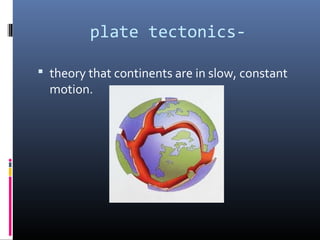
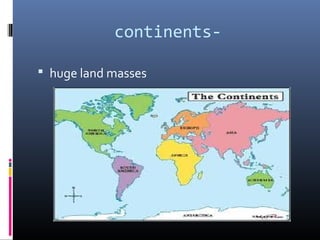
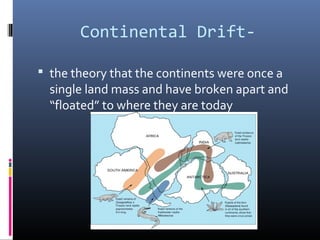
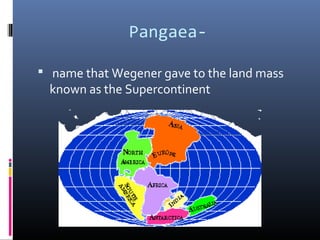
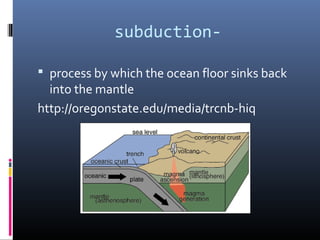
The document defines key terms related to plate tectonics and continental drift including: plate tectonics, continents, continental drift, Pangaea, mid-ocean ridge, sea-floor spreading, magma, lava, volcano, fault, earthquake, uplift, intrusion, subduction, and rift valley. Continental drift is the theory that the continents were once joined together and have since drifted apart. Sea-floor spreading at mid-ocean ridges causes the ocean floors to expand and push older sections downward.