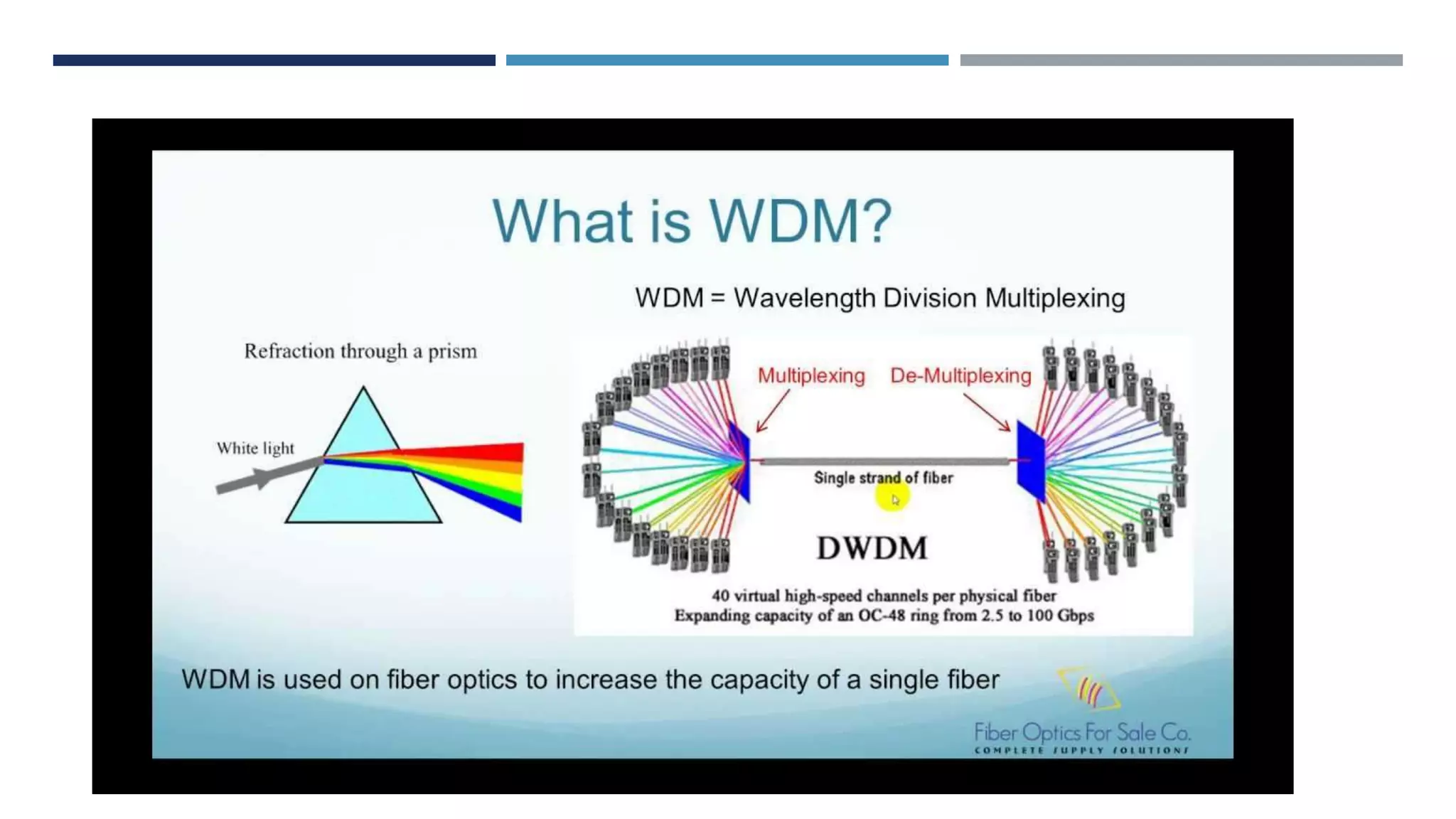
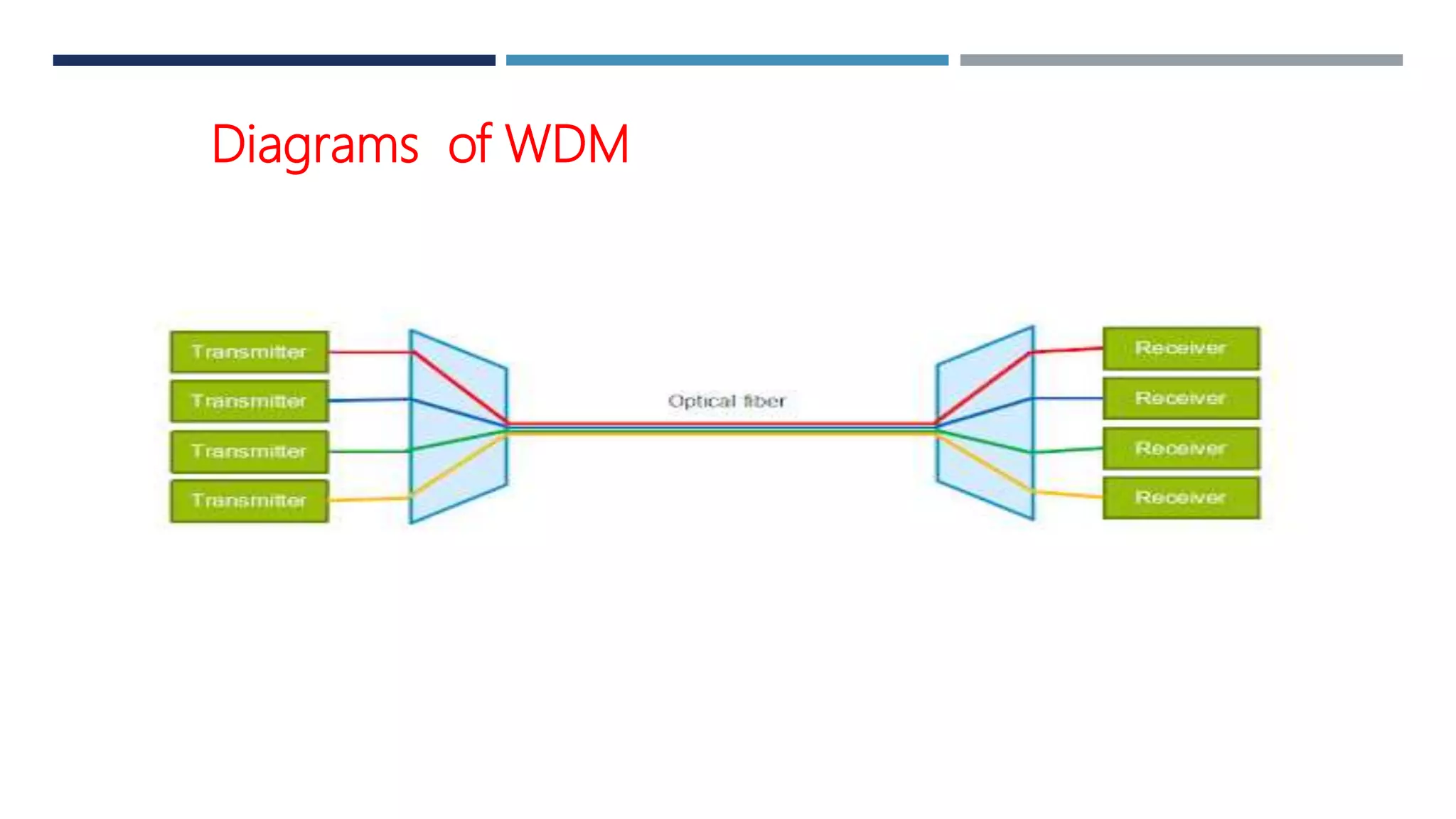
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) allows multiple optical carrier signals to be transmitted through a single optical fiber by using different wavelengths of laser light. In WDM, signals from different sources are combined by a multiplexer and transmitted through the fiber. At the receiving end, a demultiplexer splits the signal into its different wavelength components and sends each to the corresponding receiver. WDM can be divided into coarse WDM (CWDM) and dense WDM (DWDM). CWDM uses wider spacing between wavelengths and supports fewer channels, while DWDM uses narrower spacing and supports more channels. WDM enables multiplying the effective bandwidth of fiber optic systems and reducing transmission costs.