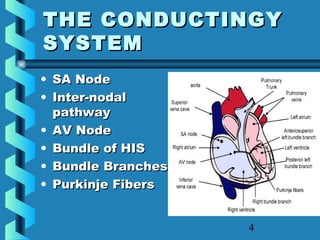
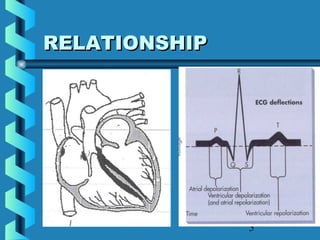
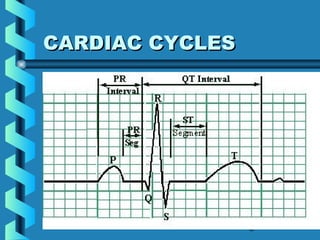
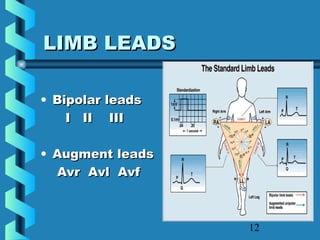
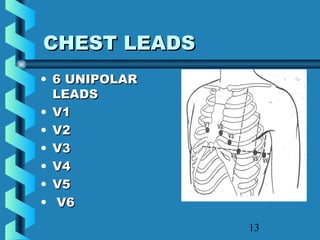
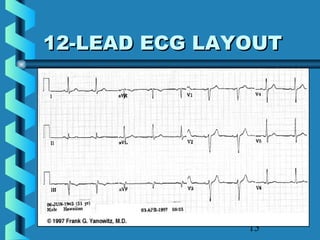
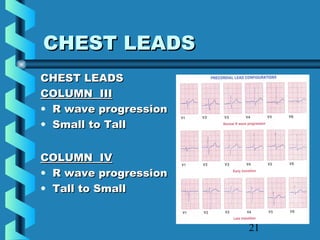
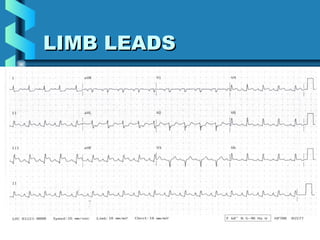
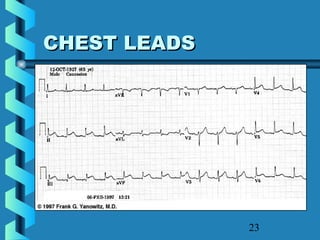
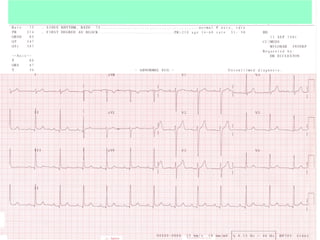
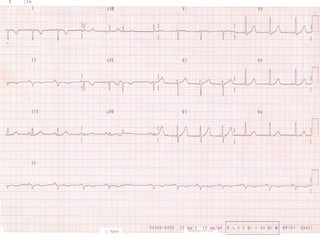
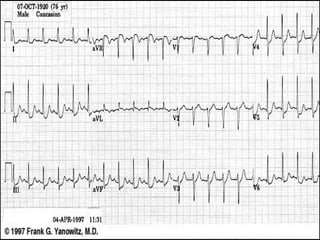
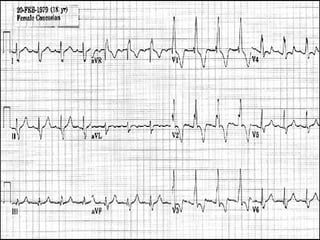
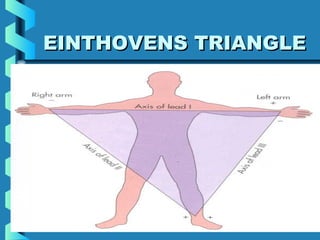
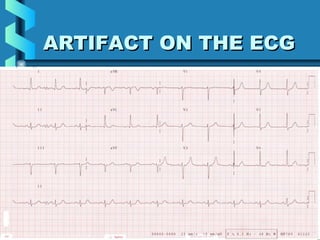
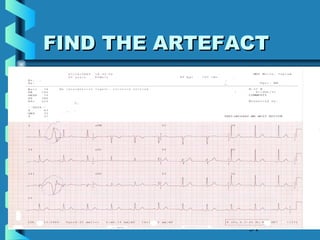
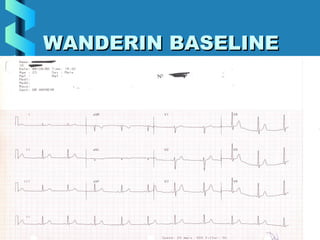
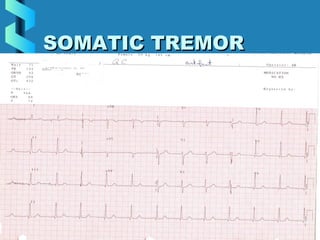
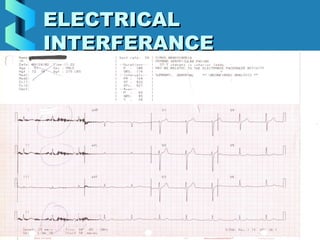
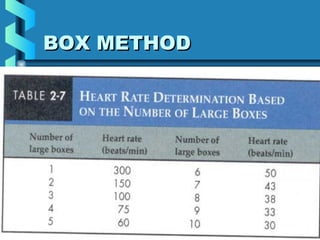
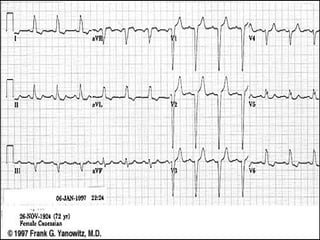
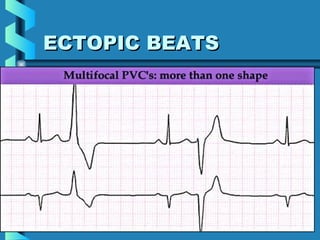
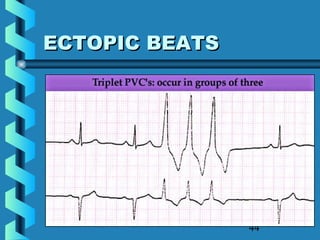
This document provides instructions for performing and interpreting a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). It describes the proper procedure for electrode placement on the limbs and chest to record the ECG. It also explains how to identify normal ECG waveforms, arrhythmias, artifacts and basic critical values like bradycardia and tachycardia. The overall goal is to equip users to efficiently obtain high quality 12-lead ECGs and evaluate them for normal rhythms and abnormalities.