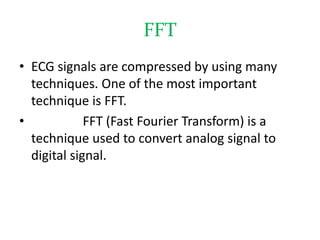
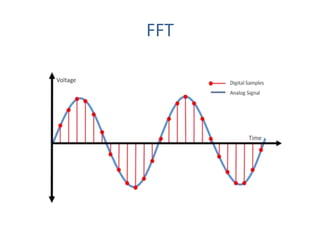
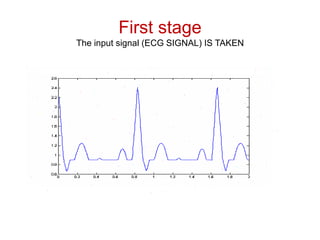
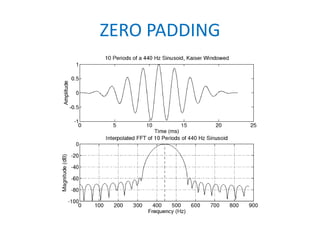
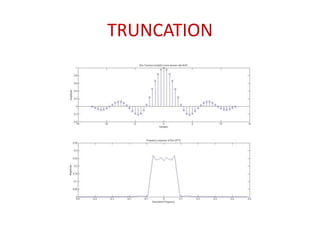
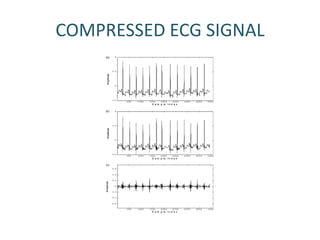
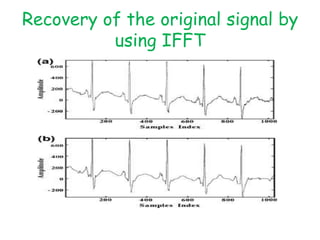
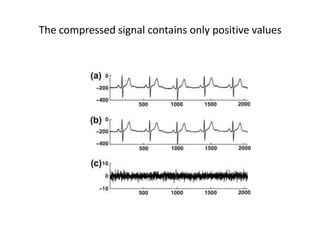
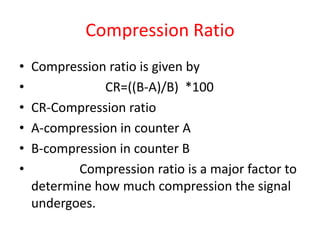
The document discusses ECG signal compression using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to facilitate the transfer of ECG signals by reducing their amplitude and frequency. The compression process involves five stages: input signal, two compression counters, recovery using Inverse FFT (IFFT), and error checking. It emphasizes the importance of compression ratio and its applications in medical contexts, such as transmitting patient reports between doctors.