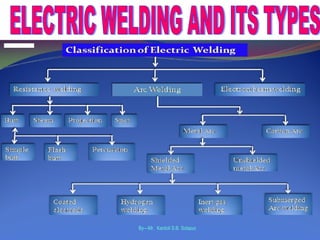
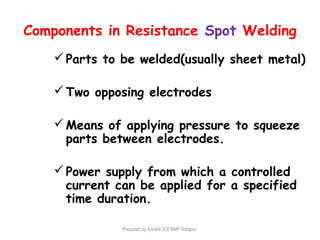
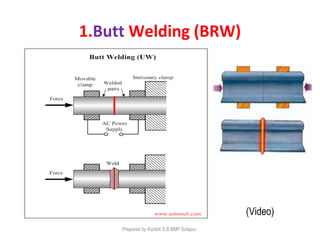
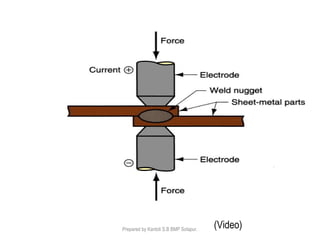
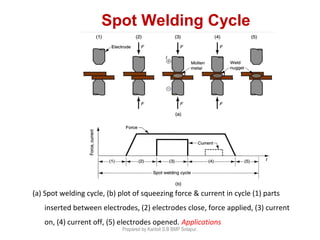
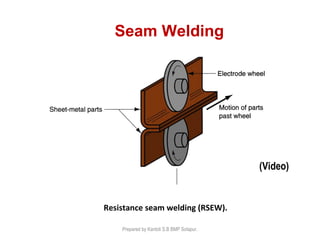
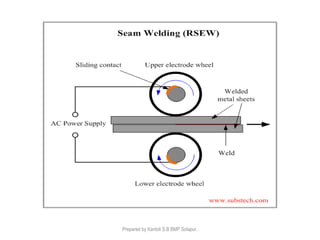
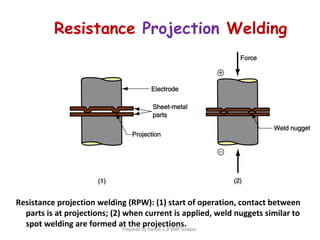
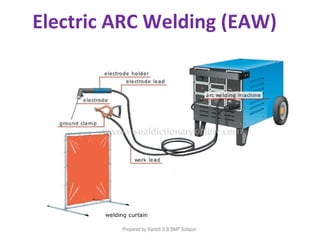
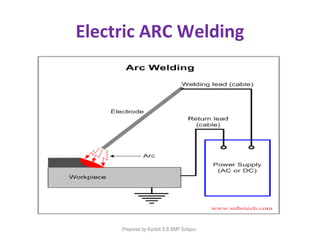
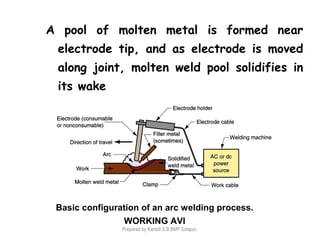
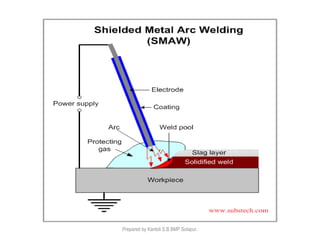
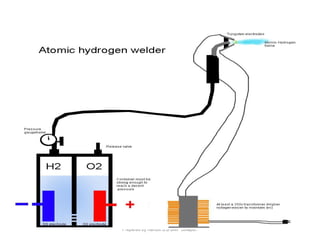
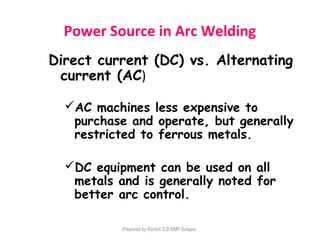
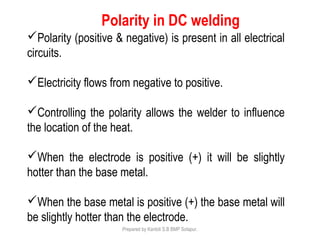
This document discusses two main types of electrical welding: resistance welding and arc welding. Resistance welding uses heat generated by electrical resistance to fuse metals and includes spot welding, seam welding, and projection welding. Arc welding uses an electric arc between an electrode and the workpiece to generate temperatures over 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit and melt the metals. Different arc welding processes use direct or alternating current and different polarities to influence the heat distribution. Shielded metal arc welding is commonly used and provides versatility but with lower productivity than continuous wire processes.