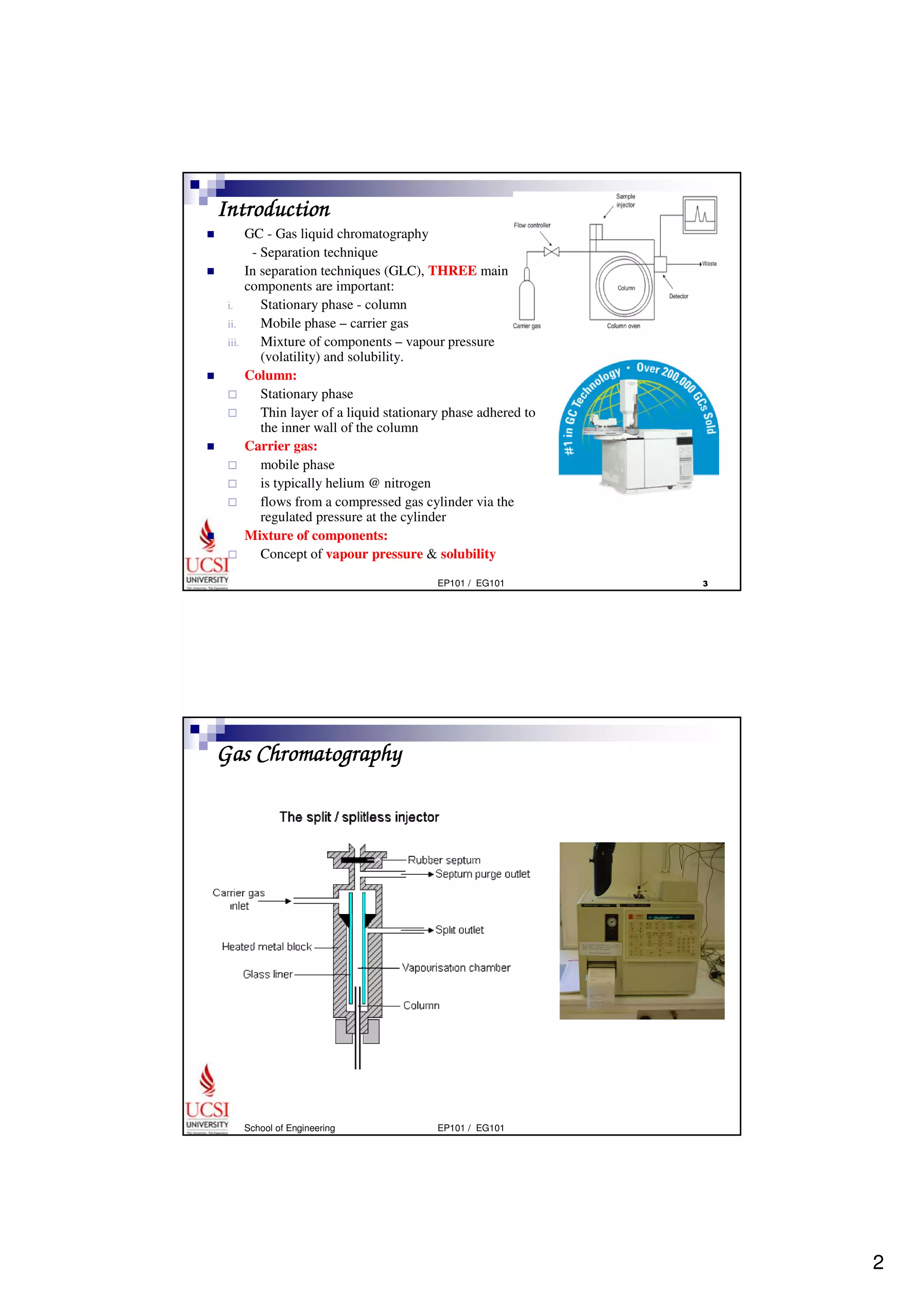
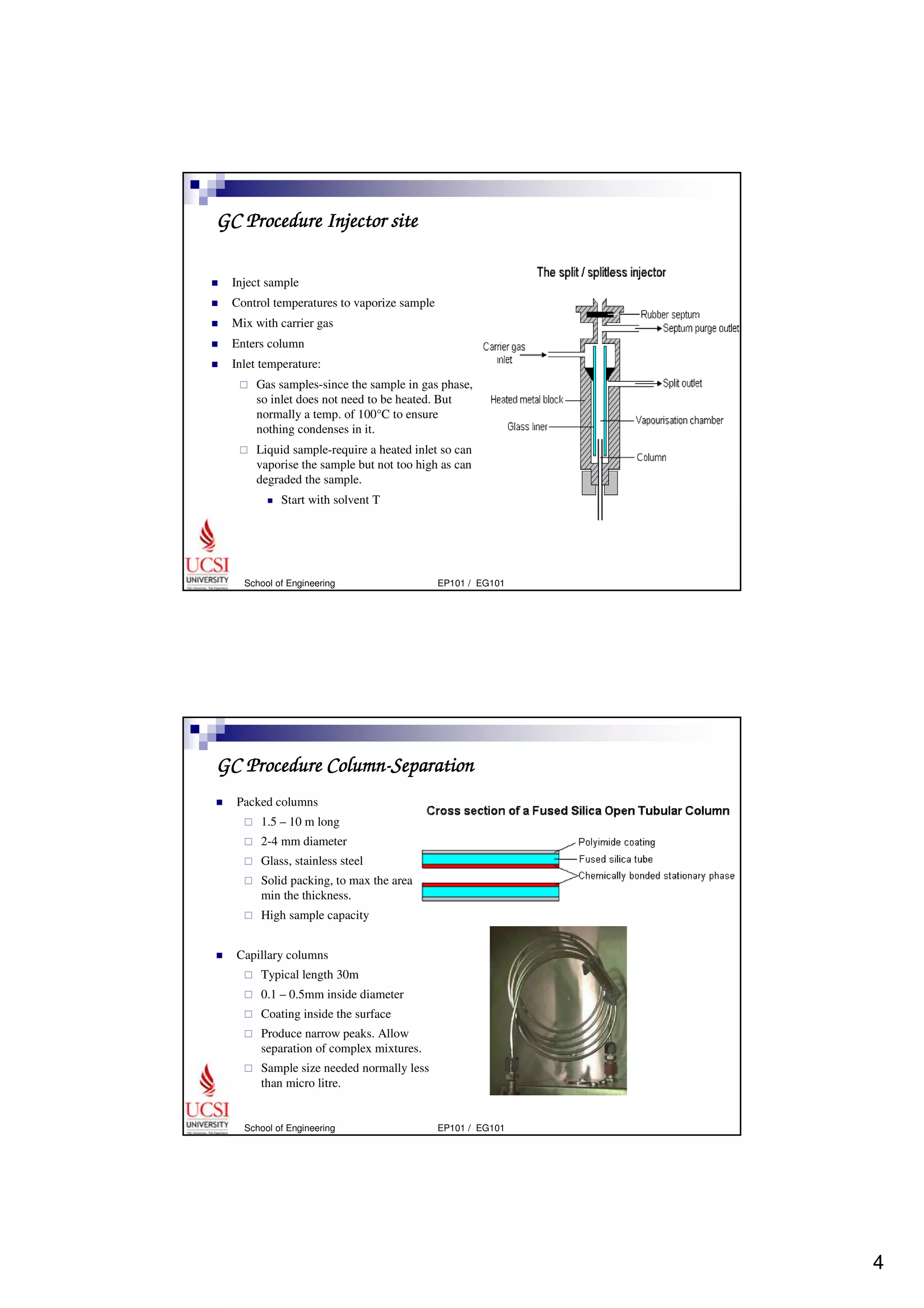
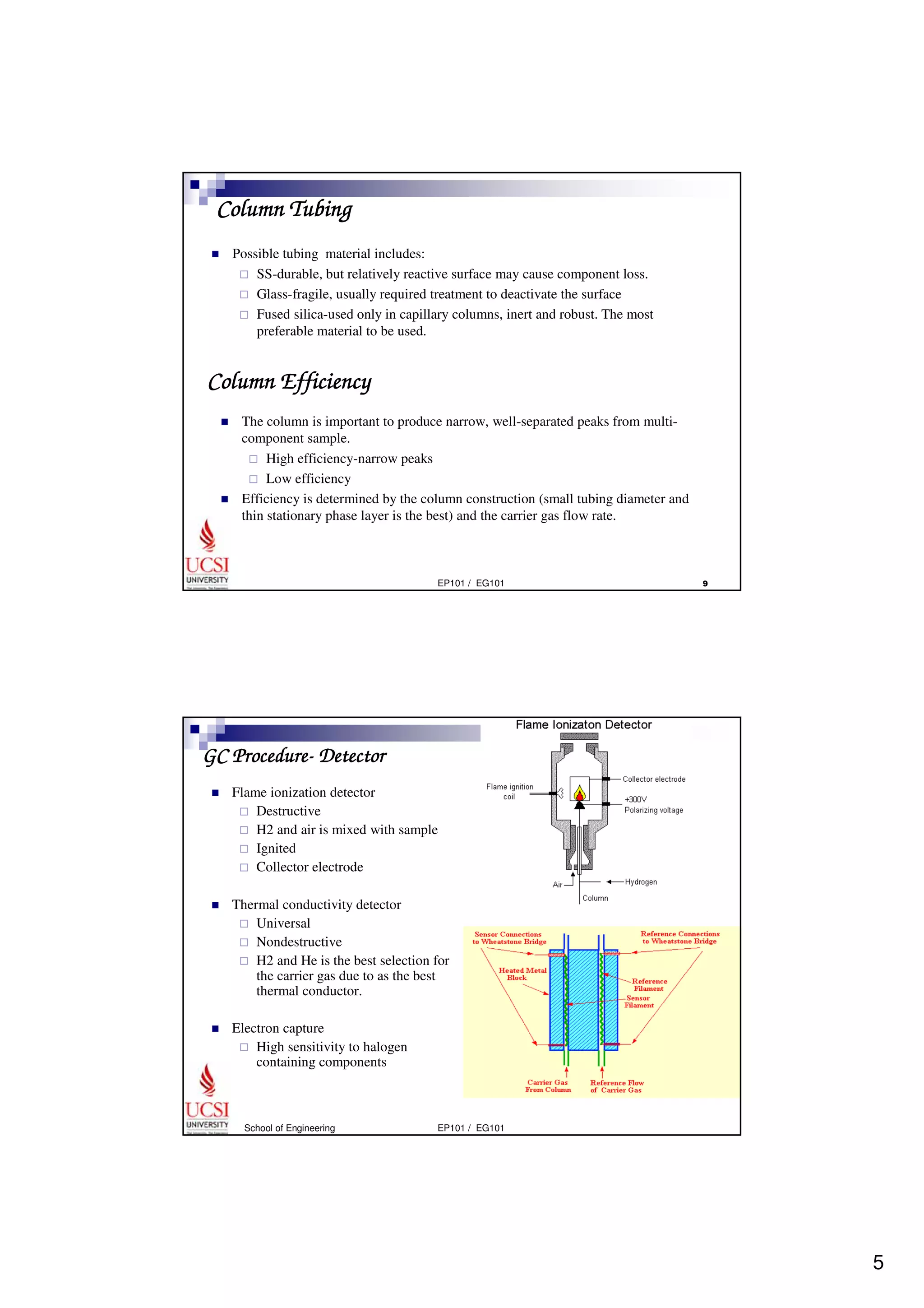
Gas chromatography (GC) is a separation technique that uses a stationary phase coated on the inside of a column and a carrier gas as the mobile phase. The mixture of components is injected and separates into individual components as they travel through the column at different rates depending on their volatility and solubility. GC can be used to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze mixtures by measuring the retention times and peak sizes/areas of the separated components detected by the instrument. Key components of a GC system include the injector, column, detector, and recorder/integrator.