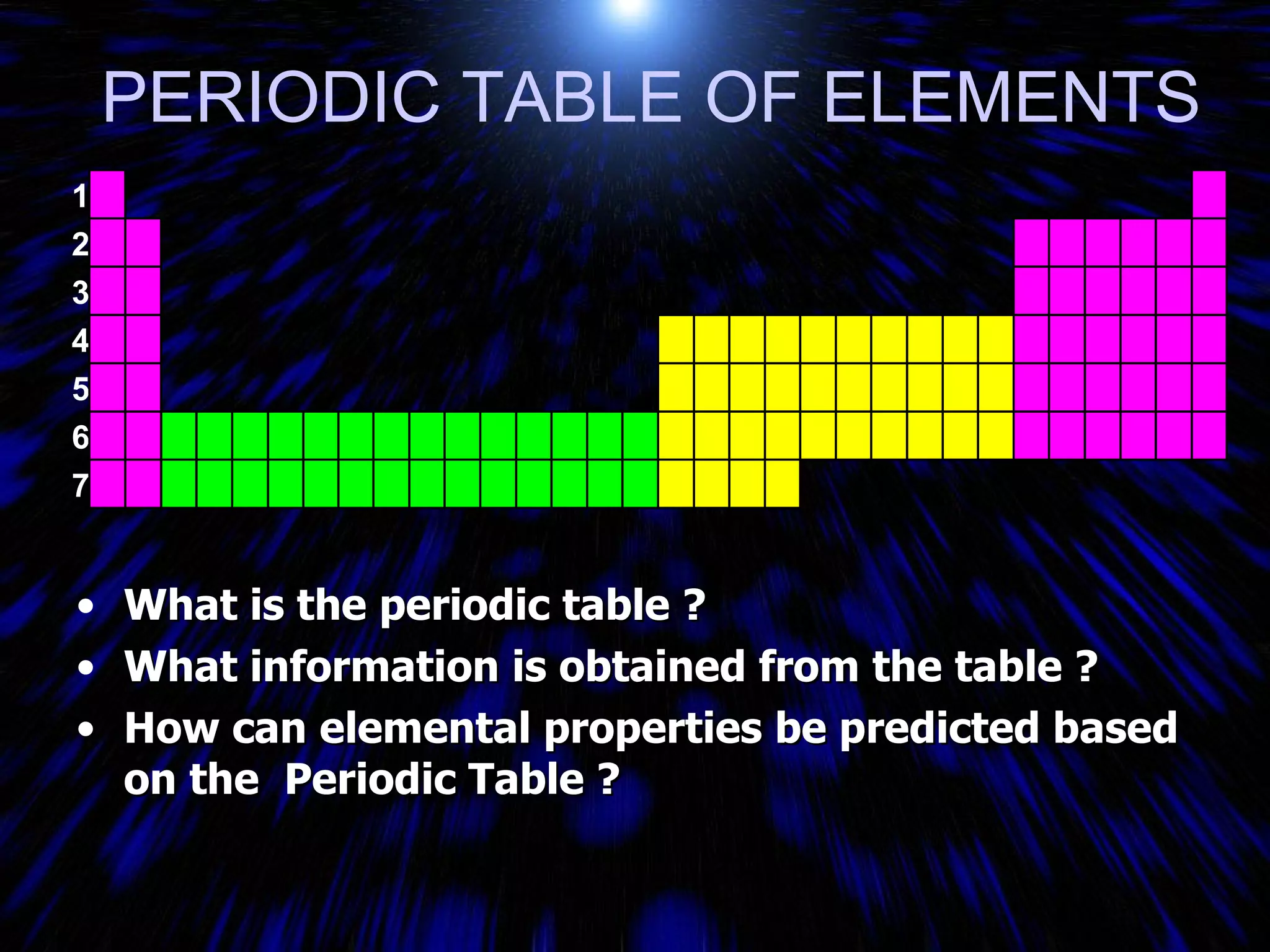
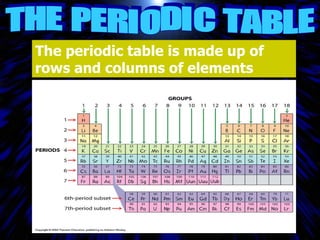
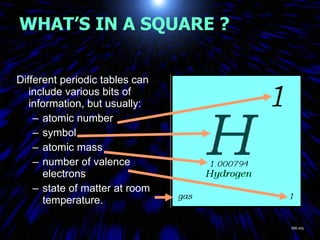
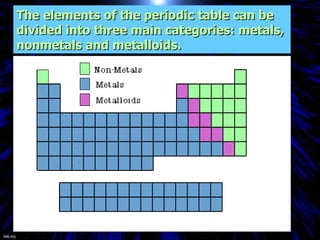
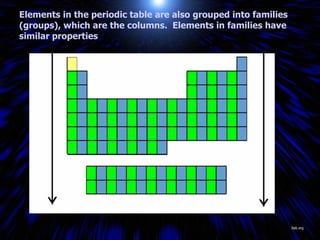
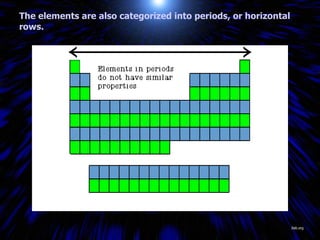
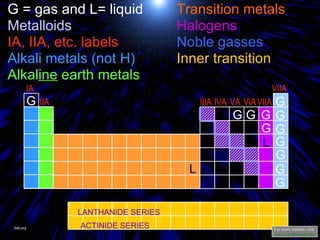
The periodic table organizes the chemical elements by their atomic number. It arranges elements in rows and columns, with each element having a unique symbol and atomic properties that can be predicted from its location on the periodic table. Elements in the same column have similar valence electron configurations and chemical properties, while elements in the same row have similar increases in atomic size. The periodic table is a fundamental tool for understanding chemistry.