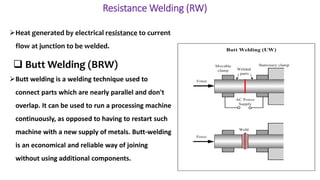
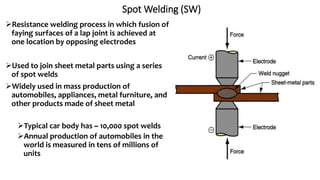
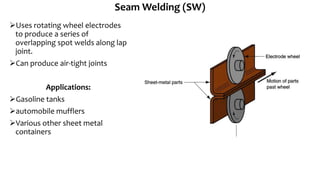
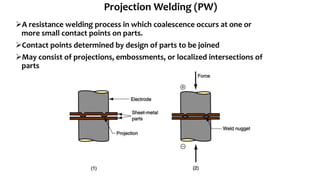
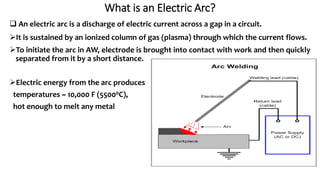
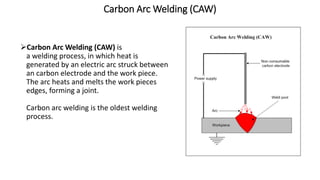
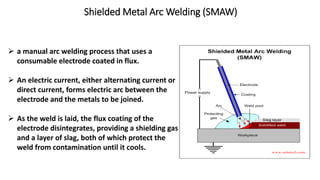
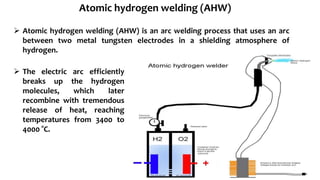
The document presents a detailed overview of electric welding, its definitions, processes, and various types including resistance and arc welding. It covers specific methods like butt welds, spot welds, and seam welds, highlighting their applications in industries such as automotive manufacturing. Additional focus is given to the electric arc and processes like carbon arc welding and atomic hydrogen welding.