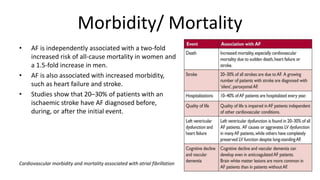
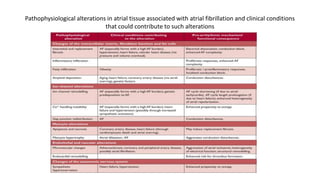
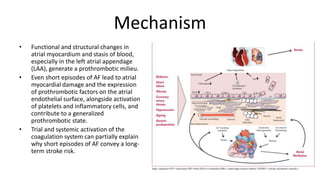
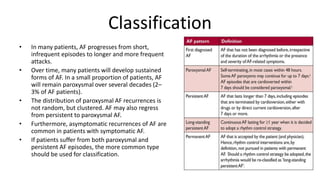
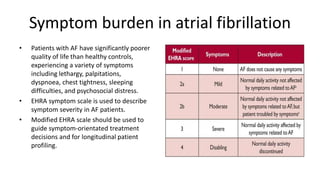
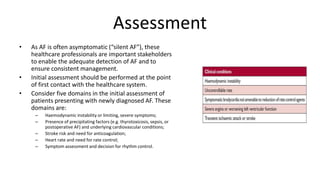
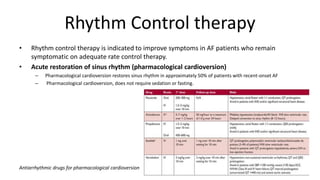
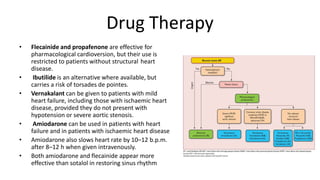
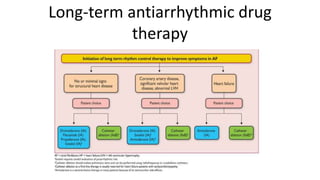
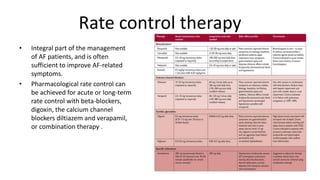
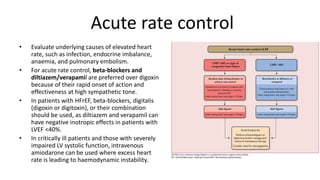
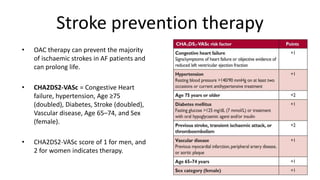
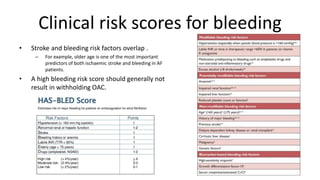
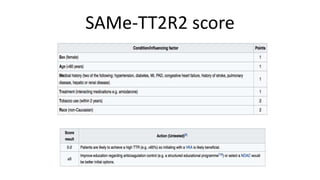
Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia and becomes more prevalent with age. It is associated with increased risks of mortality, stroke, and heart failure. The estimated global prevalence is over 30 million people and is expected to rise significantly by 2030. Treatment involves rate or rhythm control, with rhythm control indicated to improve symptoms in those remaining symptomatic on rate control. Anticoagulation therapy is crucial to prevent stroke in high risk patients based on risk scores like CHA2DS2-VASc. Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants are suitable alternatives to warfarin for stroke prevention.