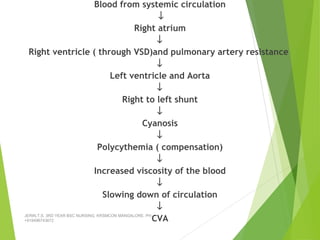
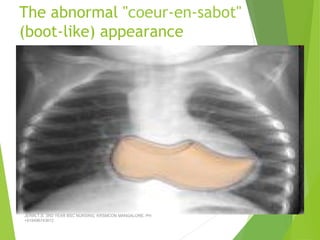
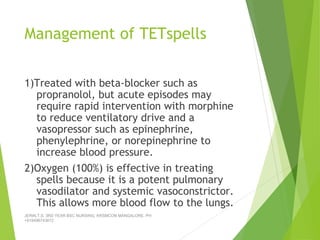
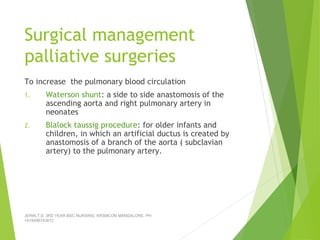
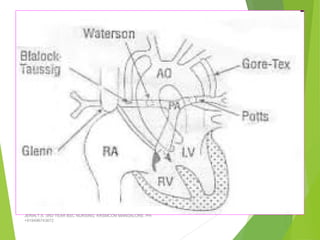
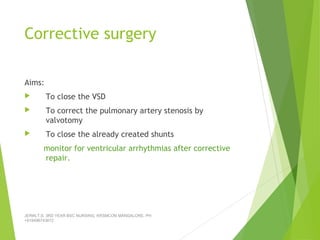
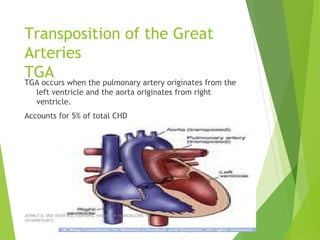
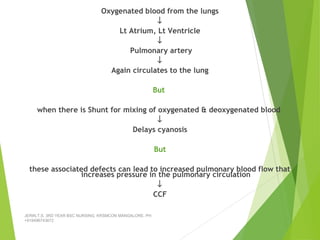
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is the most common cyanotic congenital heart defect, characterized by four abnormalities: pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy. It causes cyanosis and spells where blood cannot get enough oxygen. Treatment includes medications to manage spells, surgery to improve blood flow such as shunt procedures, and eventually total repair surgery. Nursing care focuses on managing spells with oxygen and positioning, treating infections, and preparing for surgery.