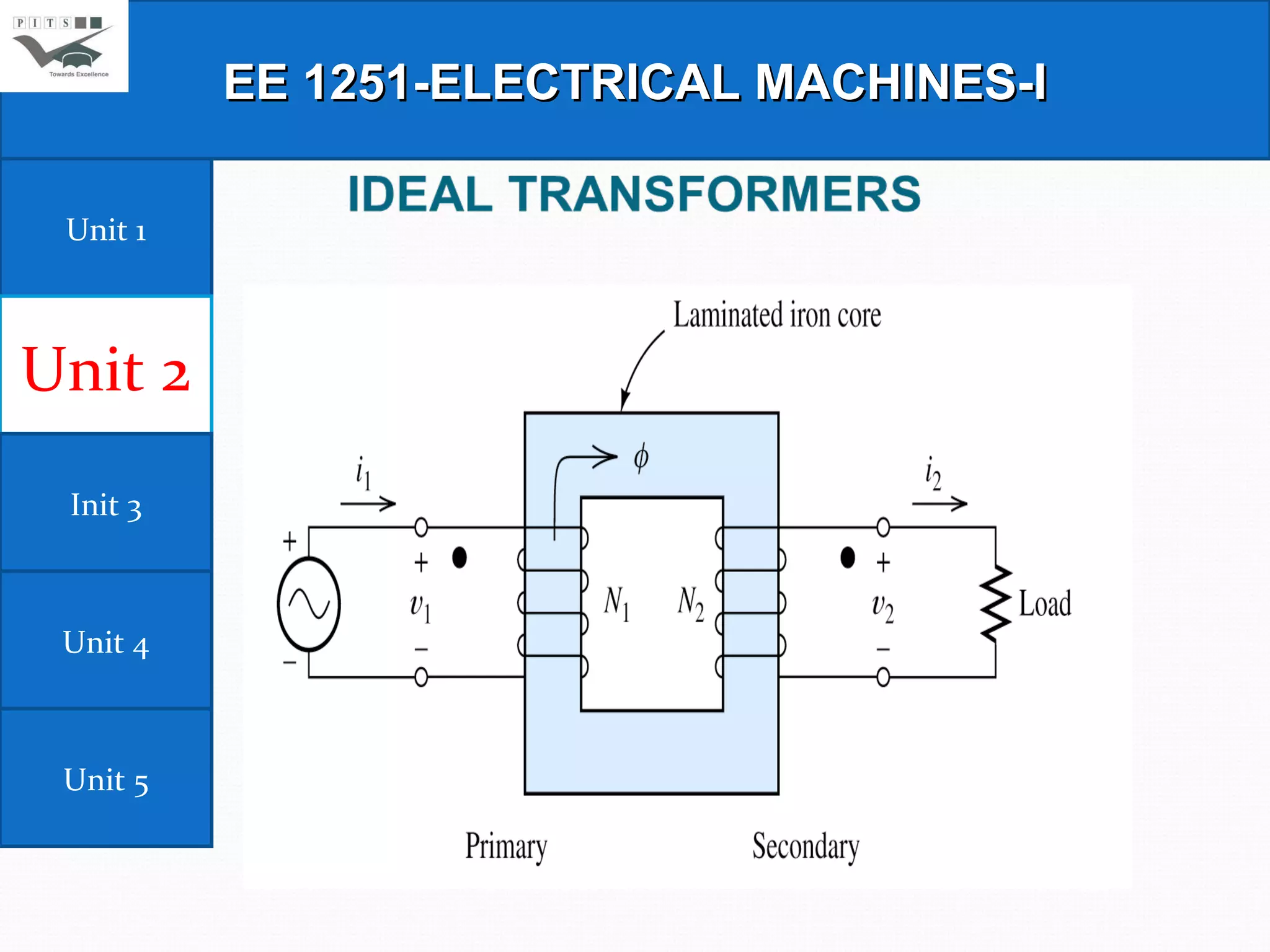
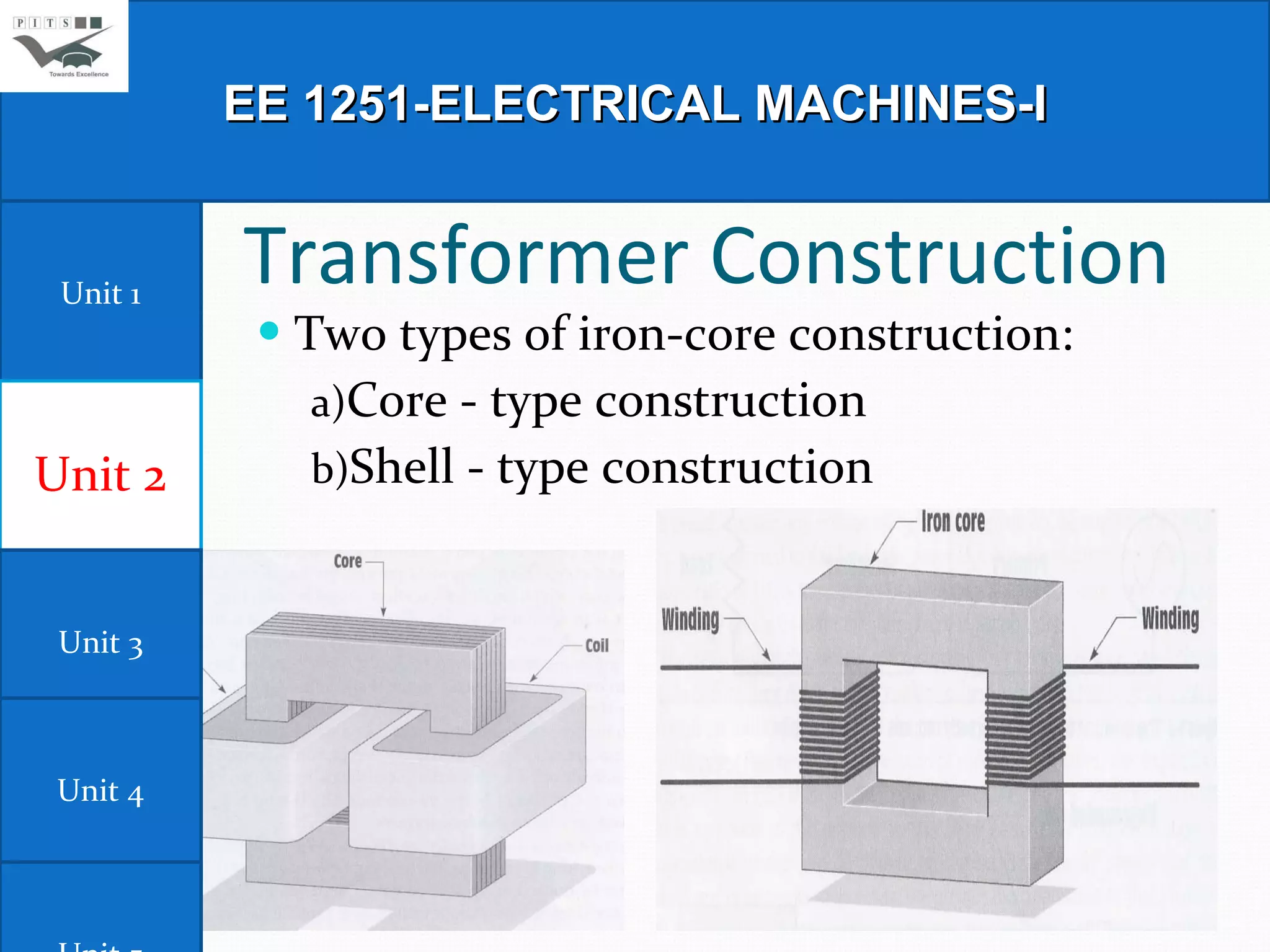
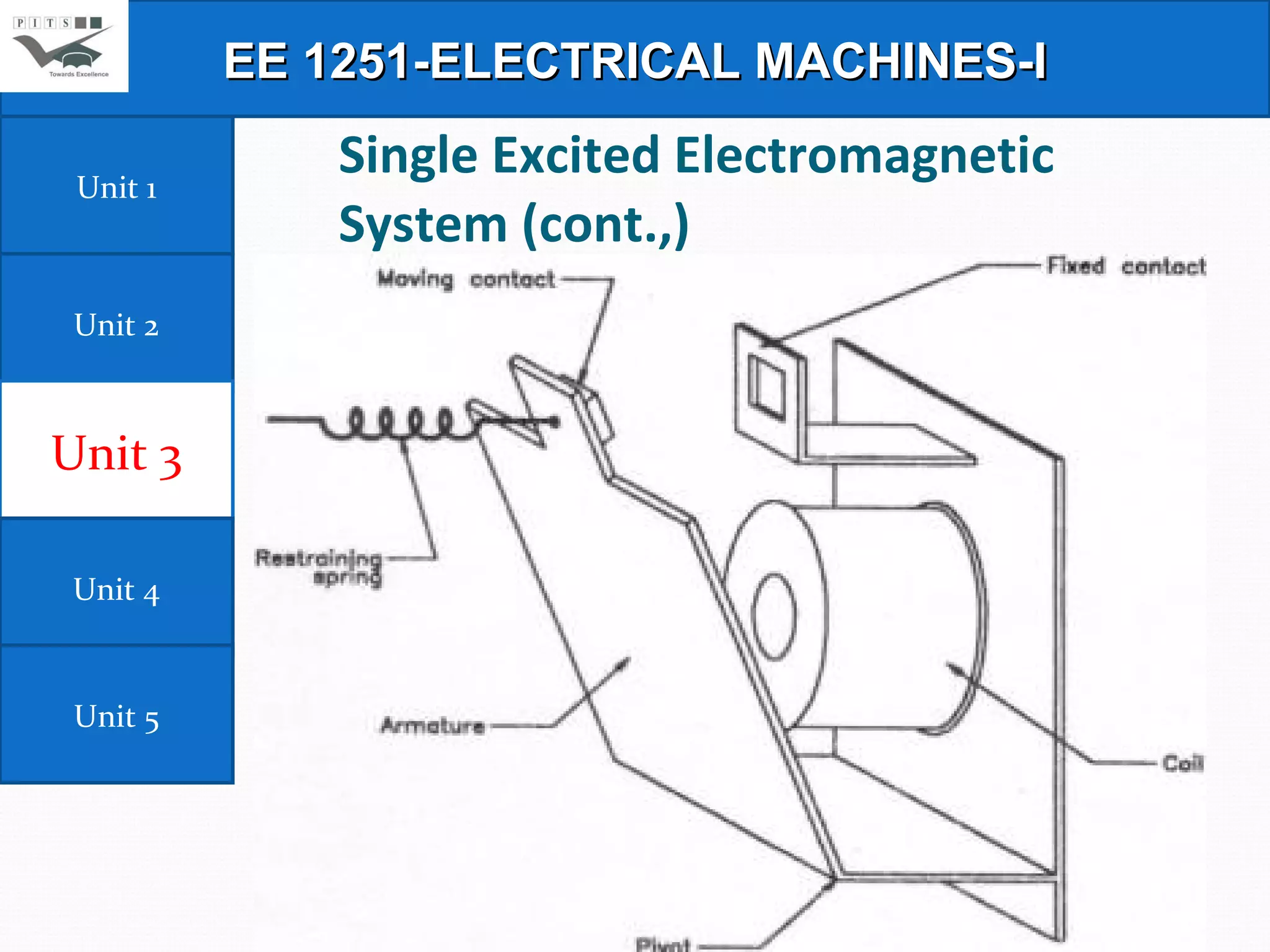
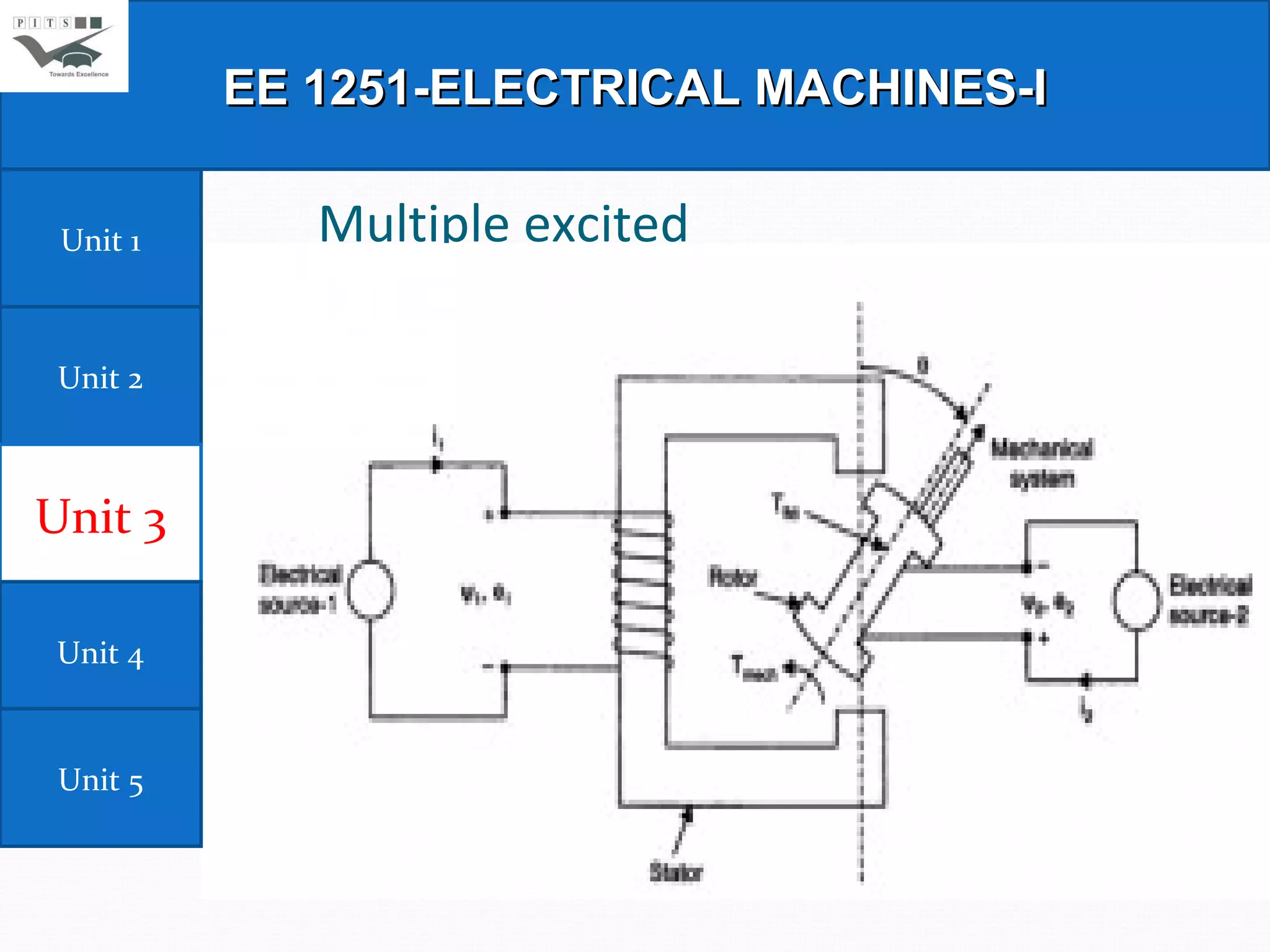
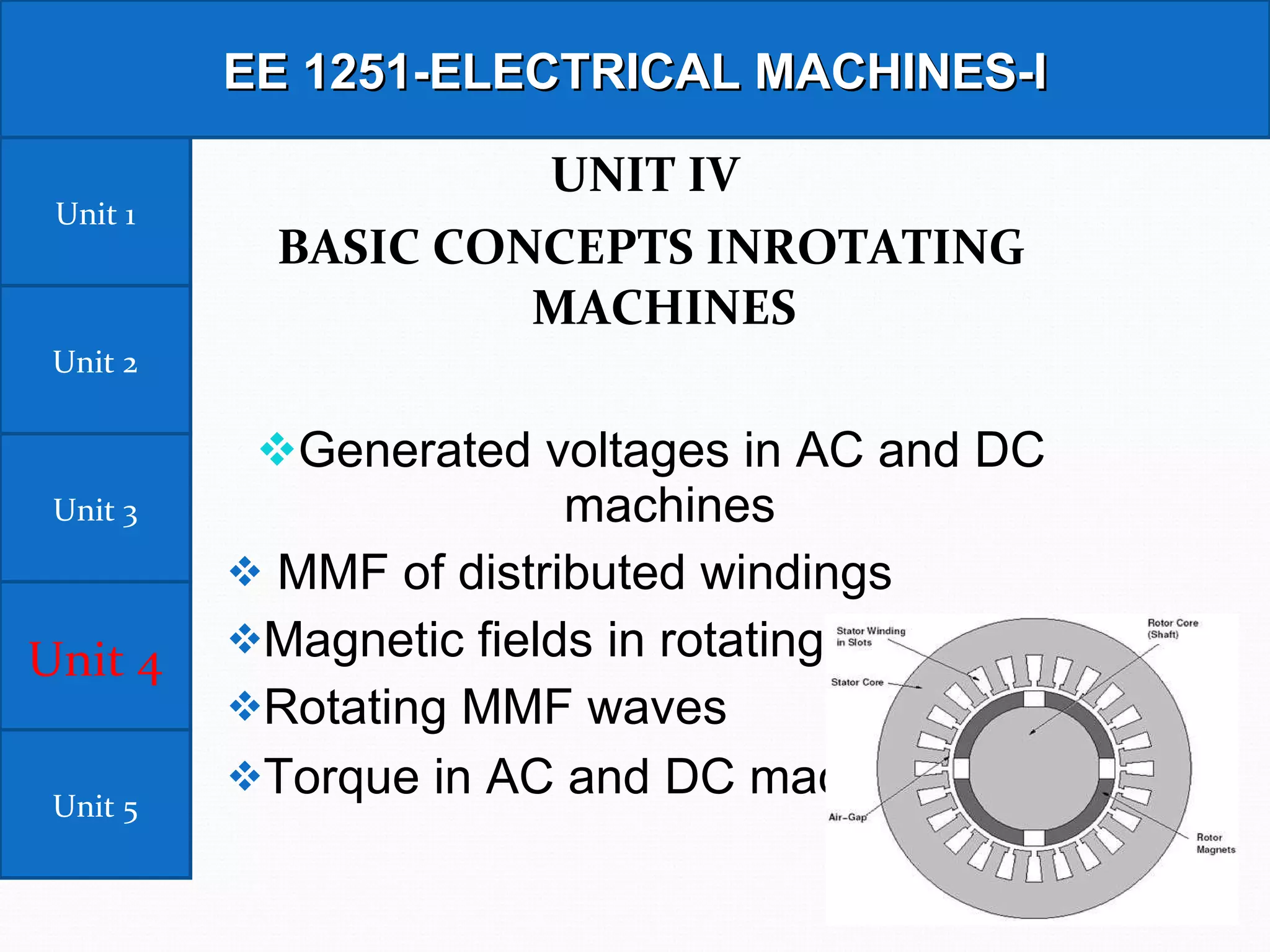
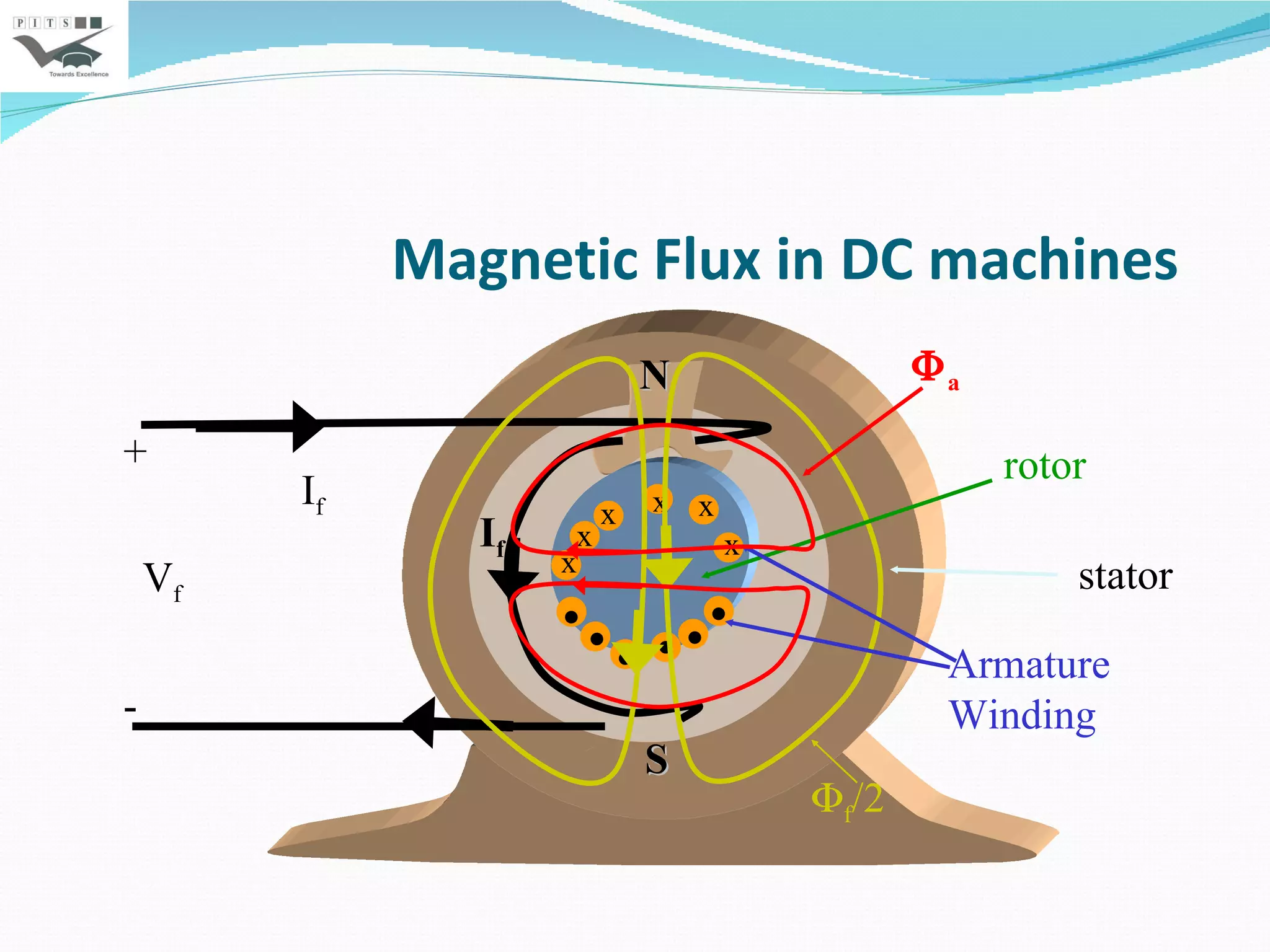
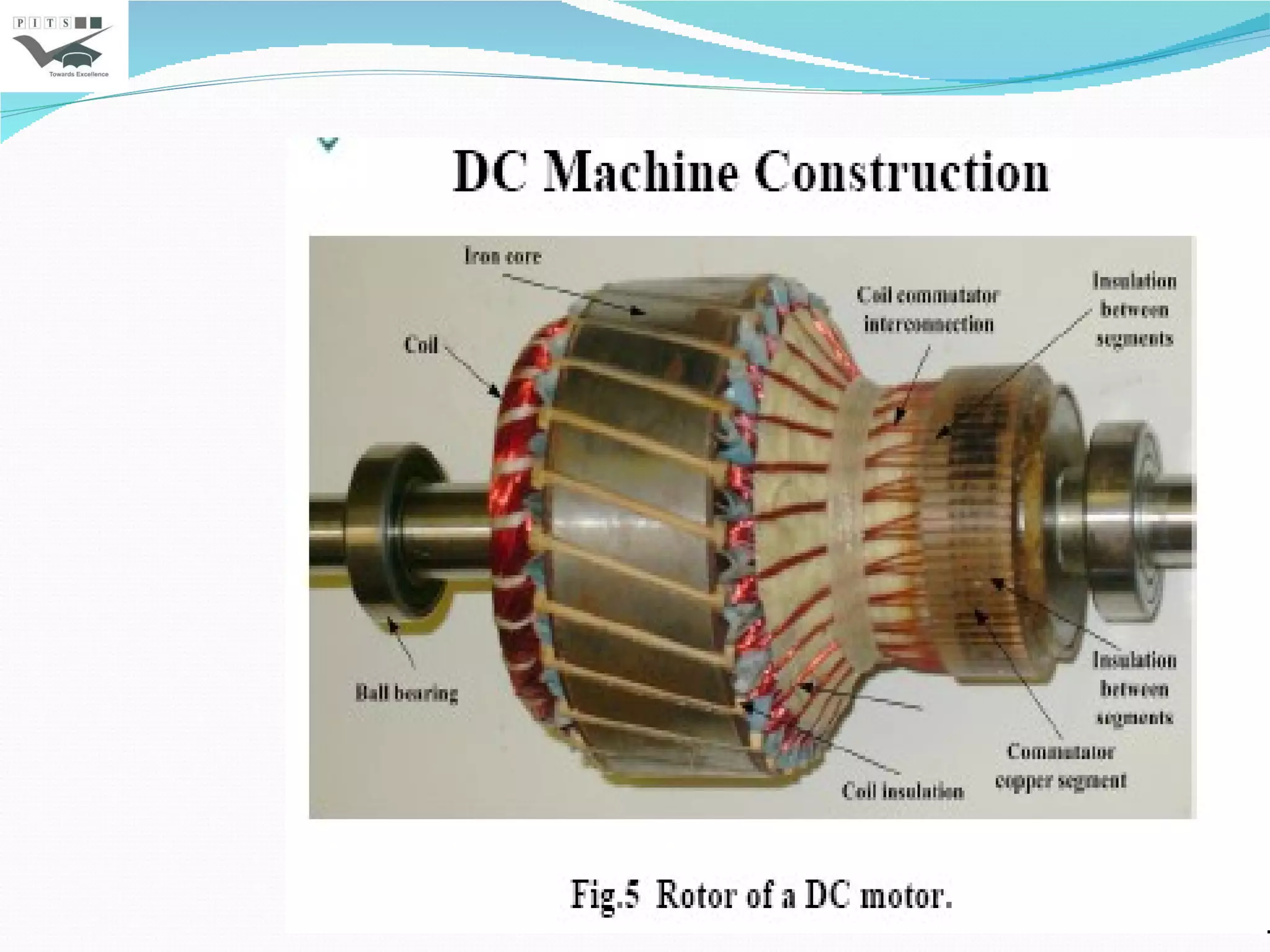
This document outlines the syllabus for an Electrical Machines course. The course aims to teach students the basic principles of electromechanical energy conversion and the operation of transformers and DC machines. The syllabus covers 5 units - introduction to electrical machines, transformers, electromechanical energy conversion, basic concepts in rotating machines, and DC machines. Key topics include transformer construction, operation, and testing, principles of single and multiple excitation, torque production in AC and DC machines, and characteristics and control of DC generators and motors.