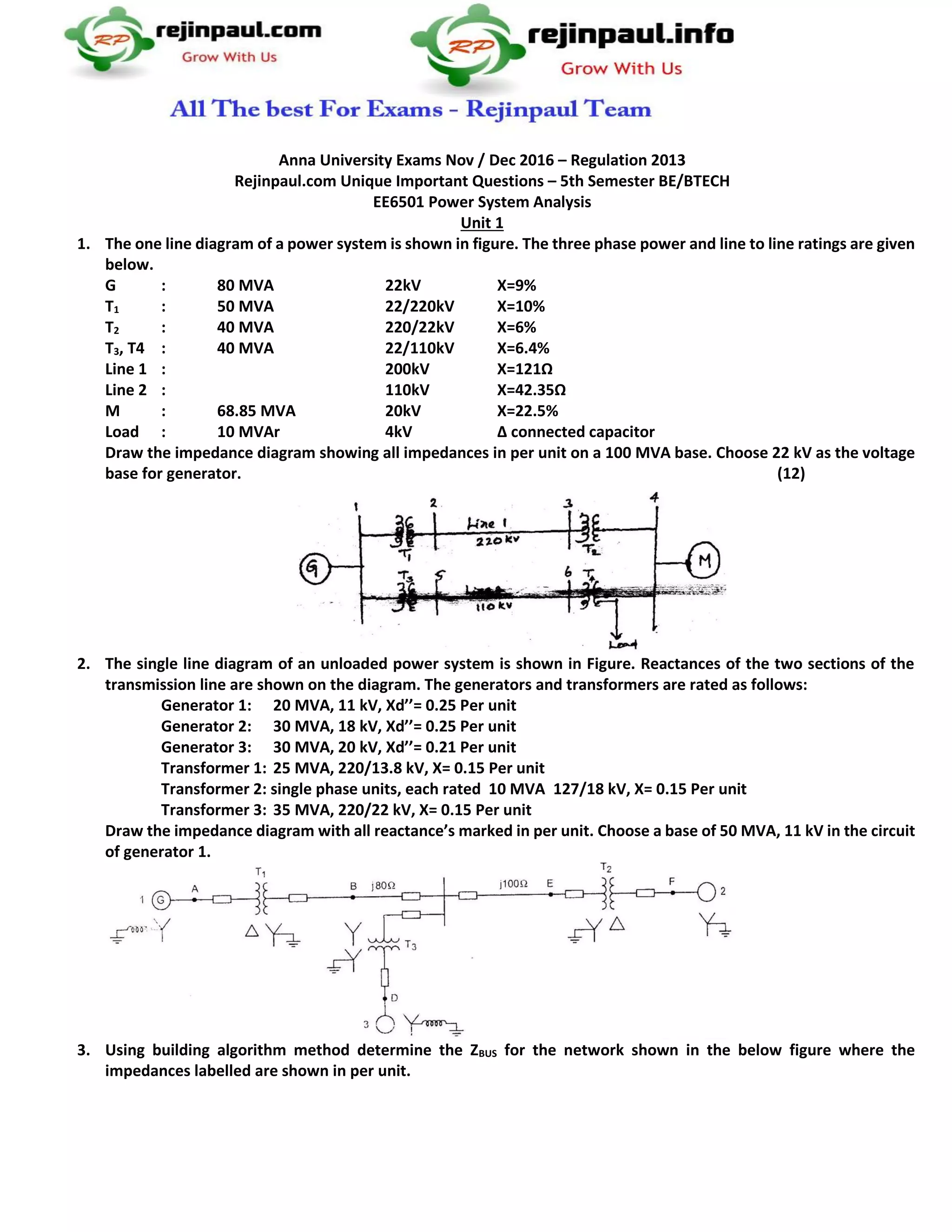
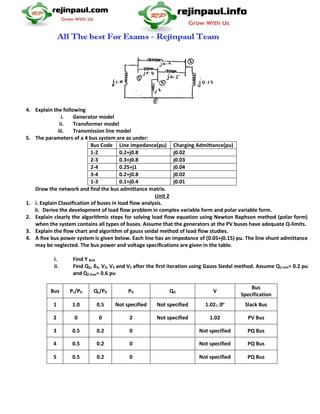
This document provides sample exam questions for a 5th semester power systems analysis course. It covers topics like power flow analysis, fault analysis, sequence networks, transient stability, and swing equations. The questions involve calculating fault currents, drawing impedance diagrams, solving load flows, determining critical clearing angles, and more. In total, there are 5 units covering different power systems analysis concepts, and each unit provides 5 sample exam questions related to those concepts for review.