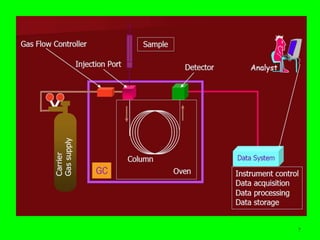
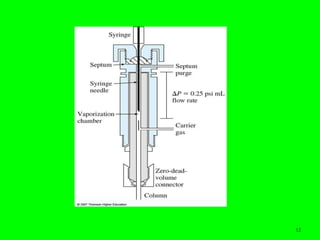
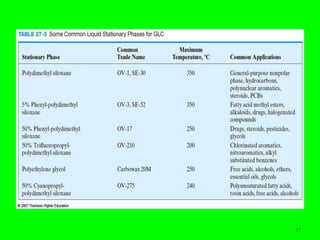
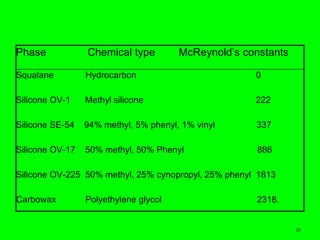
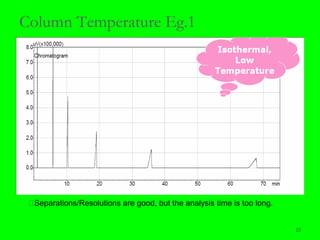
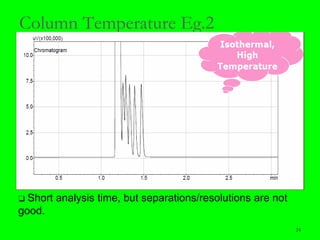
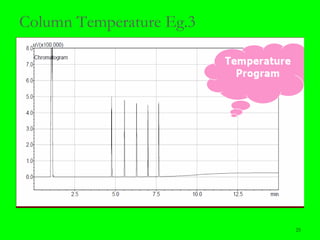
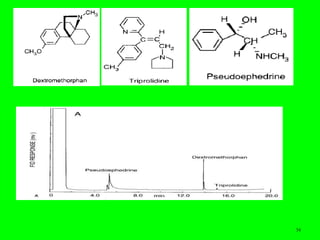
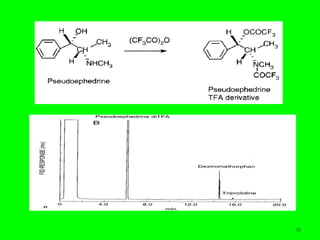
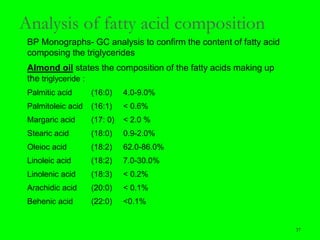
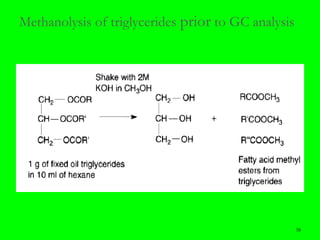
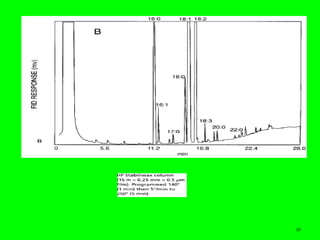
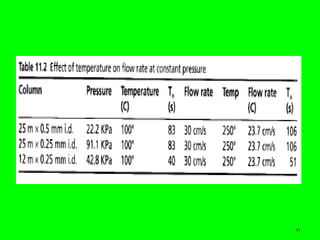
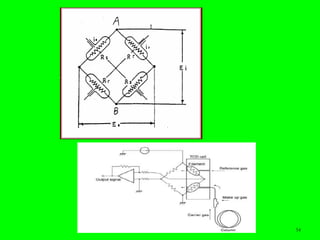
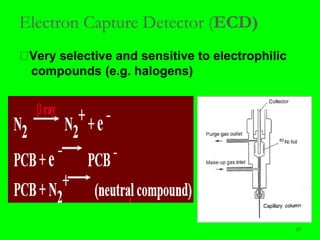
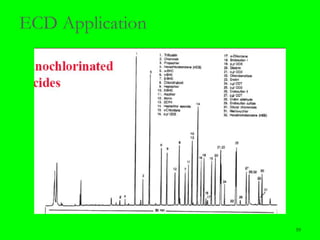
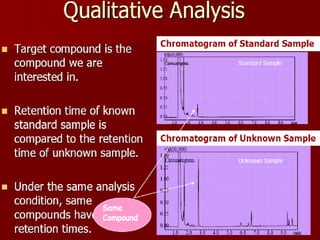
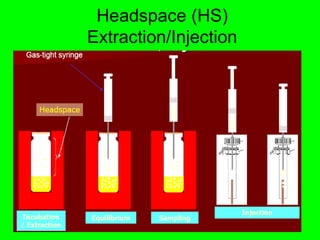
Gas chromatography (GC) is a technique used to separate and analyze mixtures of substances. It works by vaporizing the sample and carrying it by a carrier gas through a column coated with a stationary phase. Components interact differently with the stationary phase and emerge from the column at different retention times, allowing for separation. Key aspects of GC include the carrier gas, column parameters like temperature and phase, and detectors used for analysis. GC is useful for characterizing compounds and quantifying components in mixtures.