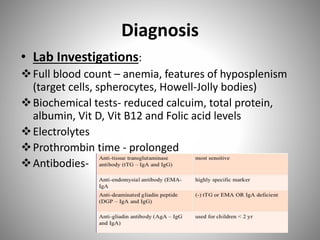
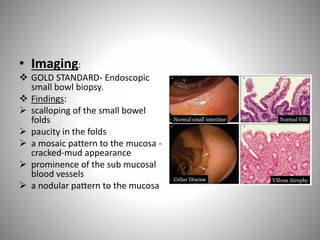
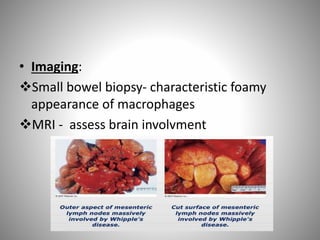
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder caused by a reaction to gluten, resulting in damage to the small intestine and malabsorption. It is characterized by the absence of intestinal villi and infiltration of lymphocytes into the epithelium. Symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and malnutrition. Diagnosis is confirmed via small bowel biopsy showing damage to intestinal villi. Treatment requires strict lifelong adherence to a gluten-free diet. Whipple's disease is a rare infection caused by a bacterium that infiltrates the small intestine, causing macrophages to obstruct lymphatic drainage and resulting in malabsorption. It commonly affects the joints and brain and is treated with intravenous antibiotics. Both conditions can lead to complications due to severe vitamin and