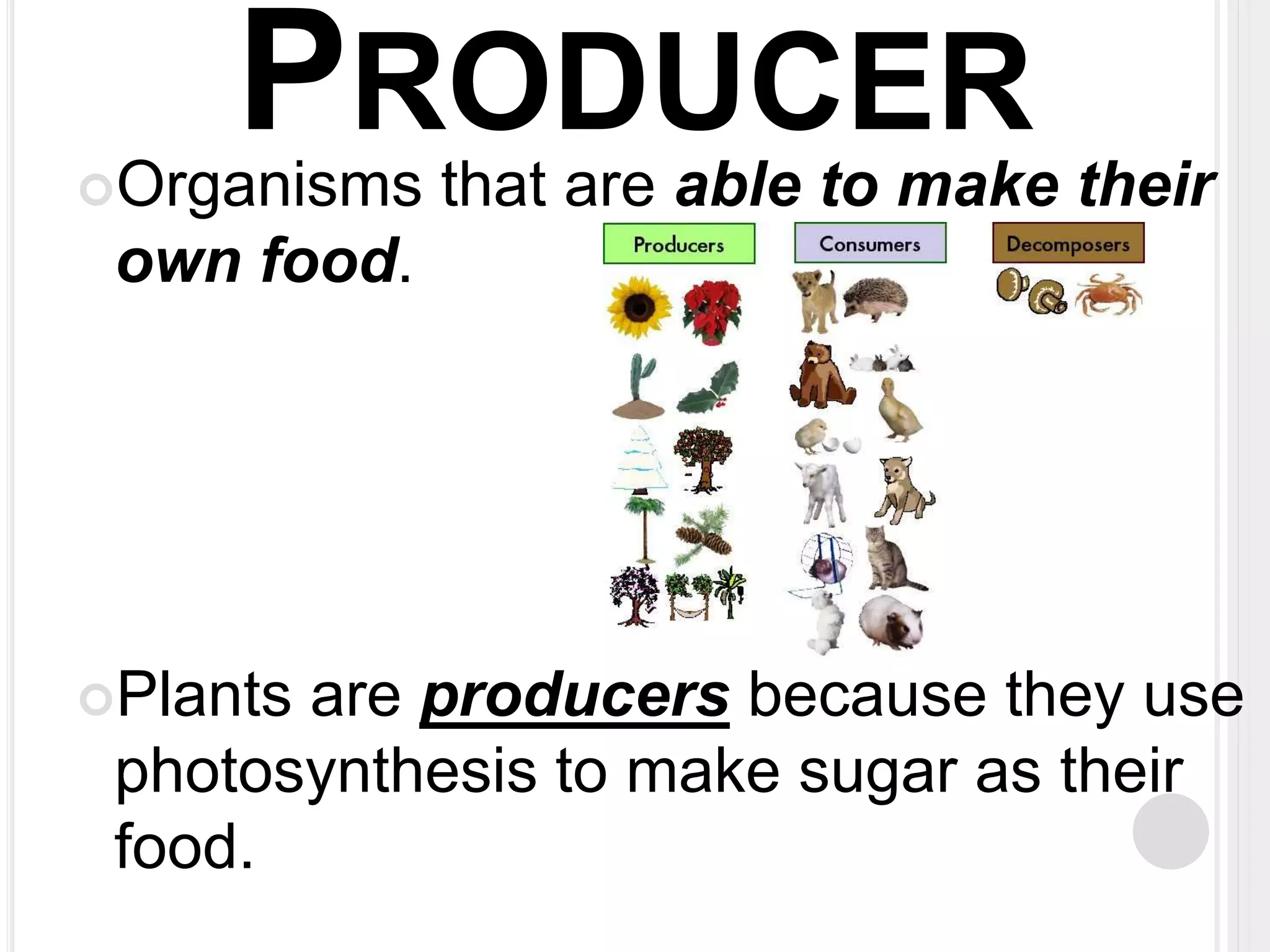
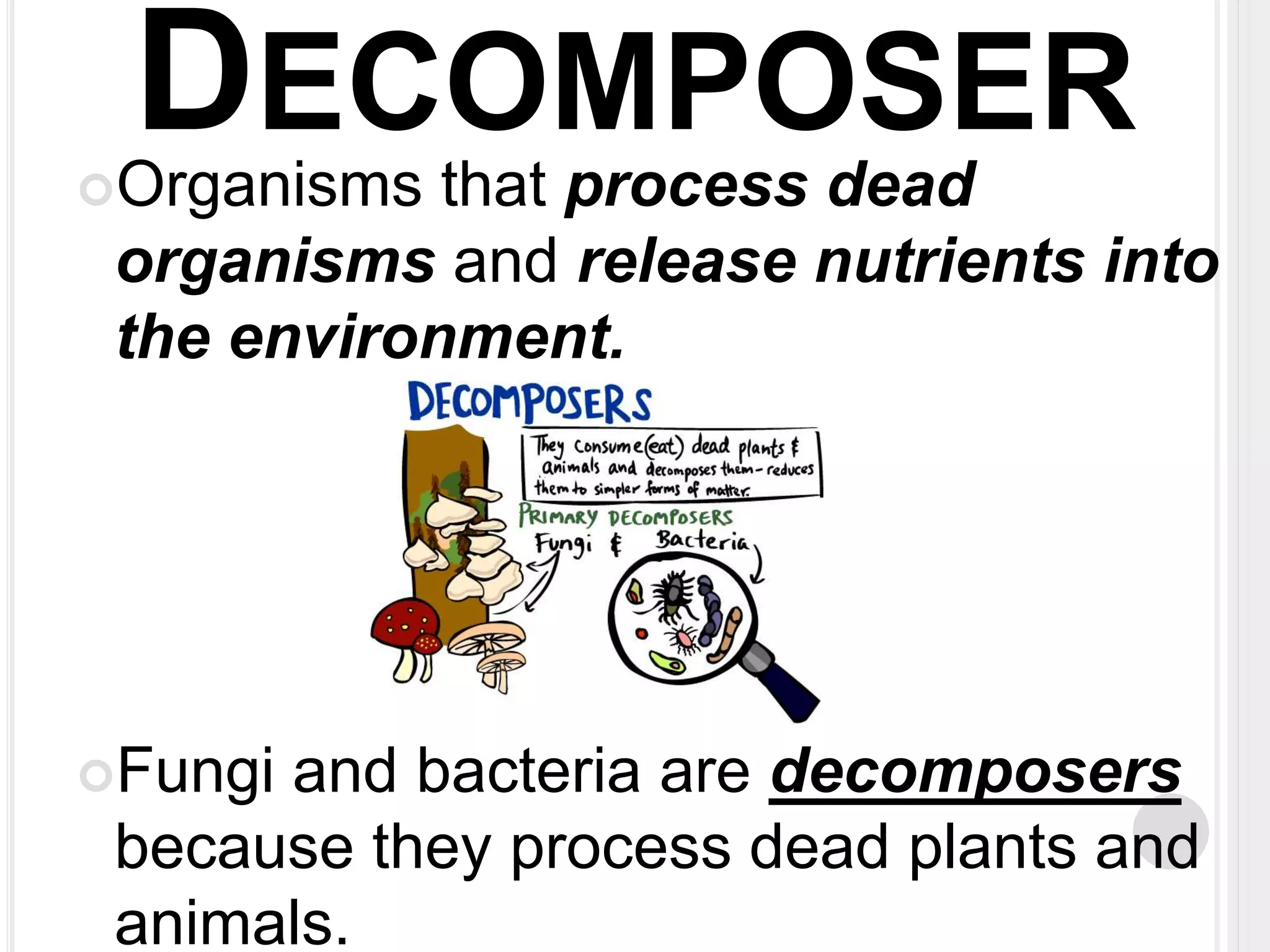
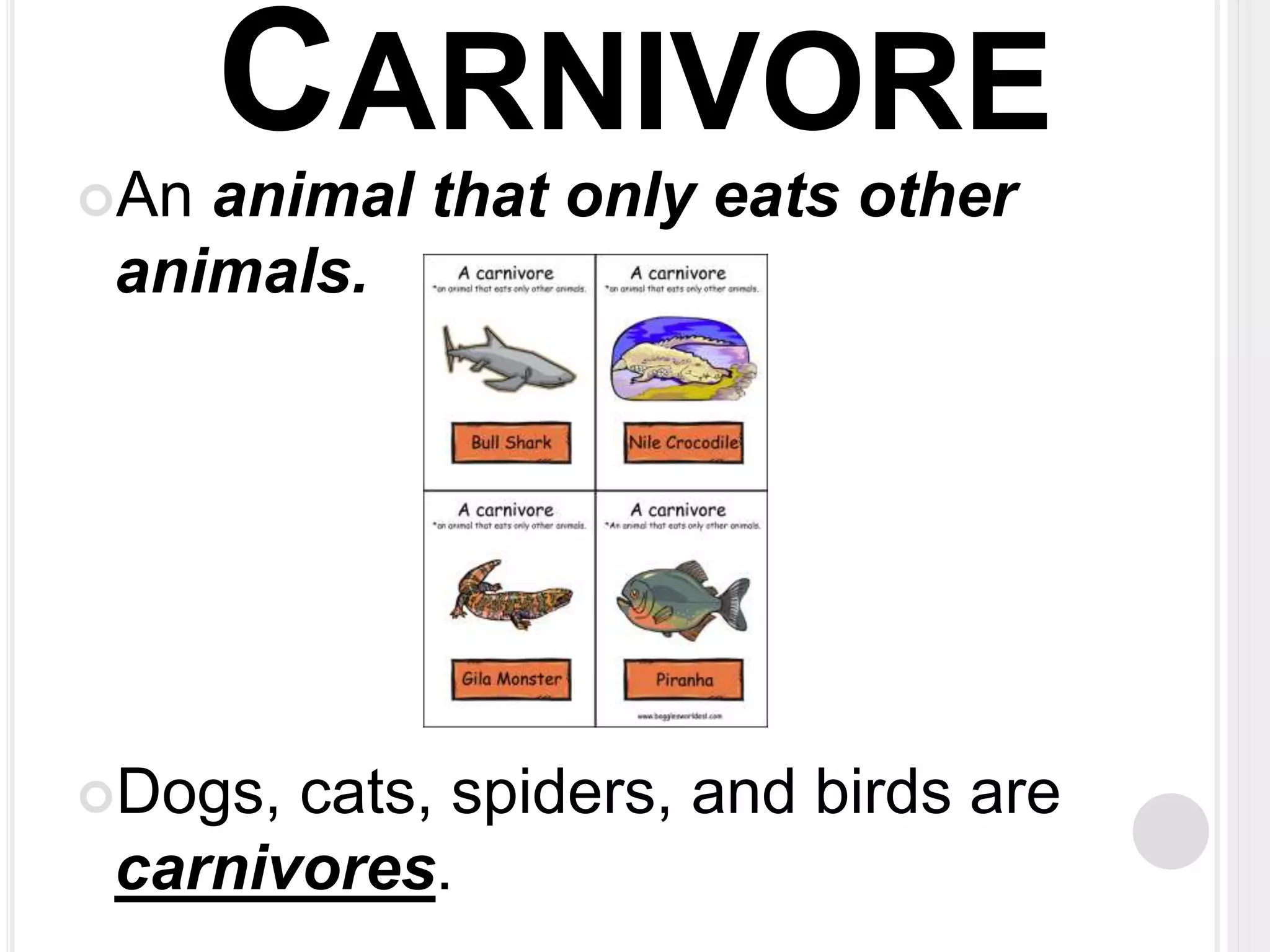
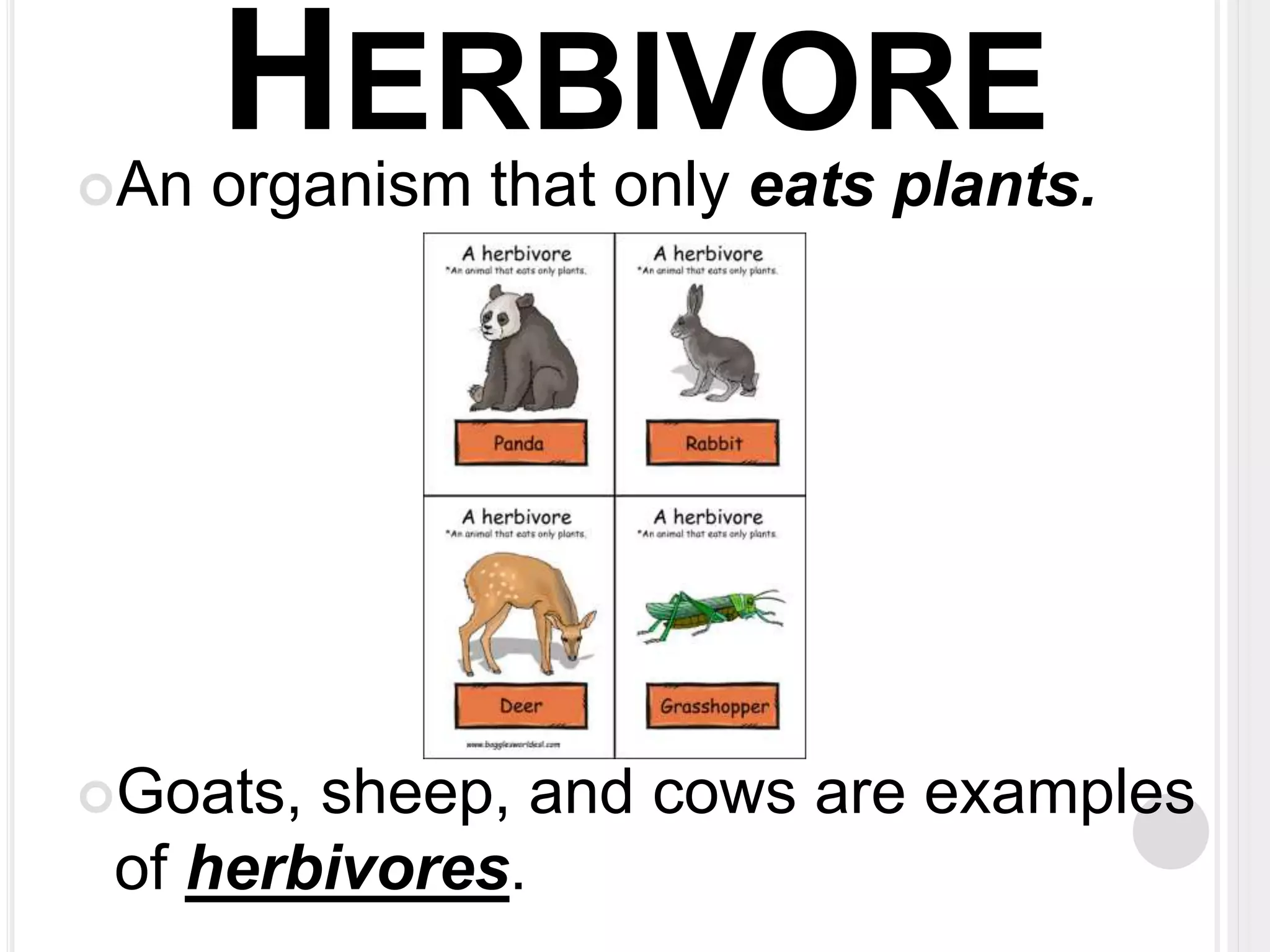
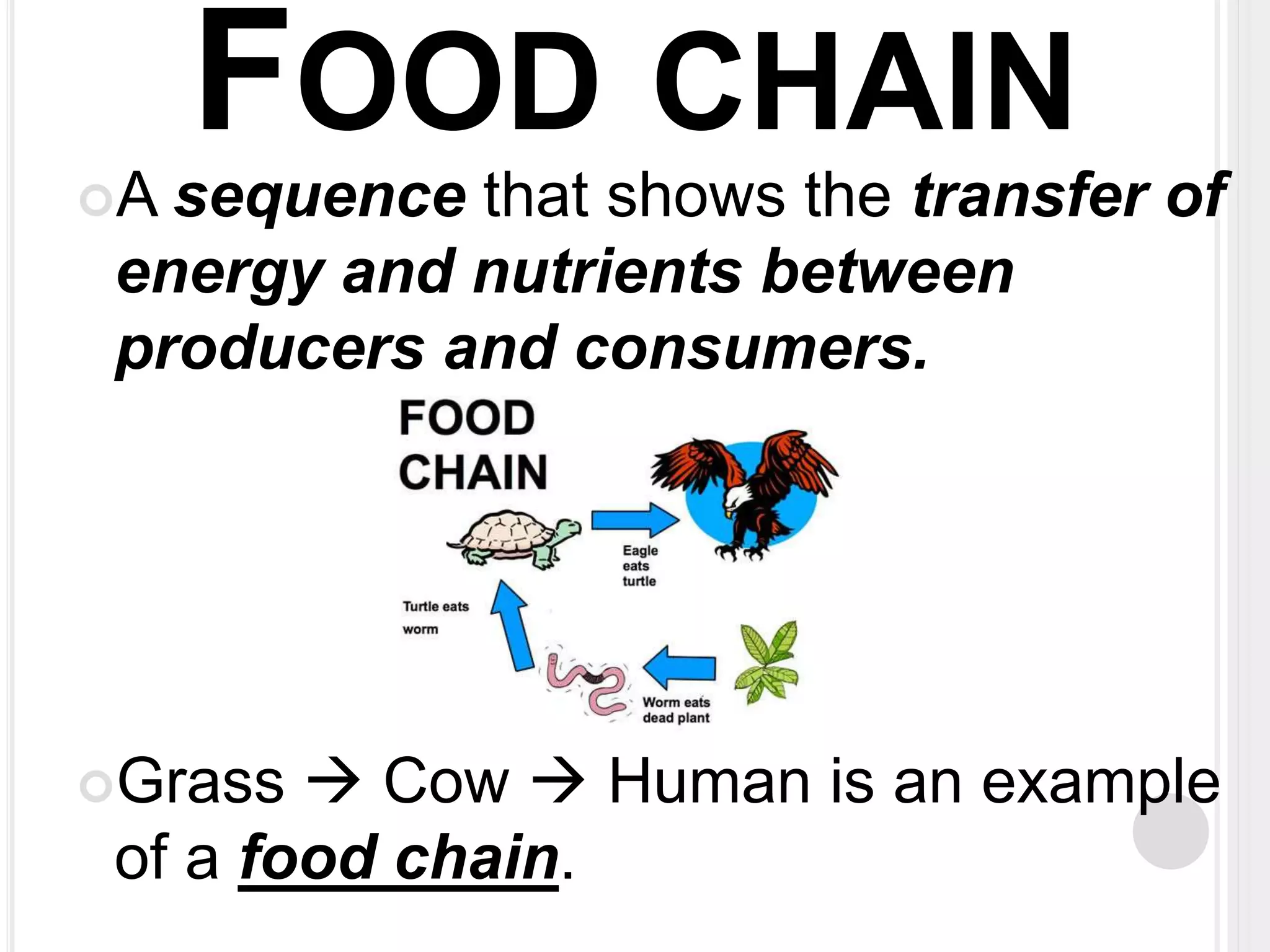
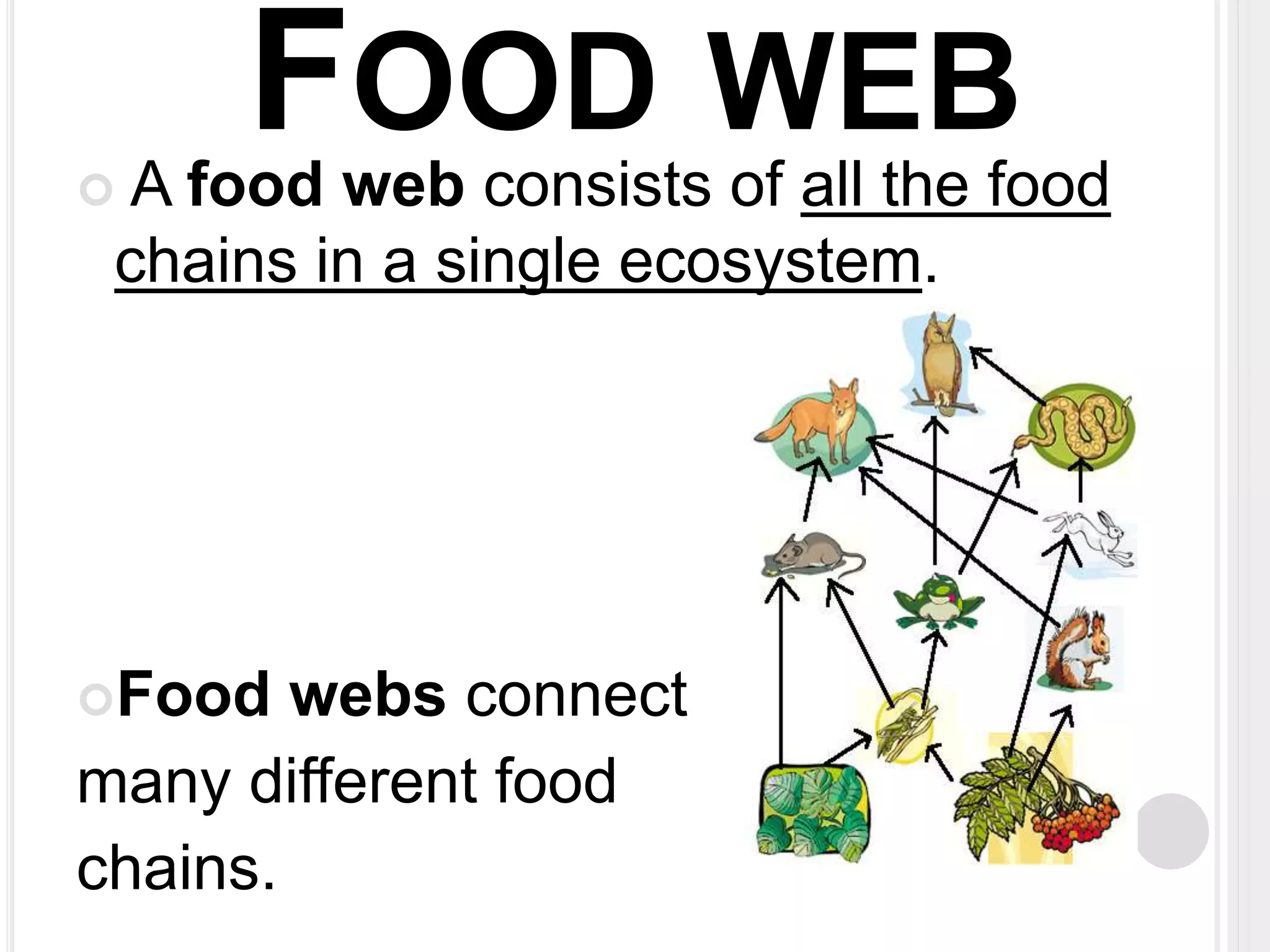
The document defines key terms related to organisms and ecology, including organism, producer, decomposer, consumer, scavenger, carnivore, herbivore, omnivore, community, population, affect vs effect, food chain, food web, and bioaccumulation. It provides examples for each term and explains producers make their own food through photosynthesis, decomposers break down dead organisms, consumers eat other organisms or their byproducts, and herbivores eat plants while carnivores eat animals and omnivores eat both. Food chains demonstrate energy transfer between organisms and food webs combine multiple chains in an ecosystem. Bioaccumulation occurs when substances build up in an organism over time.