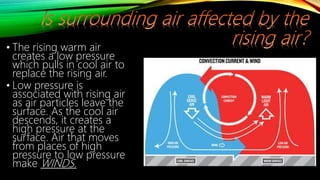
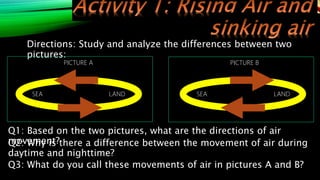
The document discusses atmospheric phenomena such as breezes, monsoons, and the intertropical convergence zone. It explains that breezes are winds that blow over short distances and are caused by the unequal heating of the Earth's surface. Monsoons are seasonal wind systems characterized by reversal of wind directions. The Philippines experiences the northeast monsoon from October to March and the southwest monsoon from July to September. The monsoons affect farming in the Philippines both positively, through providing water for irrigation, and negatively, through potential flooding.