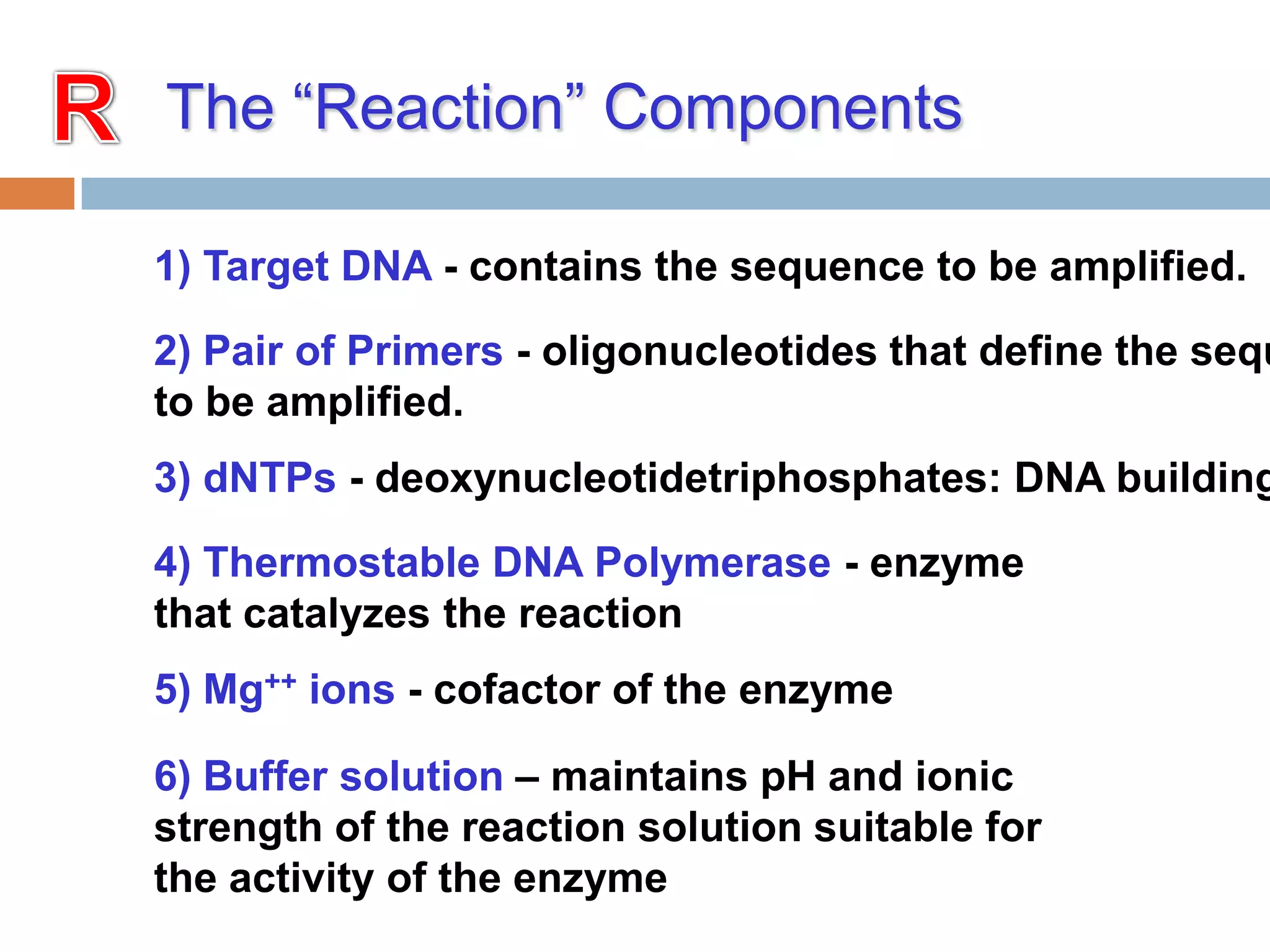
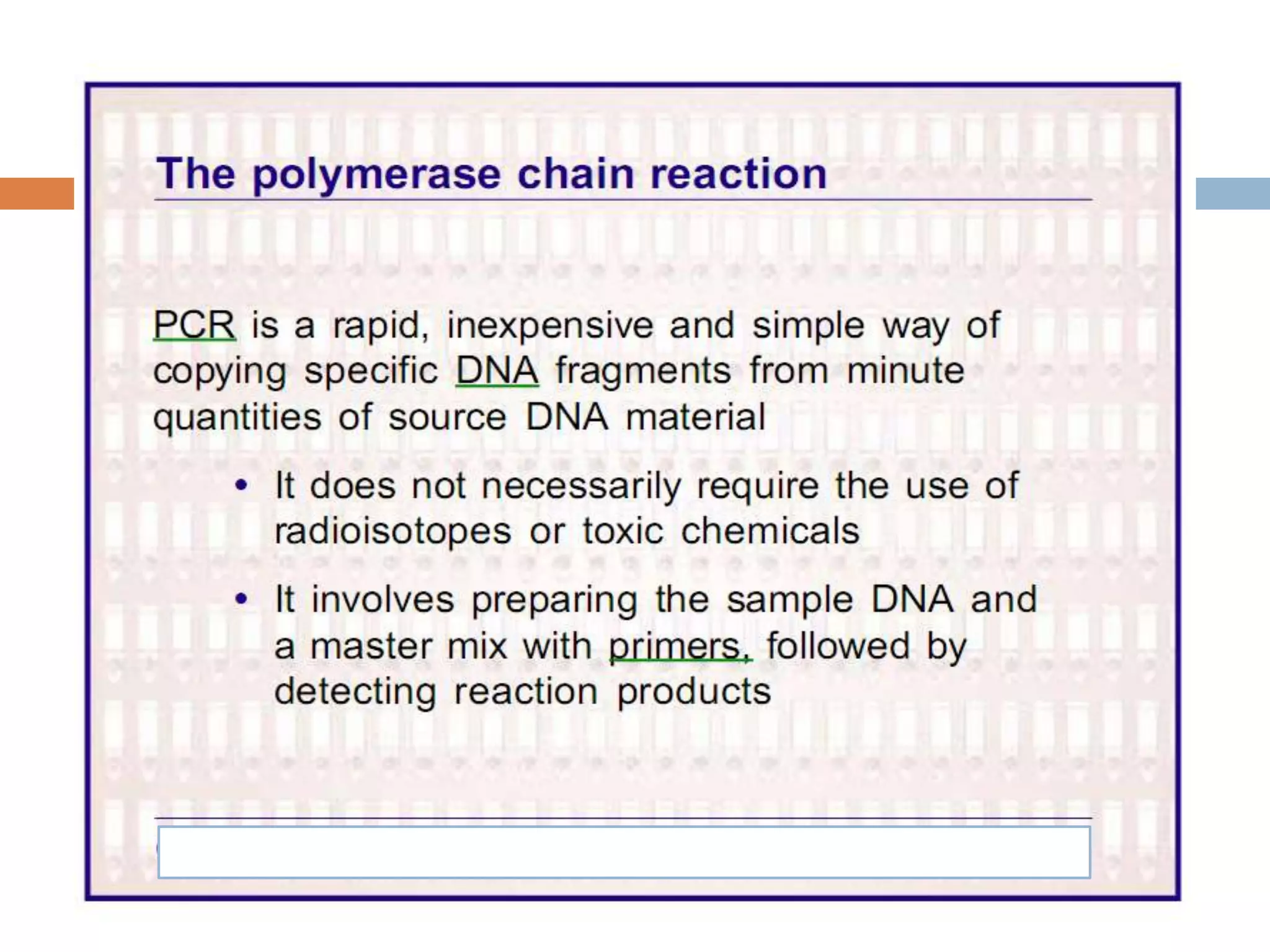
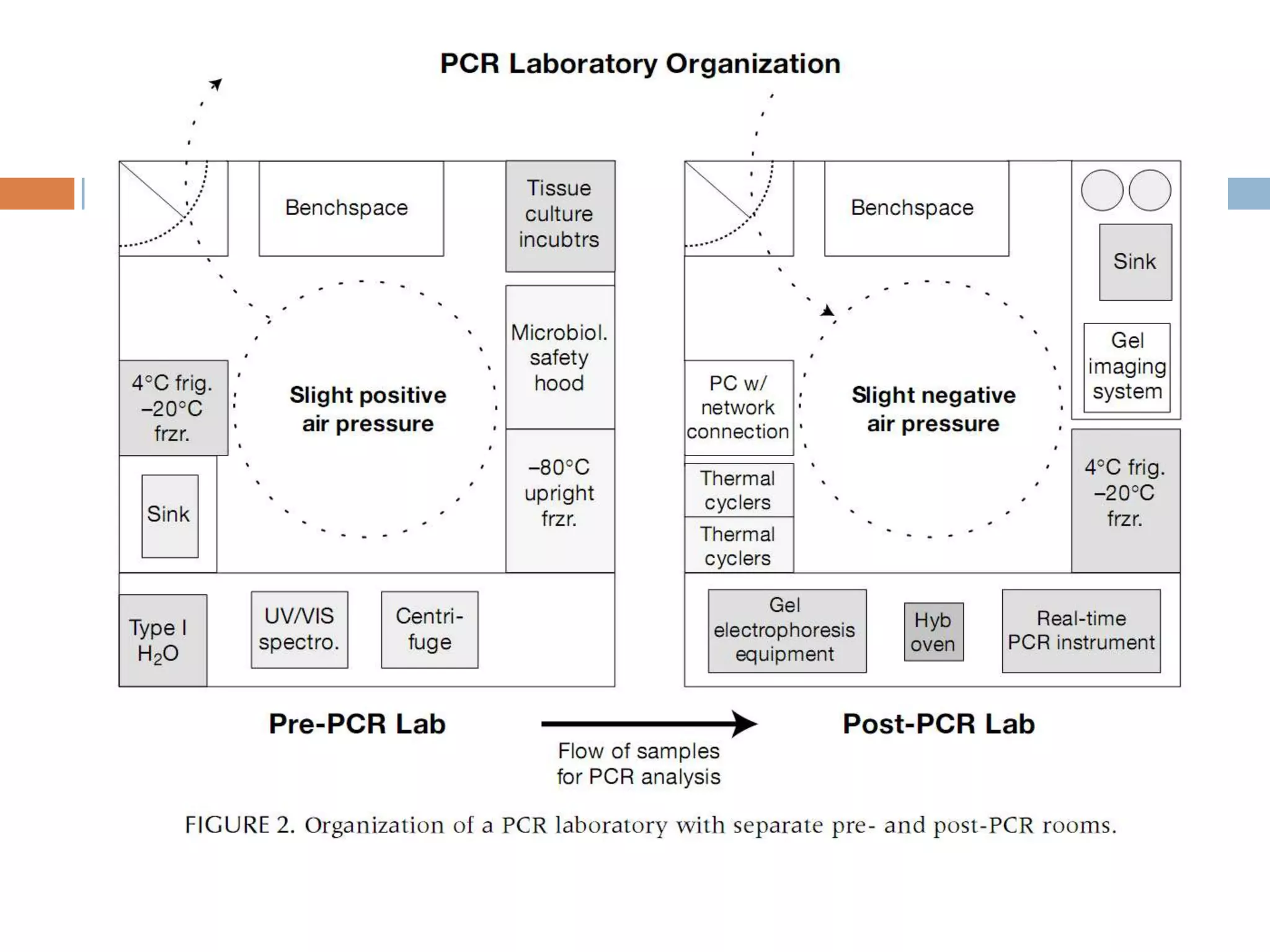
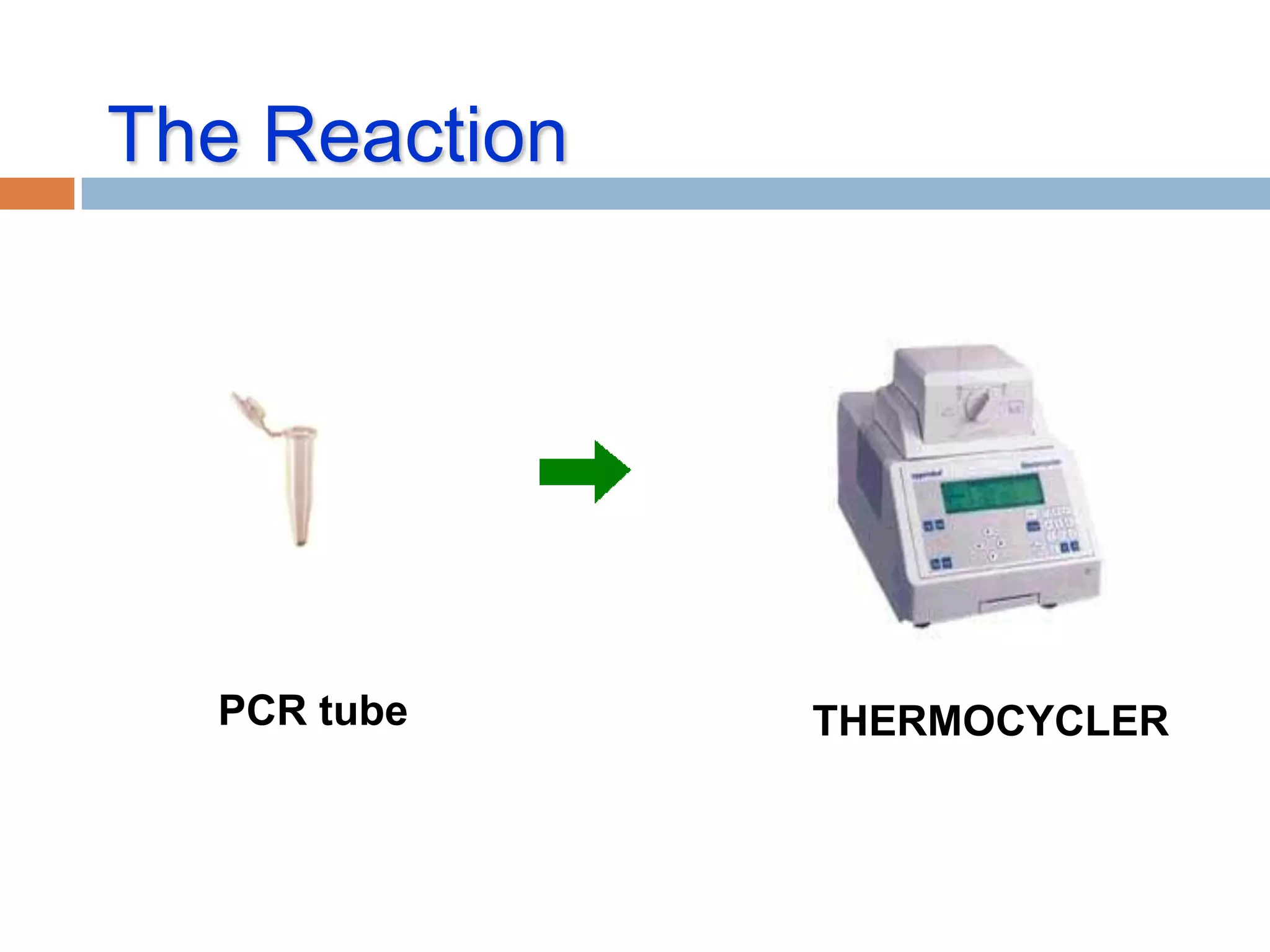
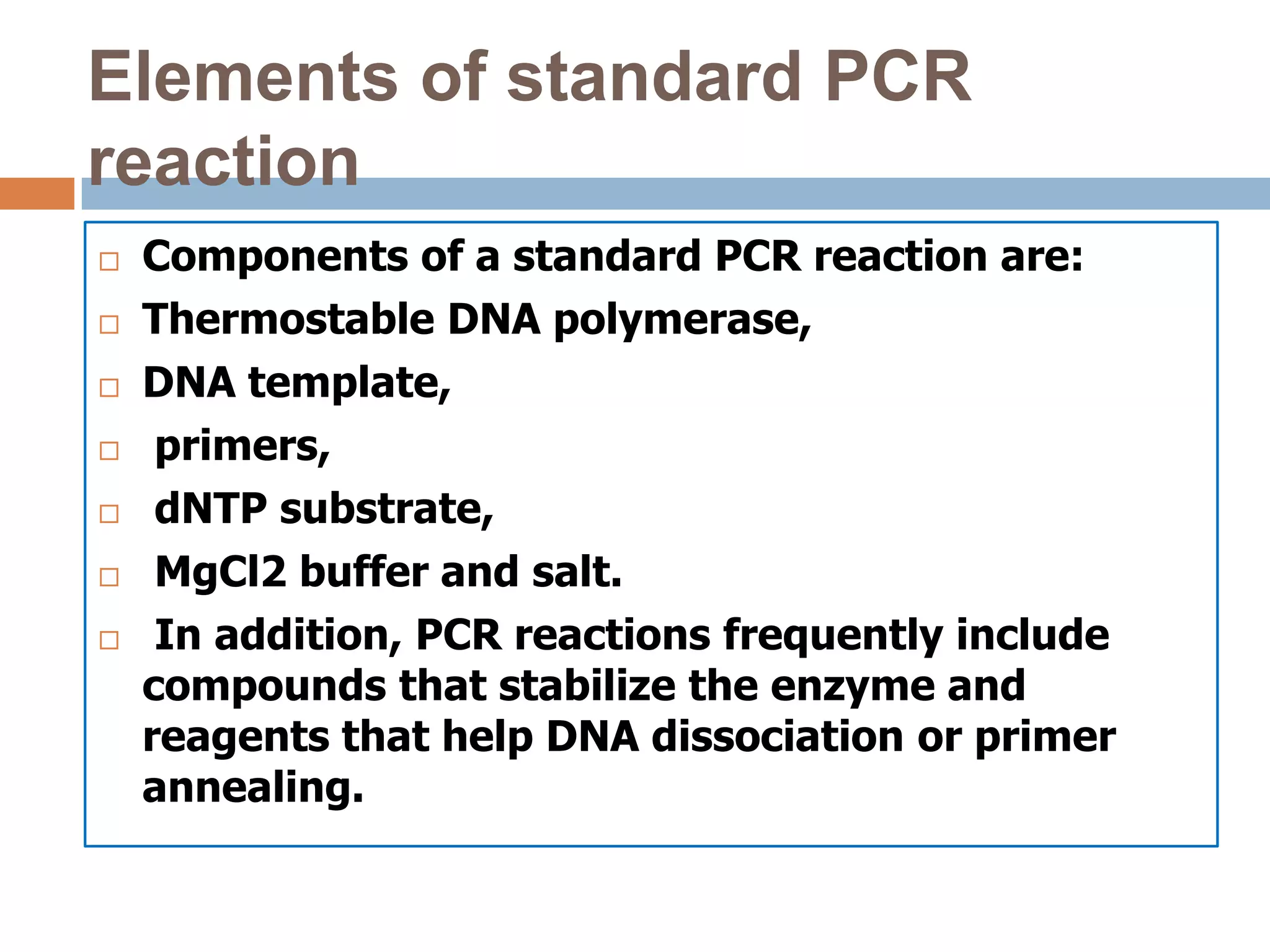
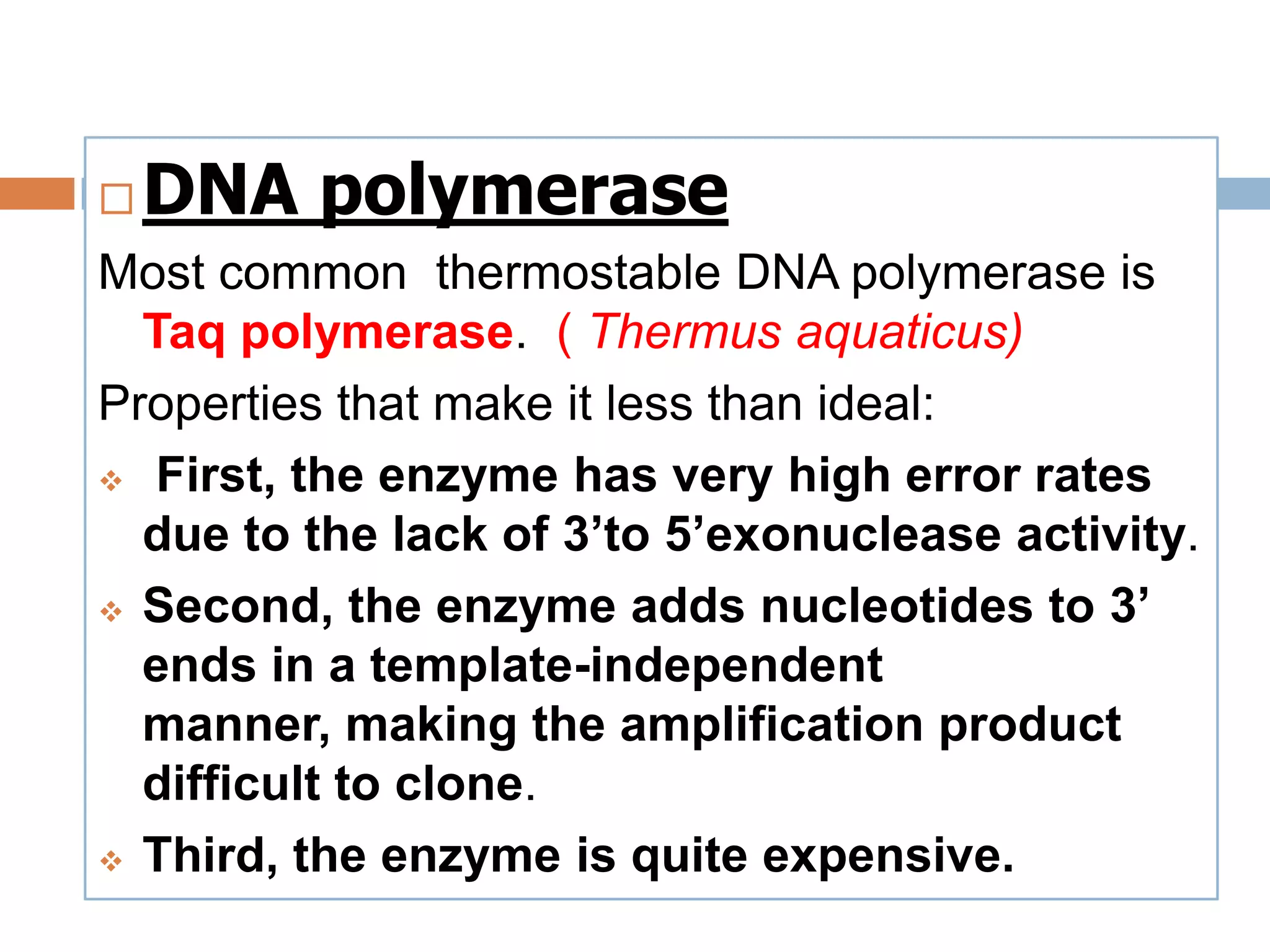
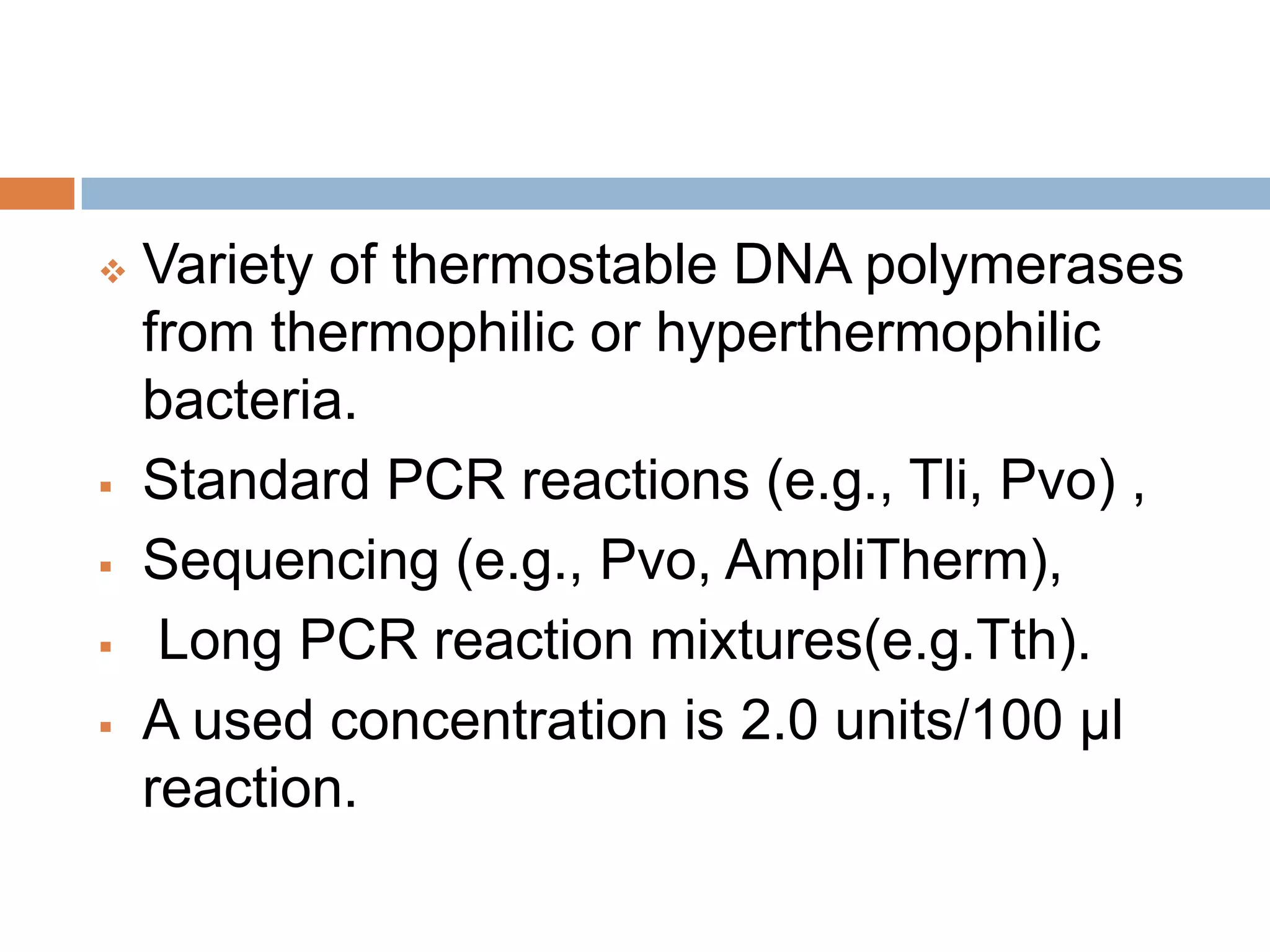
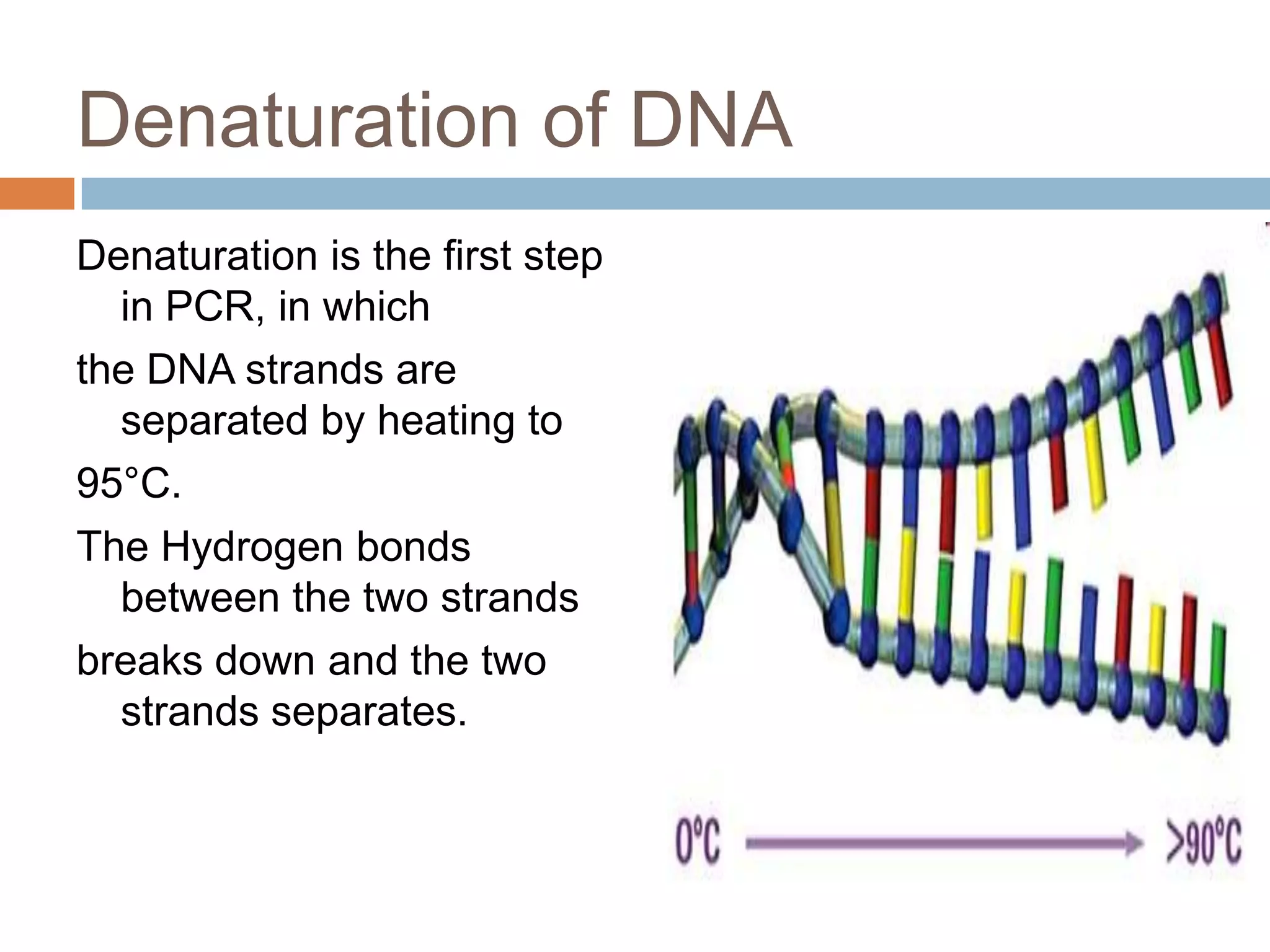
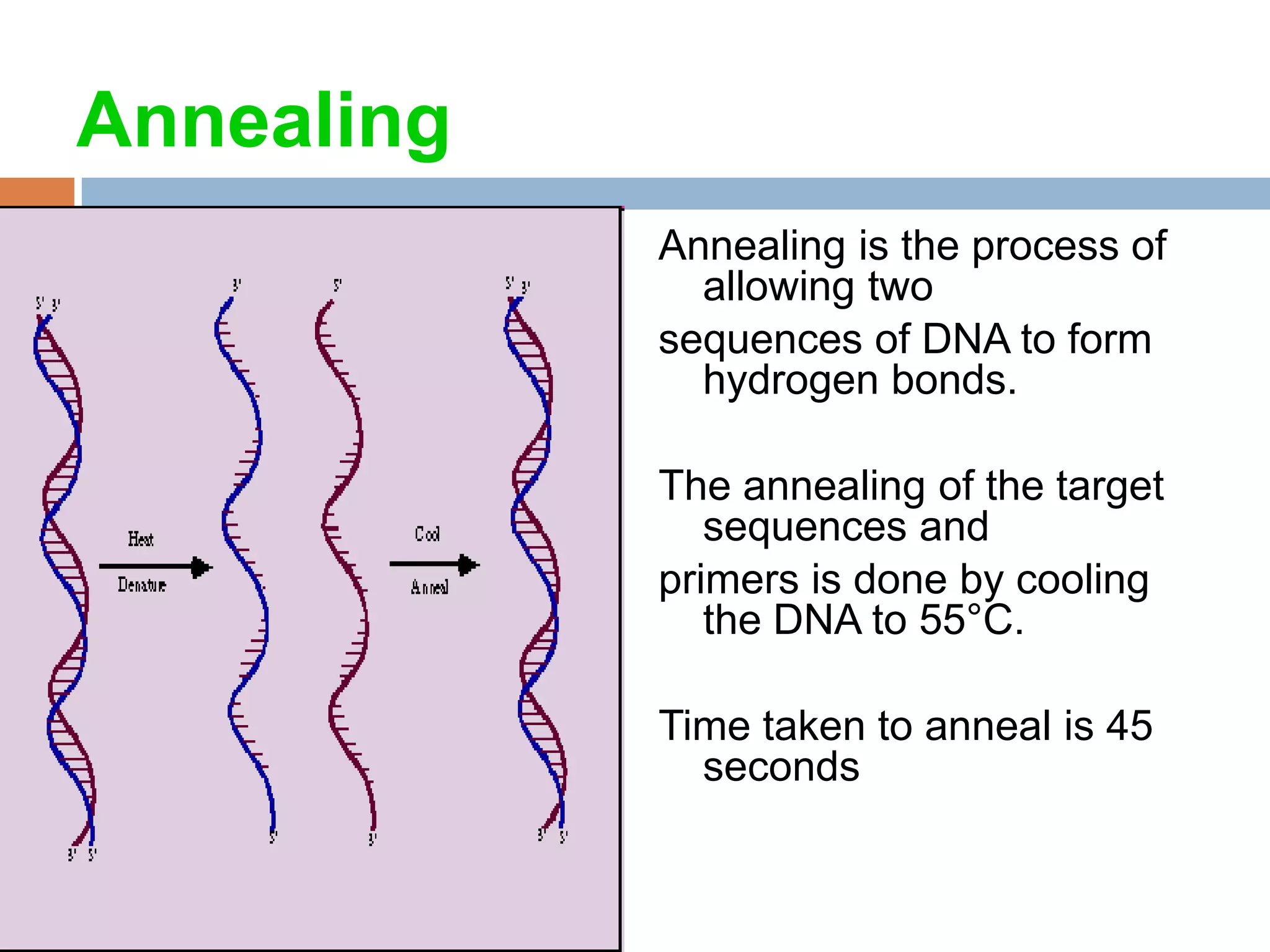
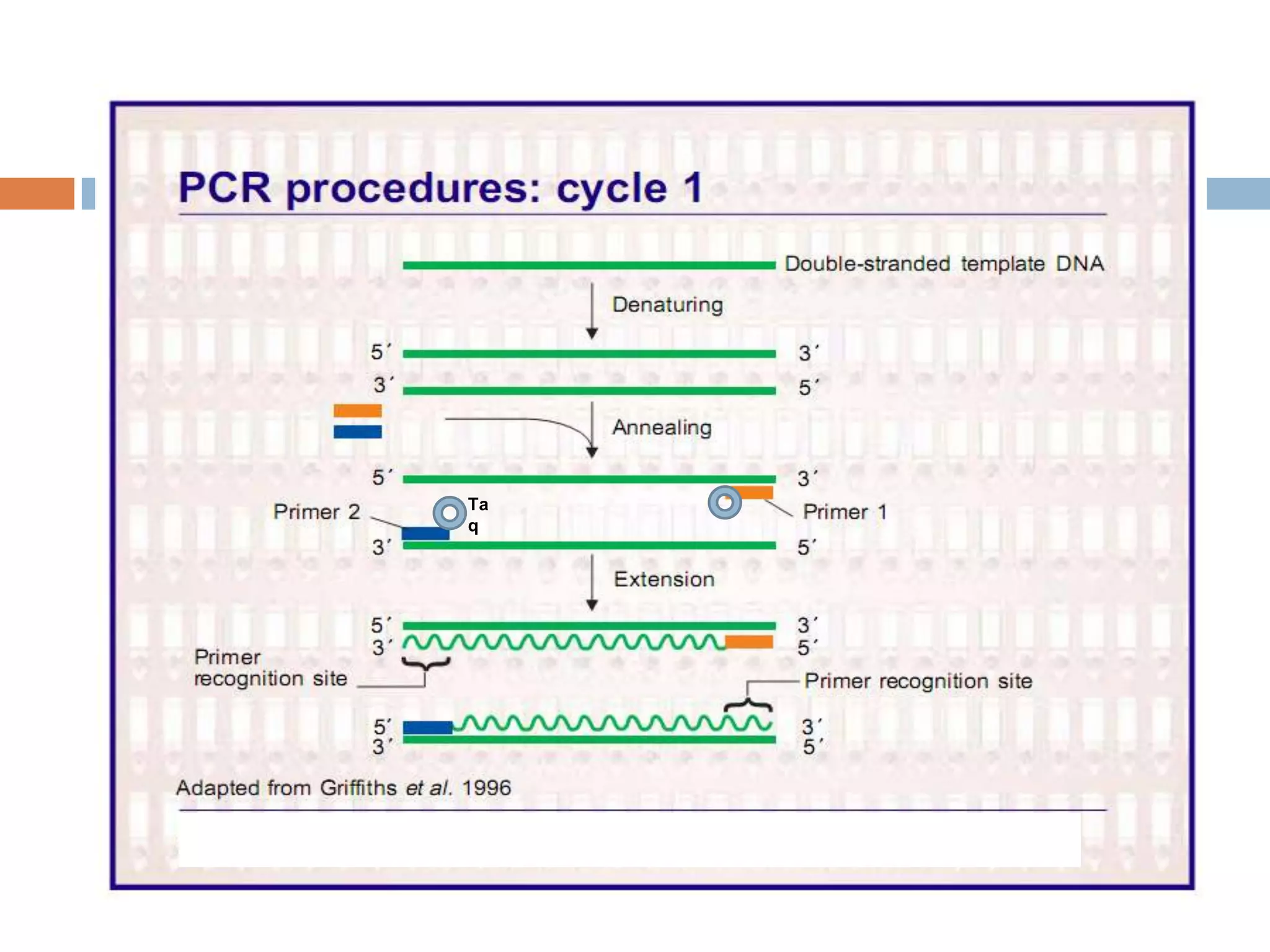
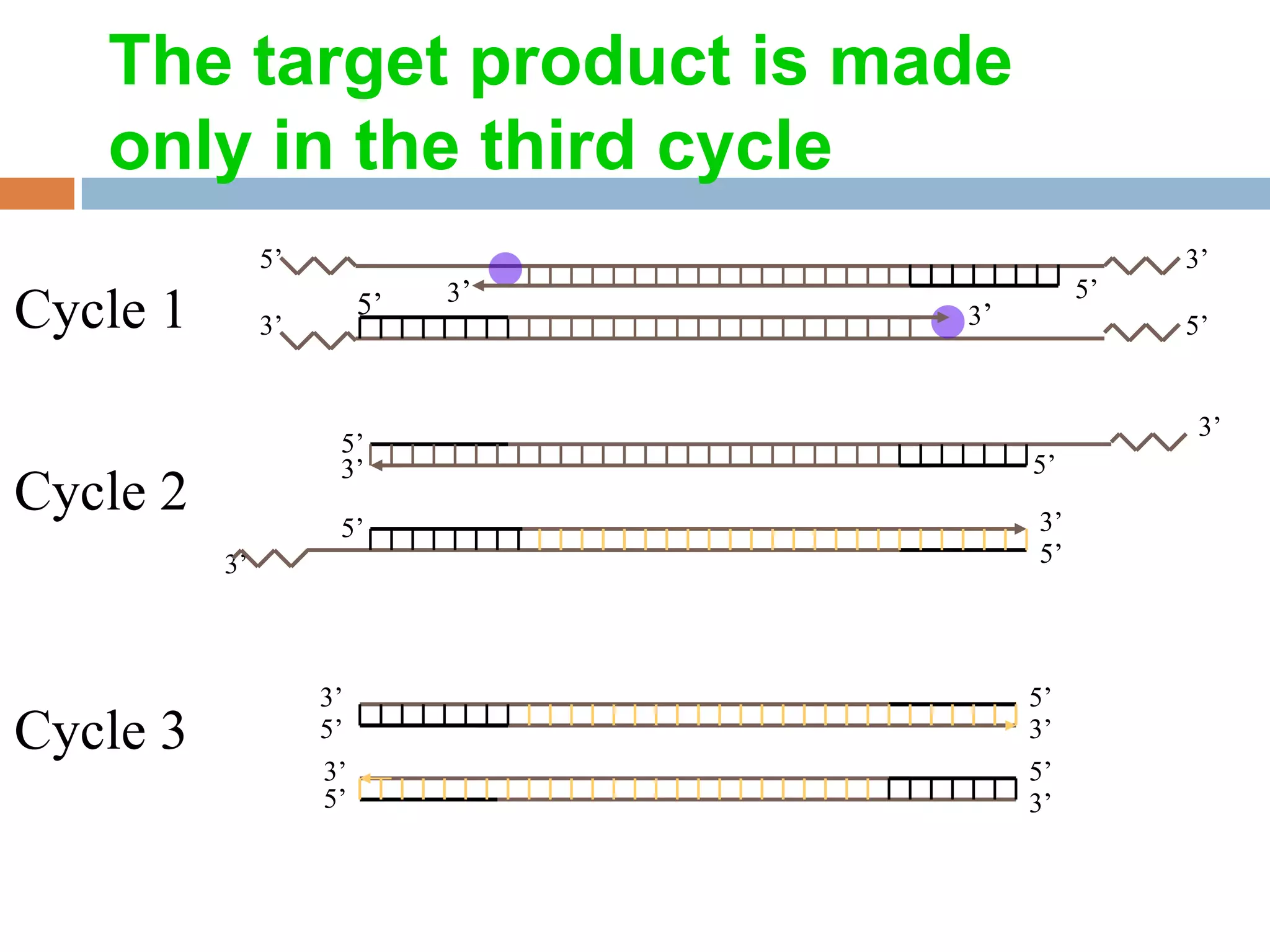
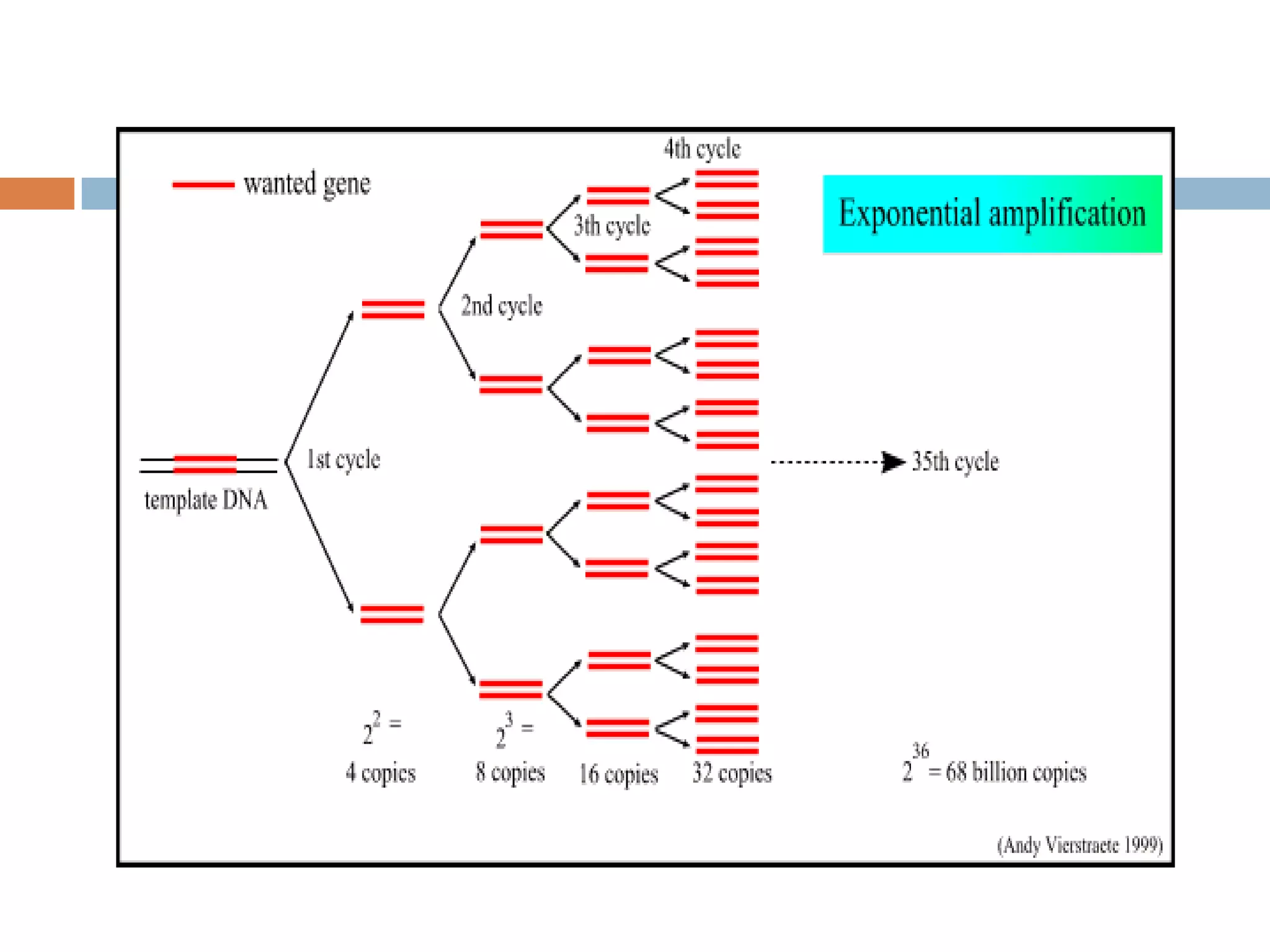
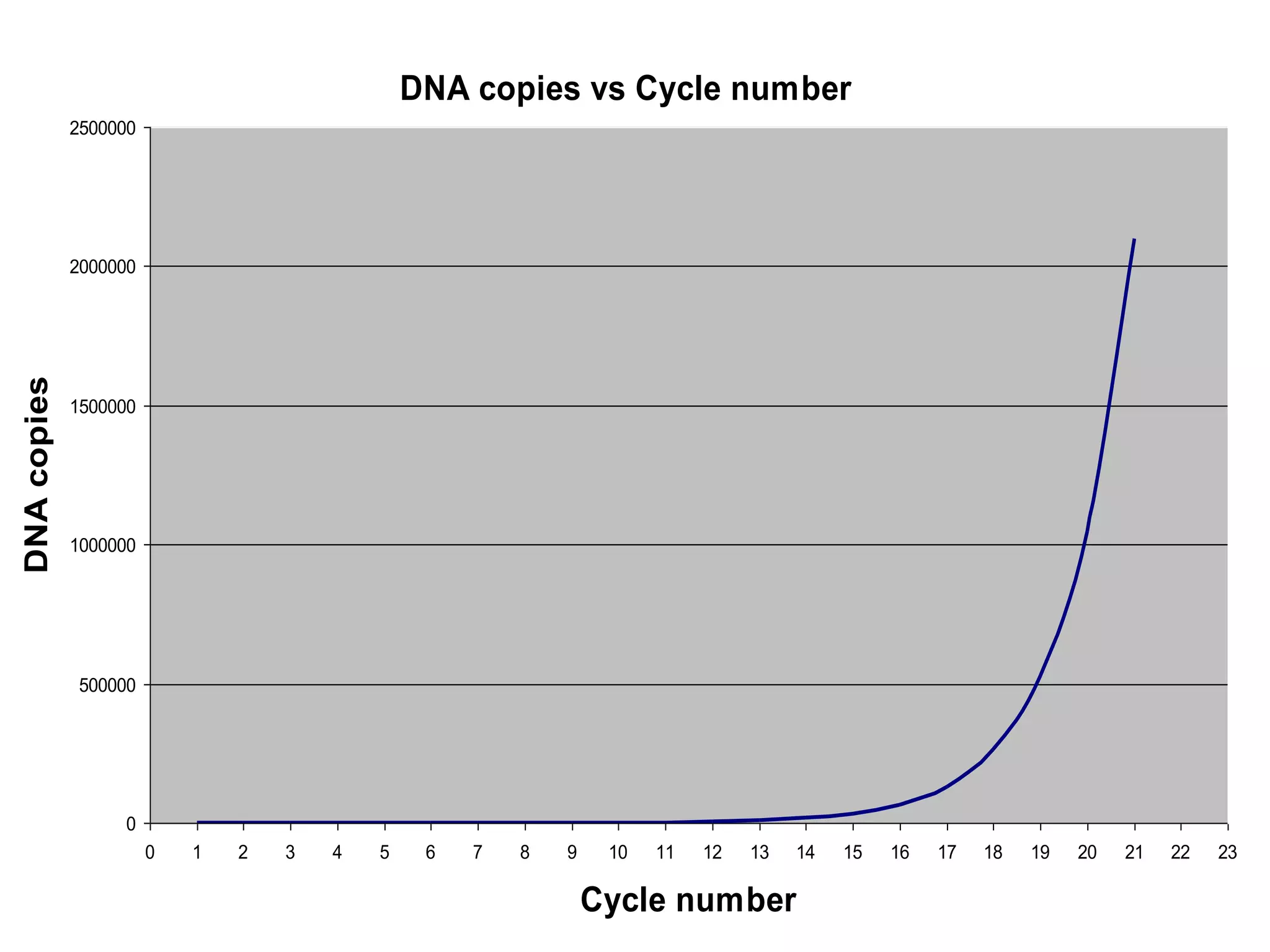
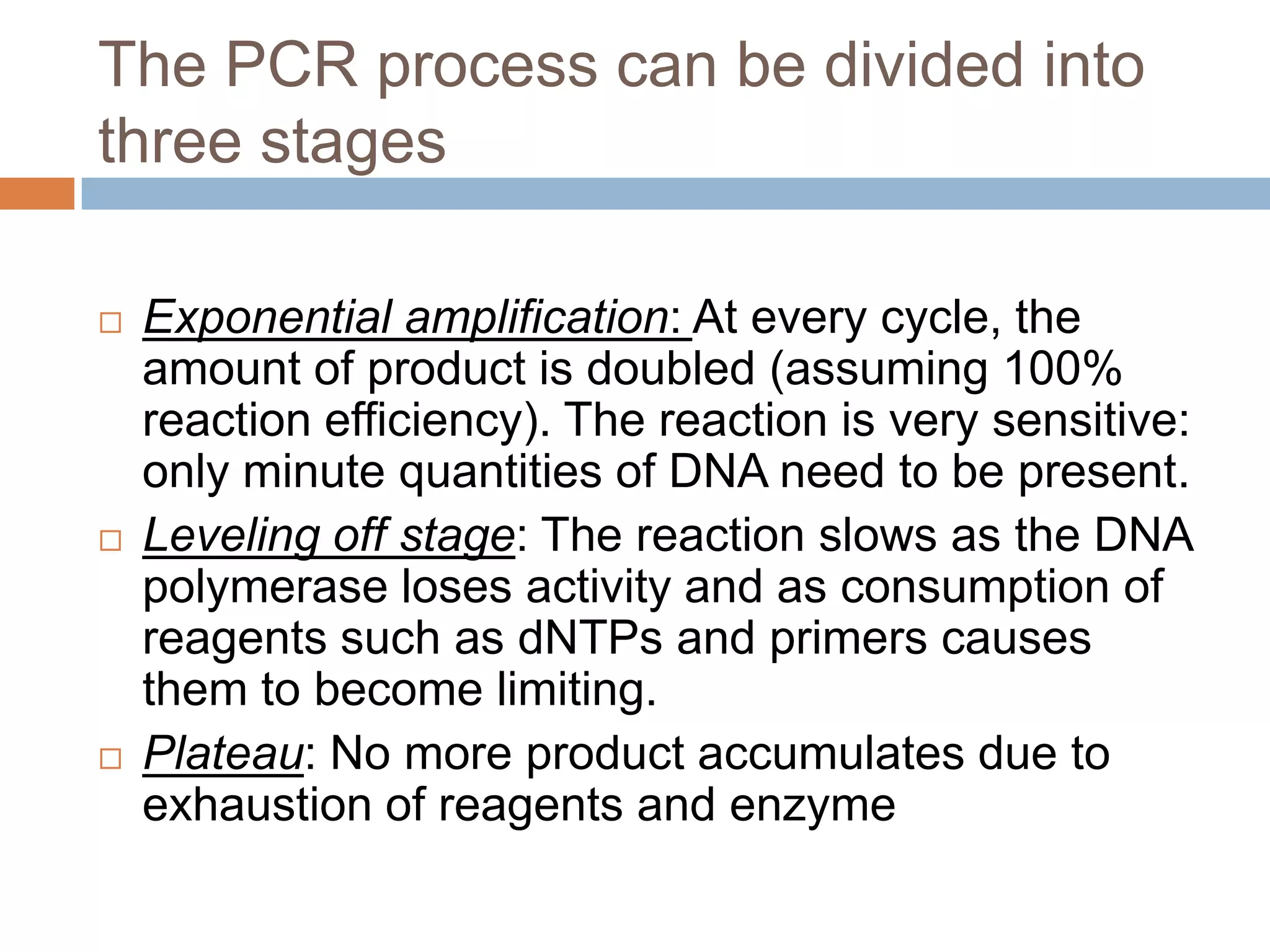
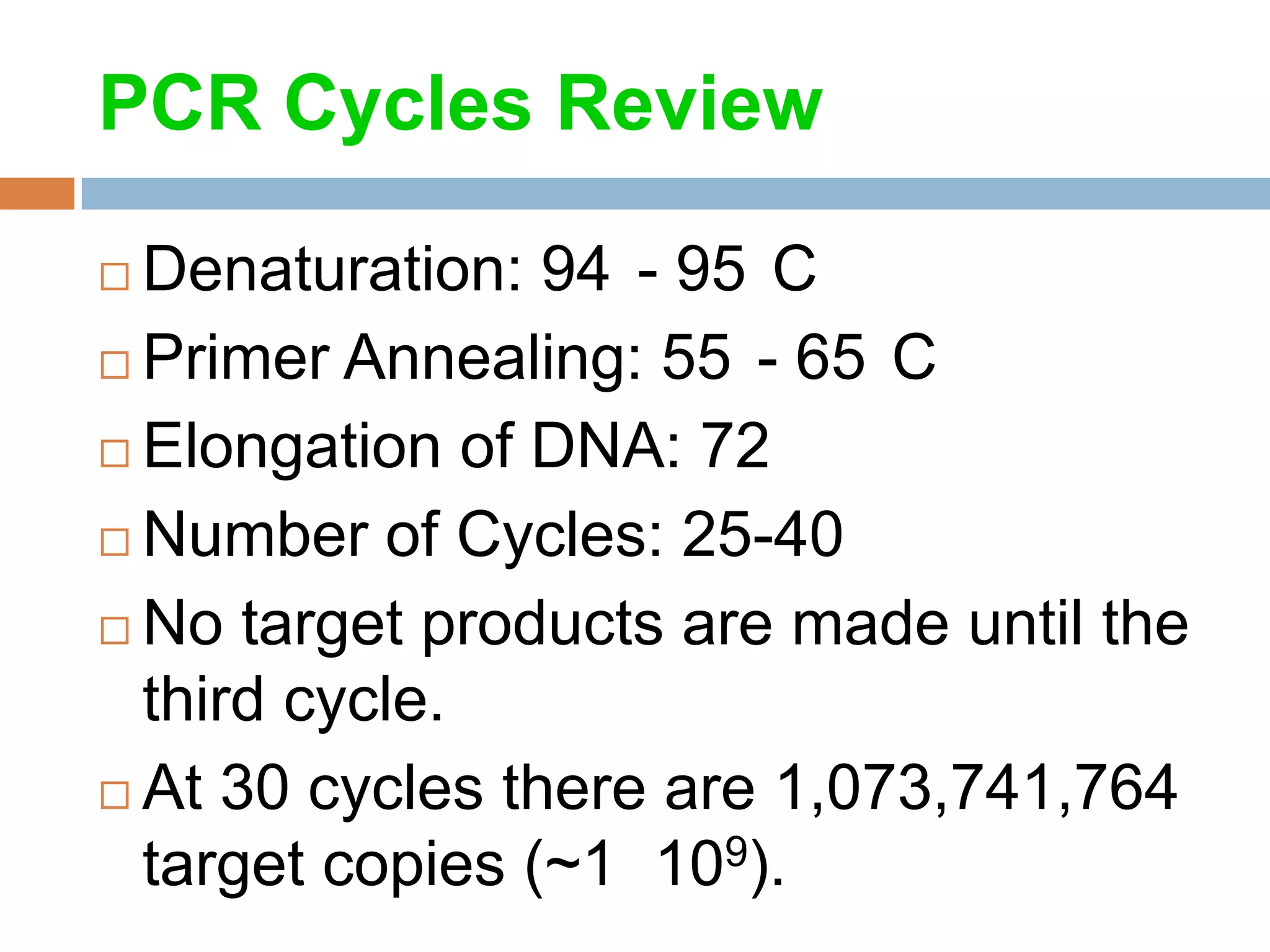
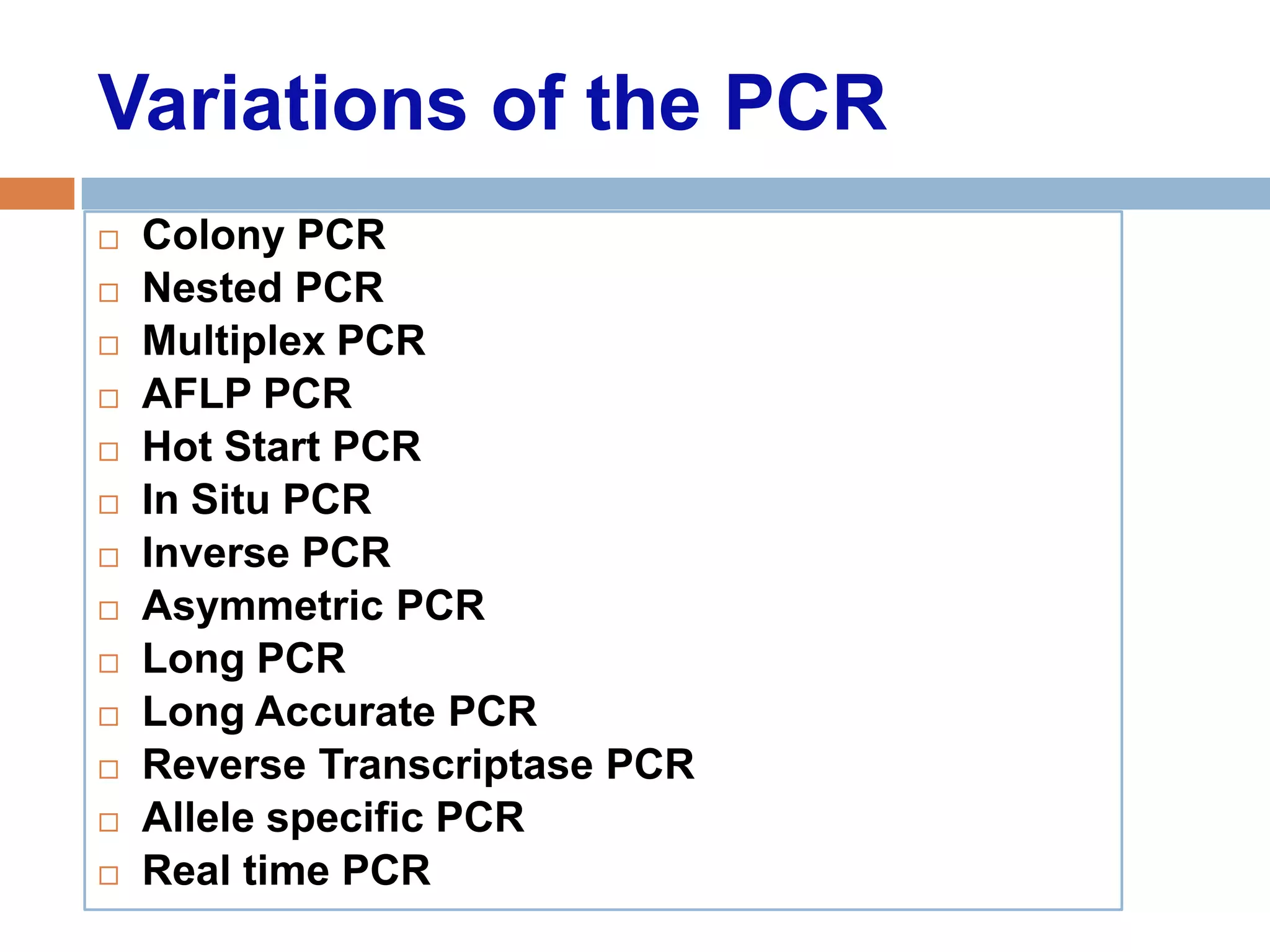
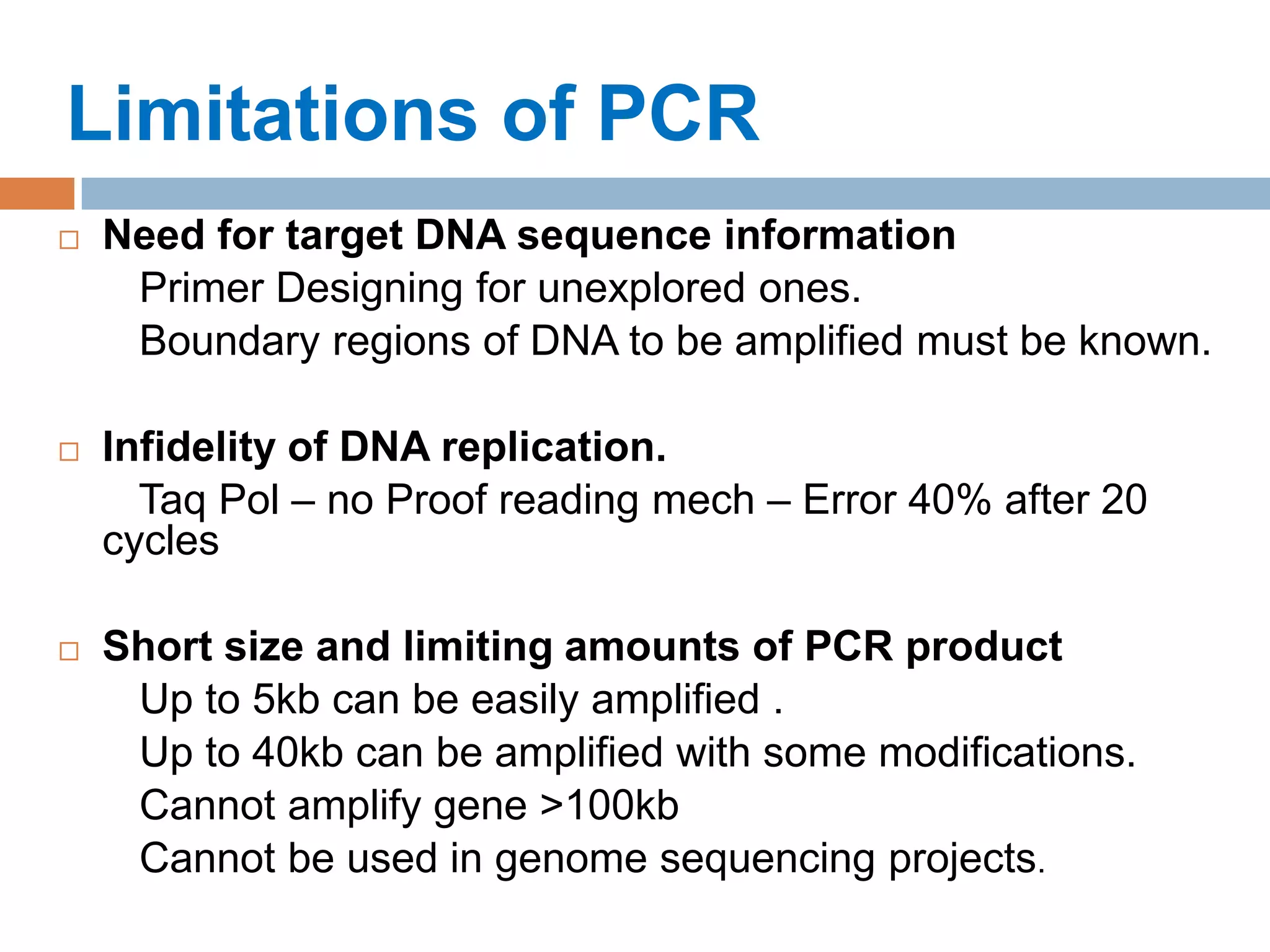
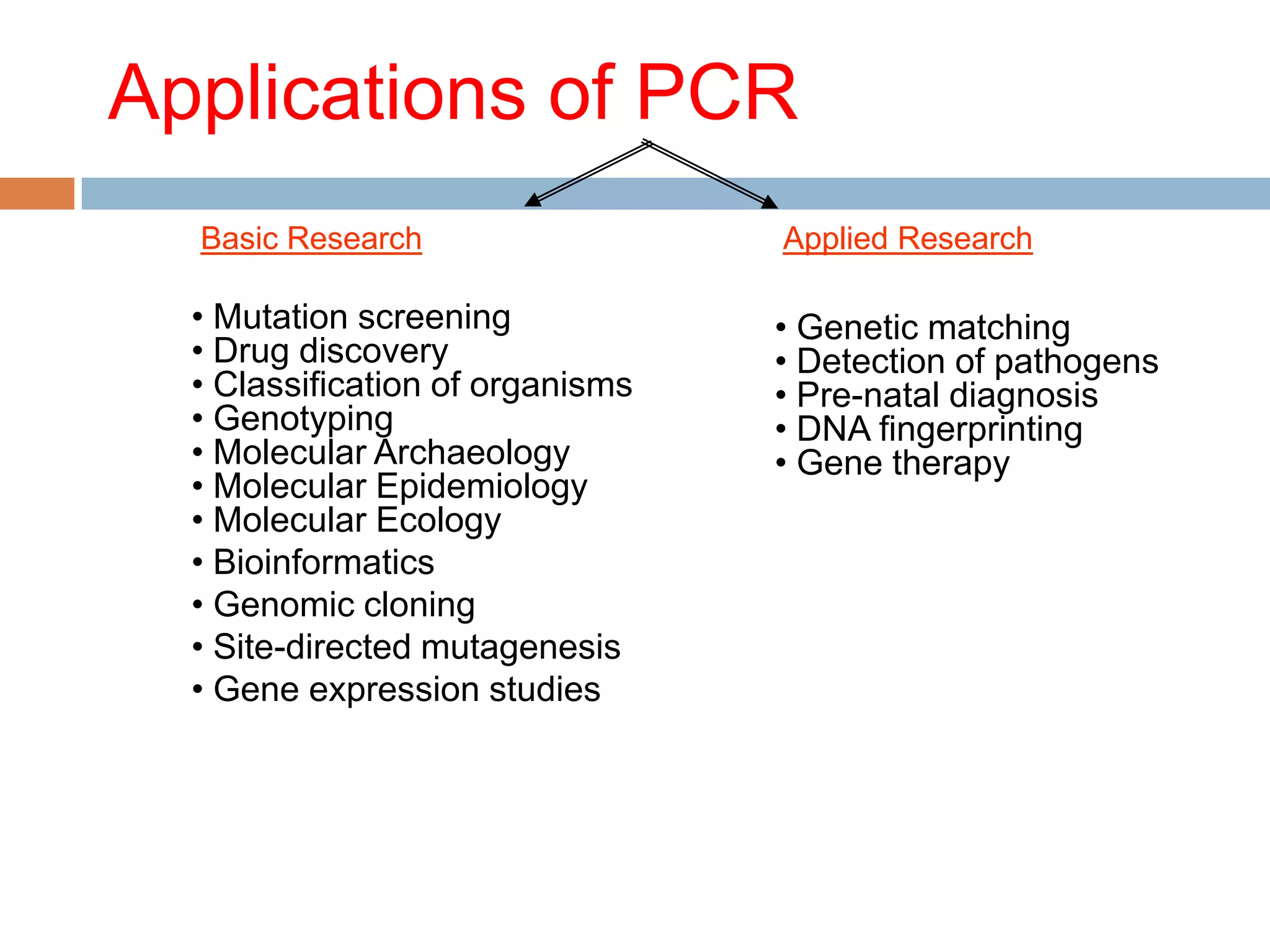
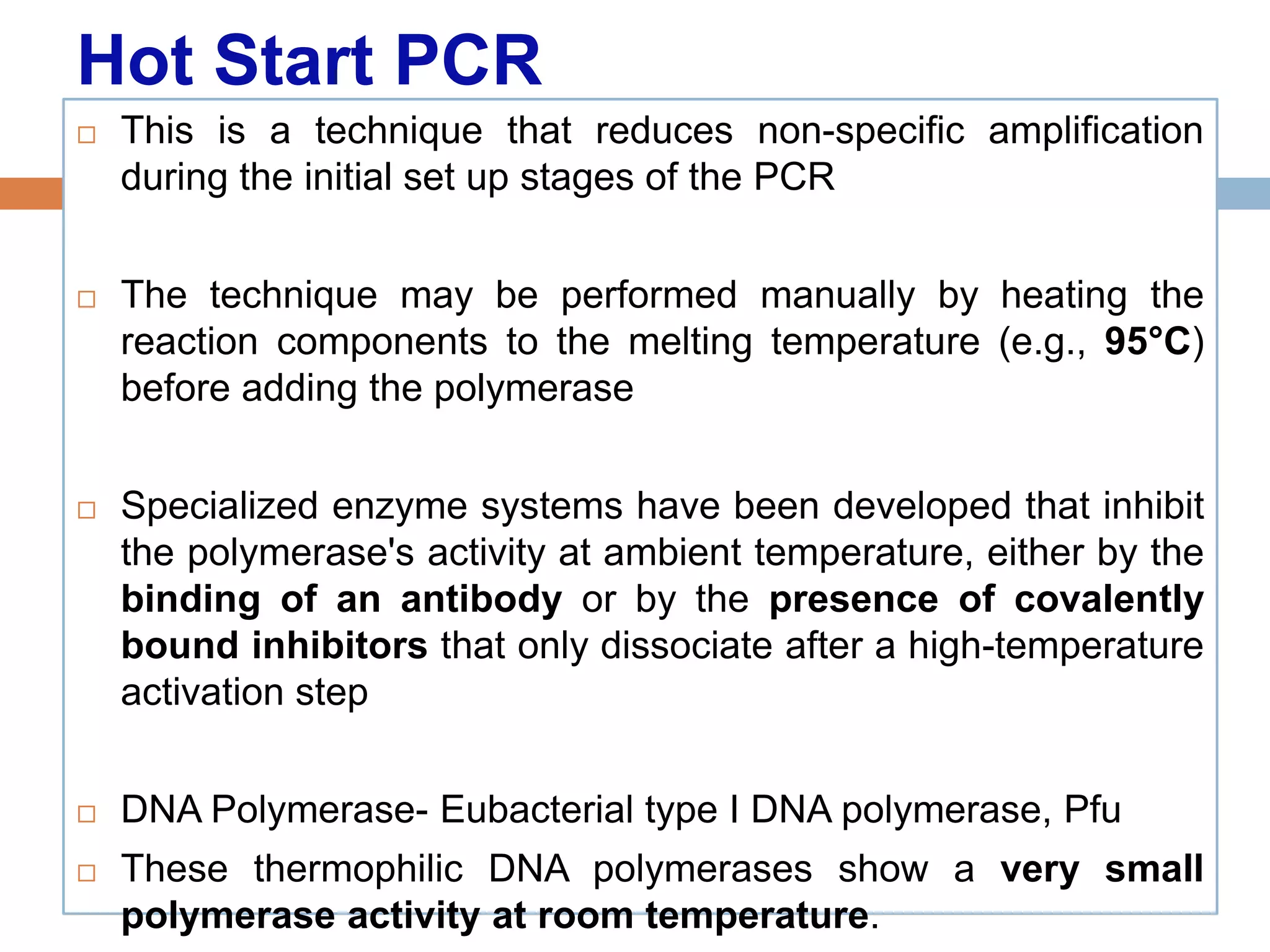
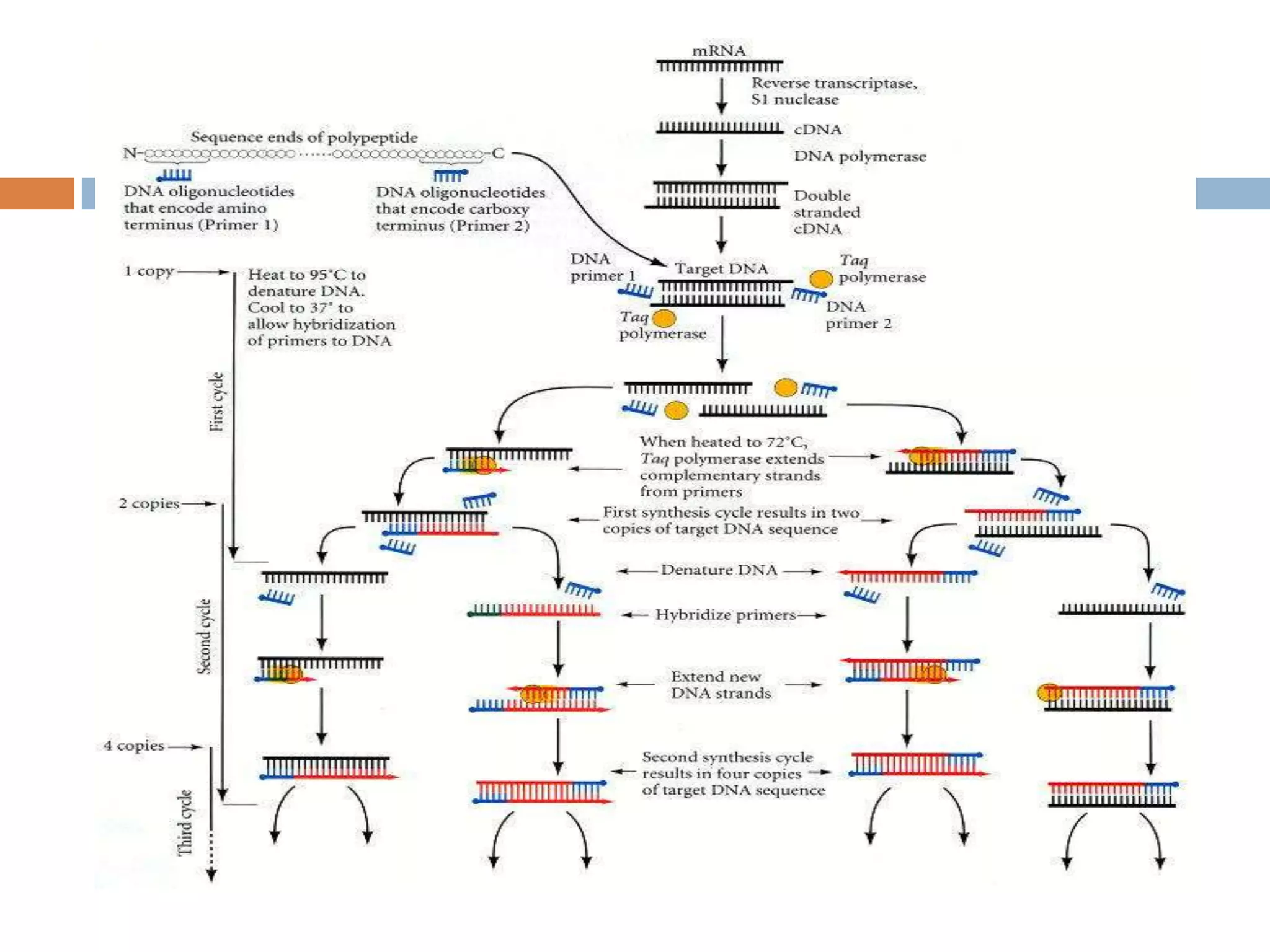
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA through repeated cycles of heating and cooling. It involves denaturing the DNA, annealing primers to the single-stranded DNA, and extending the primers with a DNA polymerase. After many cycles, the target region has been amplified exponentially. PCR is widely used in medical and biological research applications due to its ability to amplify small amounts of DNA.