Unit 2 Questions_Nagrath kothari
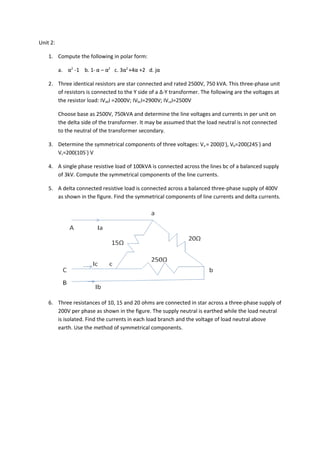
- 1. Unit 2: 1. Compute the following in polar form: a. α2 -1 b. 1- α – α2 c. 3α2 +4α +2 d. jα 2. Three identical resistors are star connected and rated 2500V, 750 kVA. This three-phase unit of resistors is connected to the Y side of a Δ-Y transformer. The following are the voltages at the resistor load: ΙVabΙ =2000V; ΙVbcΙ=2900V; ΙVcaΙ=2500V Choose base as 2500V, 750kVA and determine the line voltages and currents in per unit on the delta side of the transformer. It may be assumed that the load neutral is not connected to the neutral of the transformer secondary. 3. Determine the symmetrical components of three voltages: Va = 200(0◦), Vb=200(245◦) and Vc=200(105◦) V 4. A single phase resistive load of 100kVA is connected across the lines bc of a balanced supply of 3kV. Compute the symmetrical components of the line currents. 5. A delta connected resistive load is connected across a balanced three-phase supply of 400V as shown in the figure. Find the symmetrical components of line currents and delta currents. 6. Three resistances of 10, 15 and 20 ohms are connected in star across a three-phase supply of 200V per phase as shown in the figure. The supply neutral is earthed while the load neutral is isolated. Find the currents in each load branch and the voltage of load neutral above earth. Use the method of symmetrical components.
- 2. 7. The voltages at the terminals of a balanced load consisting of three 20 ohm Y-connected resistors are 200(0◦), 10(255.5◦) and 200(151◦) V. Find the line currents from the symmetrical components of the line voltages if the neutral of the load is isolated. What relation exists between the symmetrical components of the line and phase voltages? Find the power expended in three 20 ohm resistors from the symmetrical components of currents and voltages. 8. Draw the positive, negative and zero sequence impedence networks for the power system given in the figure. Choose a base of 50 MVA, 220kV in the 50Ω transmission lines and mark all impedences in pu. The ratings of the generators and transformers are: Generator 1: 25 MVA, 11kV, X”=20% Generator 2: 25 MVA, 11kV, X”=20% Three-phase transformer (each): 20MVA, 11 Y/220 Y kV, X=15% to its subtransient reactance. The zero sequence reactance of each machine is 8%. Assume that the zero sequence reactances of the lines are 250% of their positive sequence reactances. 9. For the power system in the figure draw the positive, negative and zero sequence networks. The generators and transformers are rated as follows:
- 3. Generator 1: 25 MVA, 11kVA, X”=0.2, X2=0.15, X0=0.03 pu Generator 2: 15 MVA, 11kVA, X”=0.2, X2=0.15, X0=0.05 pu Synchronous motor 3: 25MVA, 11kVA, X”=0.2, X2=0.2, X0=0.1 pu Transformer 1: 25MVA, 11 Δ/120 Y kV, X=10% 2: 12.5MVA, 11 Δ/120 Y kV, X=10% 3: 10MVA, 120 Y/11 Y kV, X=10% Choose a base of 50 MVA, 11kV in the circuit of generator 1. Note: Zero sequence reactance of each line is 250% of its positive sequence reactance. 10. Consider the circuit shown in the figure. Suppose Van=100(0◦), Vbn=60(60◦), Vcn=60(120◦), Xs=12Ω and Xab=Xbc=Xca=5Ω. a. Calculate Ia, Ib and Ic without using symmetrical components. b. Calculate Ia, Ib and Ic using symmetrical components.
- 4. Answers: 1. a. 1.732(210◦) b. 2(0◦) c. 1.732(150◦) d. 1(210◦) 2. Ia=j1.16 pu, Vab=1.17(109.5◦) pu, Vbc=0.953(-65.4◦) pu, Vcb=0.995(-113.1◦) pu 3. Va1=197.8(-3.3◦) V; Va2=20.2(158.1◦) V; Vao=21.61(10.63◦) V 4. Ia1=19.23(-30◦) A, Ia2=19.23(150◦) A; Iao=0A 5. IA1=27.87(-30◦ ) A; IA2=13(-44.93◦ ) A; IA0=0A 6. Ia=16.16+j1.335A, Ib=-9.24-j10.66A; Ic=-6.93+j9.32 A, VNn=Va0=40.75 V 7. 1500.2 W
