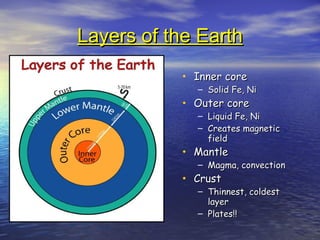
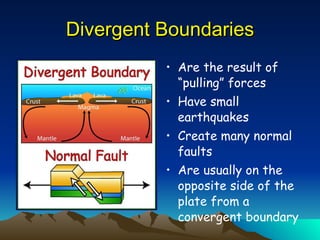
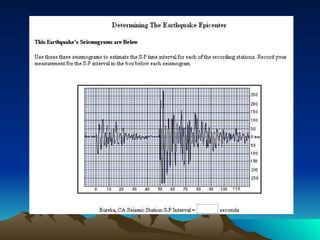
This document provides an overview of plate tectonics and its relationship to major geological features of Earth such as mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. It describes the three main types of plate boundaries - divergent, convergent, and transform - and explains their association with earthquakes, volcanoes, and landform creation. Examples are given of specific volcanic and impact crater landforms, including how Chesapeake Bay was formed by a meteor impact 36 million years ago. Classroom activities are proposed that involve mapping earthquakes and volcanoes to illustrate plate tectonic concepts.