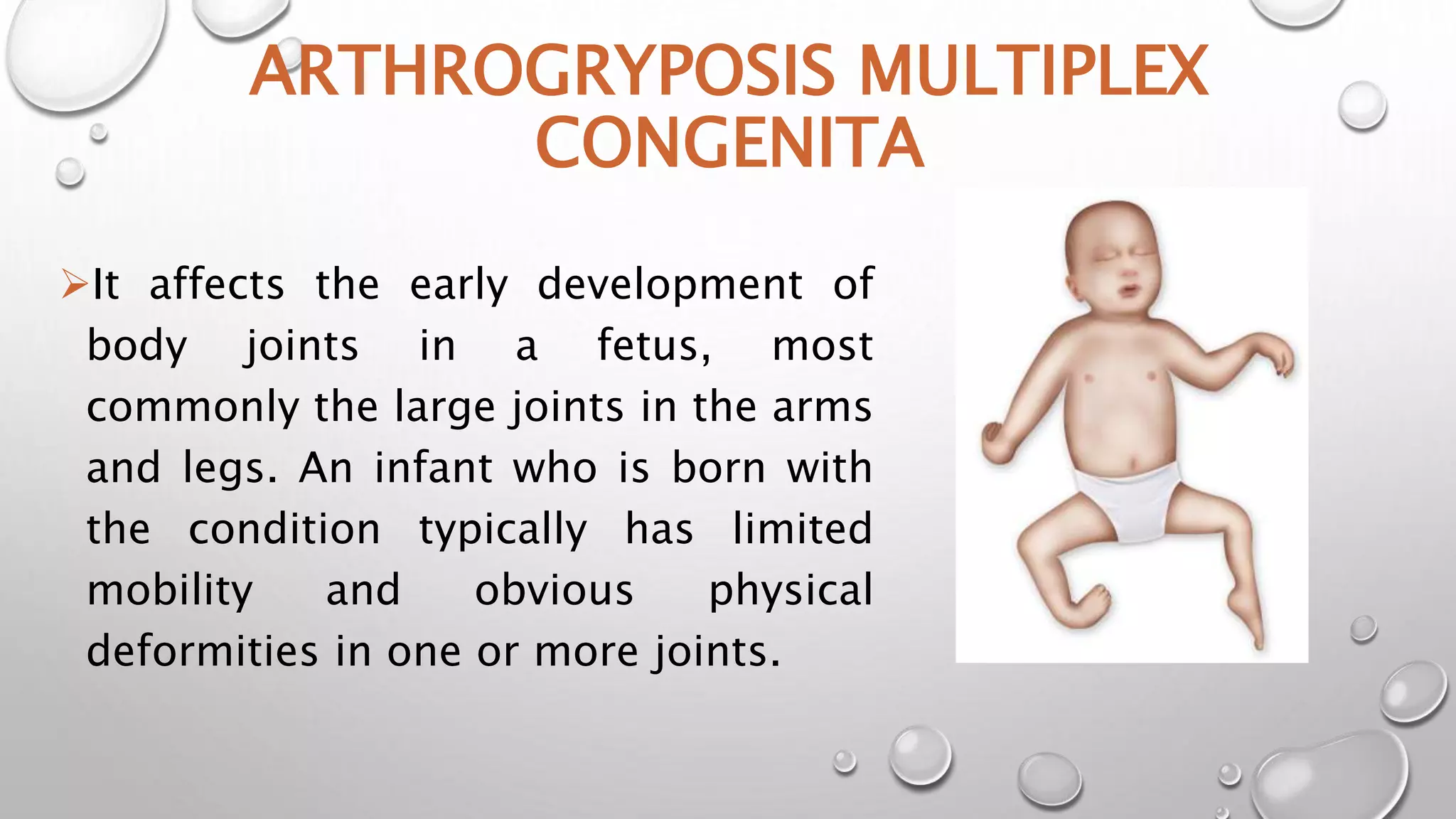
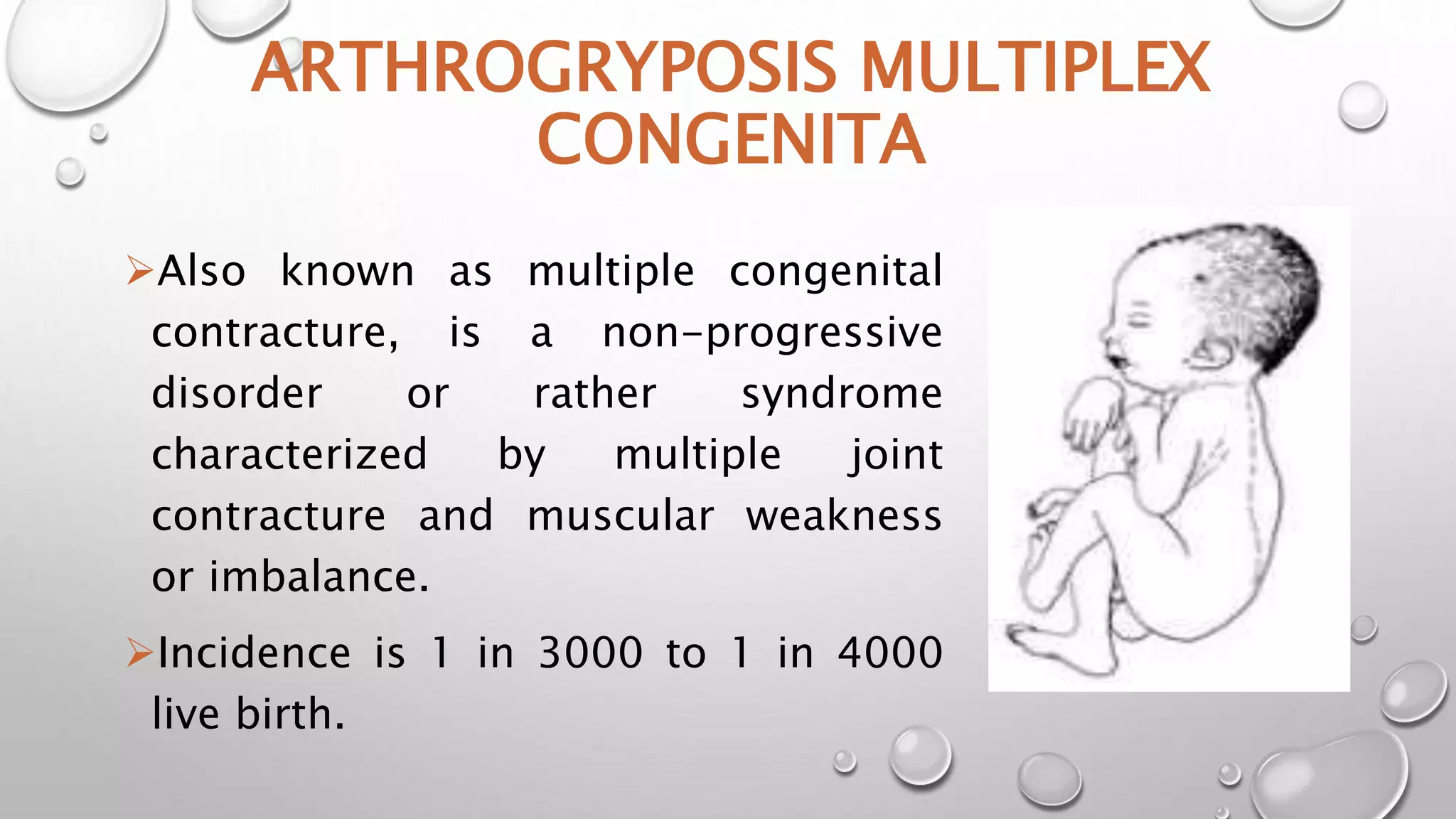
This document discusses arthrogyposis multiplex congenita (AMC), which affects joint development in fetuses, resulting in limited mobility and physical deformities at birth. AMC is caused by lack of fetal movement in the womb, which allows extra connective tissue and joint fixation to form. It has a genetic basis or can be caused by neurological or muscular disorders that impact motor function in utero. Children with AMC exhibit characteristic symmetric and rigid joint contractures at multiple sites. Management involves stretching, splinting, surgery and adaptive equipment to improve range of motion and functional skills at each stage of development.