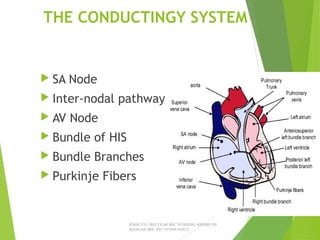
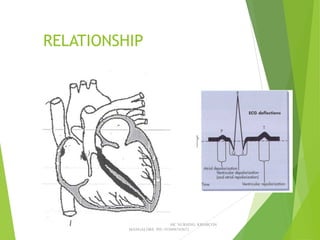
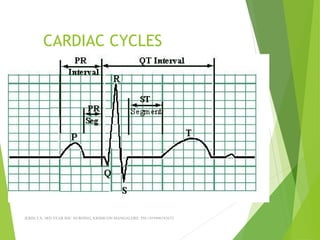
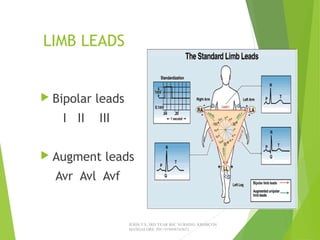
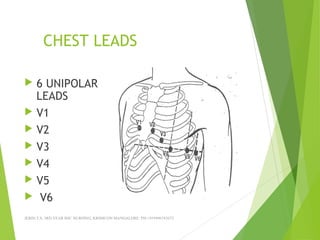
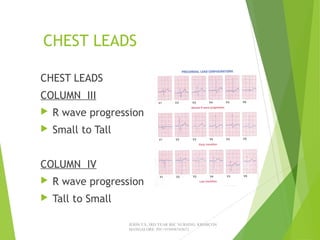
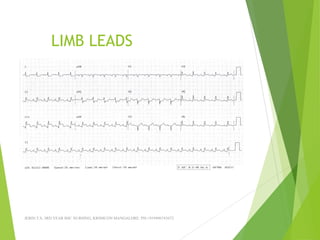
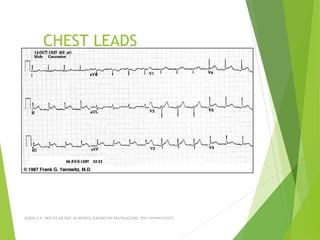
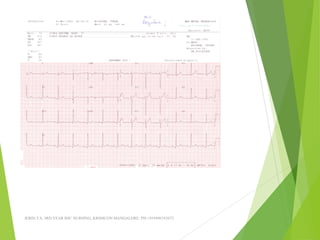
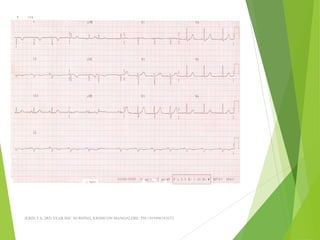
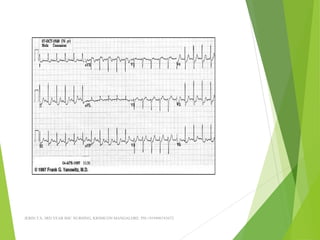
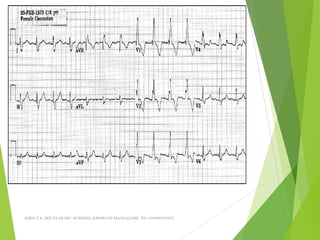
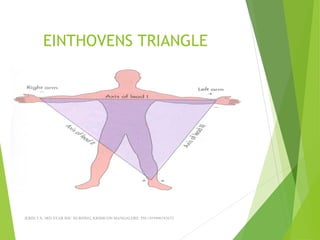
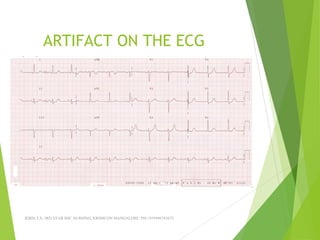
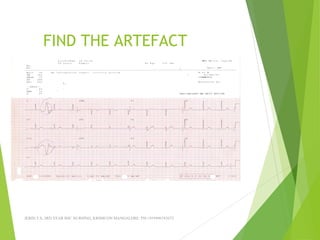
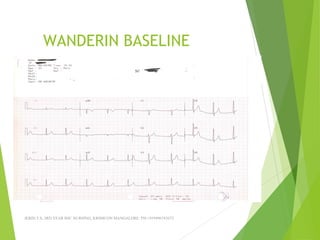
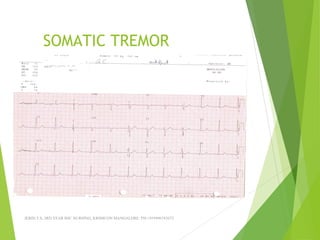
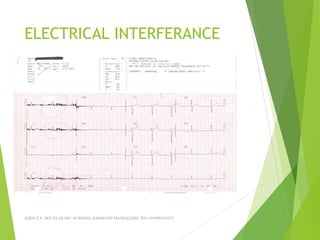
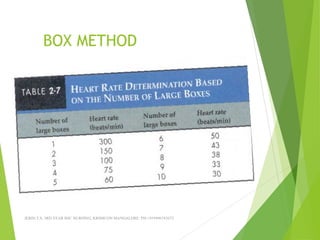
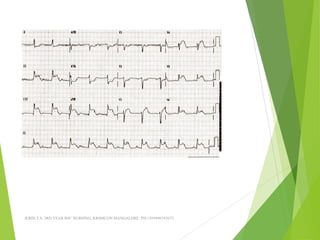
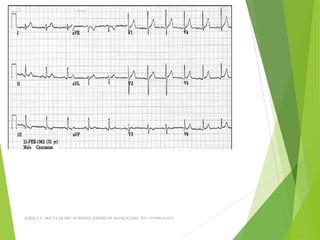
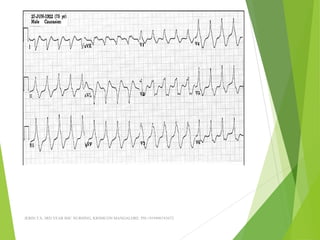
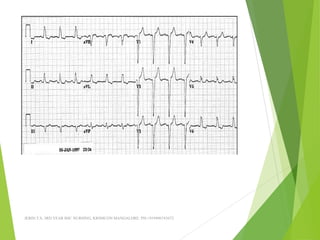
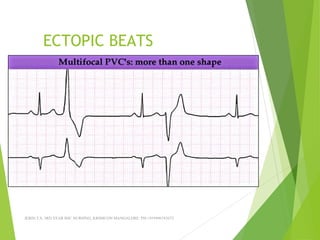
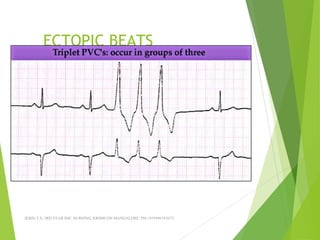
The document provides guidance on performing and interpreting 12-lead electrocardiograms (ECGs). It outlines the proper procedure for applying electrodes, including skin preparation and placement of limb and chest leads. Key aspects that must be checked include verifying the leads are attached correctly, the ECG is free of artifact, and identifying any critical findings such as arrhythmias or ST segment changes. Interpreting the ECG requires evaluating the rhythm, measuring the heart rate, identifying normal and abnormal waveforms, and relating findings to the patient's condition.