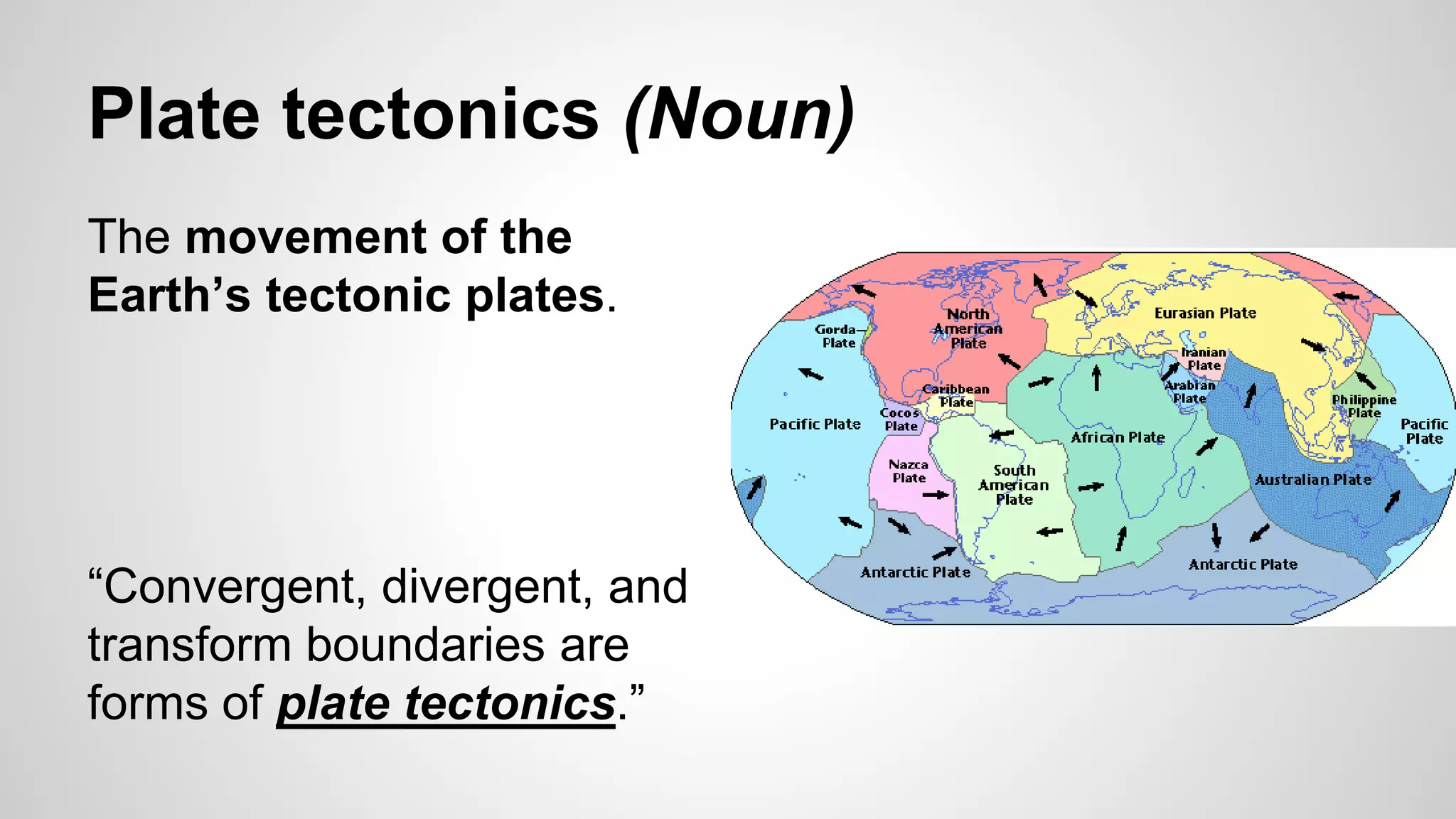
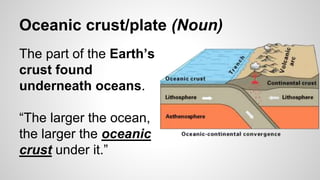
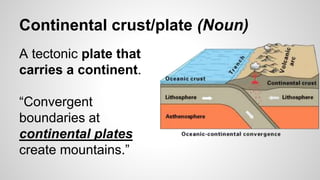
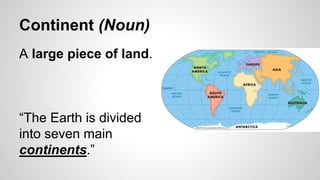
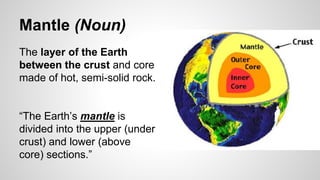
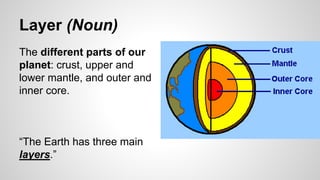
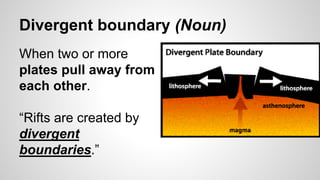
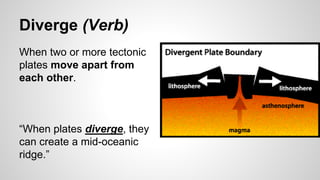
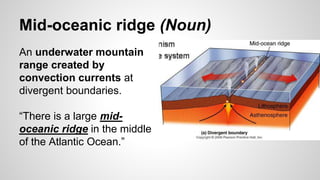
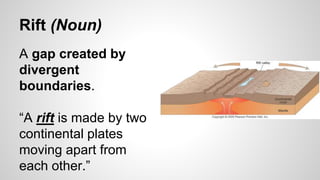
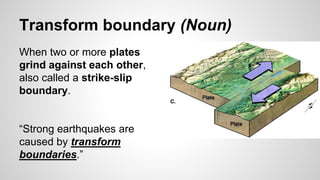
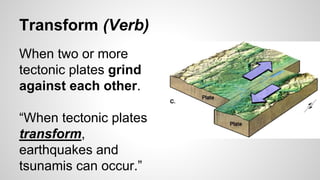
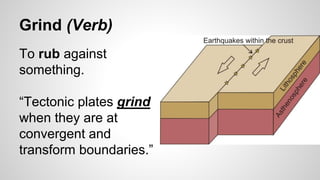
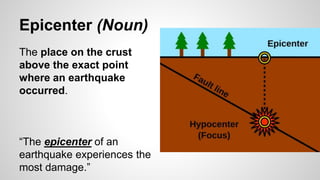
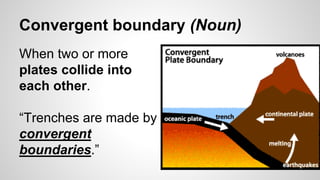
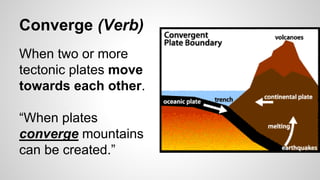
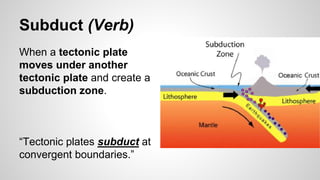
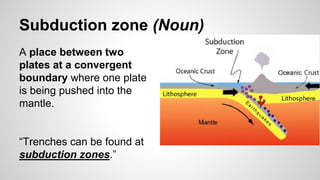
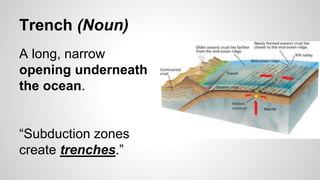
Plate tectonics involves the movement of tectonic plates via divergent, convergent, and transform plate boundaries. The Earth's crust is divided into these tectonic plates which move apart from each other at divergent boundaries, collide at convergent boundaries, or grind past each other at transform boundaries. These plate movements cause volcanic activity and earthquakes, and create geological features such as mid-ocean ridges, trenches, and mountains.