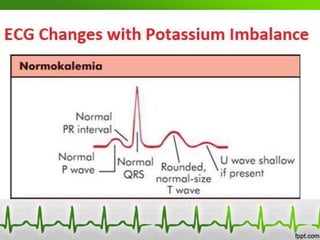
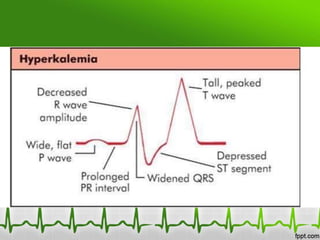
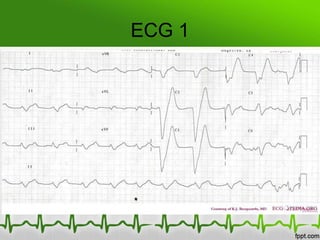
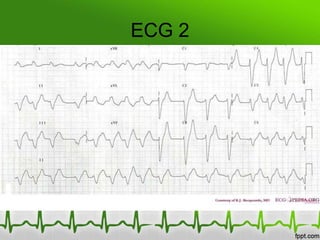
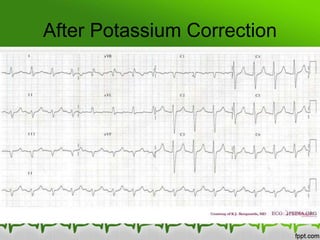
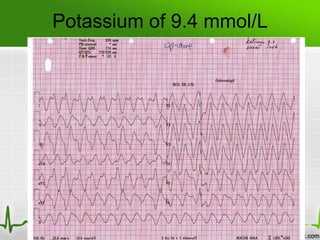
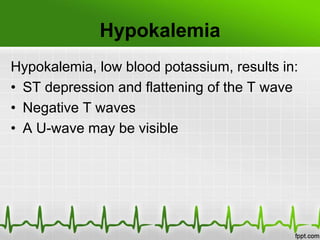
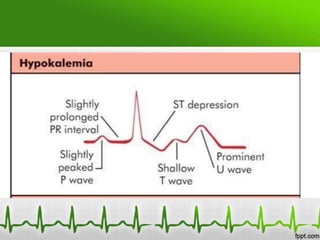
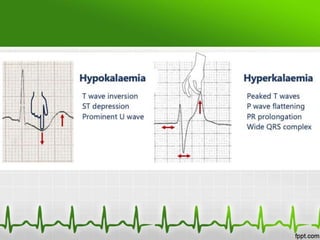
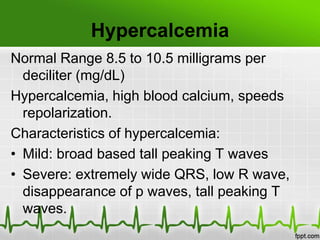
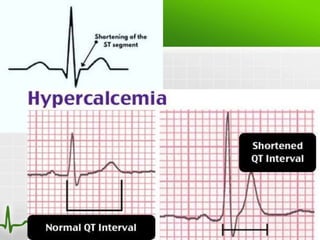
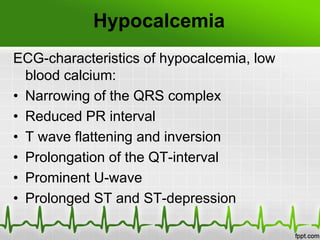
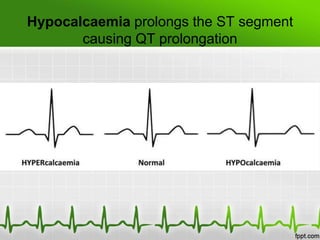
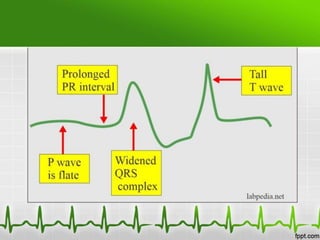
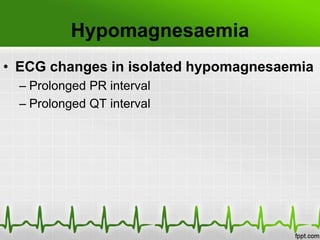
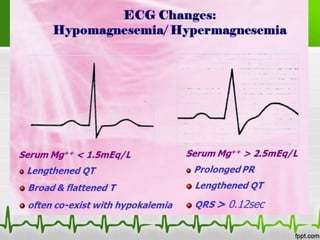
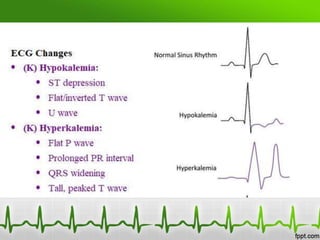
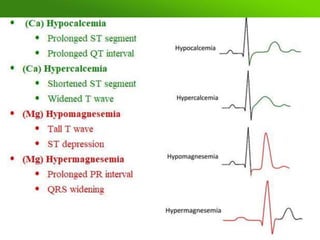
This document discusses various electrolyte abnormalities and their ECG manifestations. Hyperkalemia causes widened and low amplitude P-waves, widened QRS complex with potential fusion of the QRS-T segment and loss of the ST segment, and tall tented T-waves. Hypokalemia results in ST depression and flattened T-waves and possible negative T-waves. Hypercalcemia speeds repolarization, causing tall peaked T-waves at mild levels and extremely wide QRS complex with low R-waves and disappearance of P-waves at severe levels. Hypocalcemia causes a narrowed QRS complex, reduced PR interval, flattened and inverted T-waves, and prolonged QT and ST intervals. Hypomag