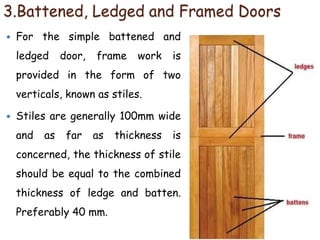
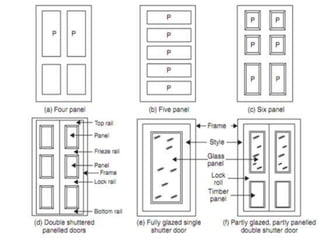
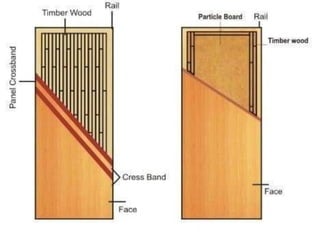
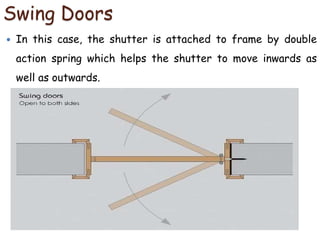
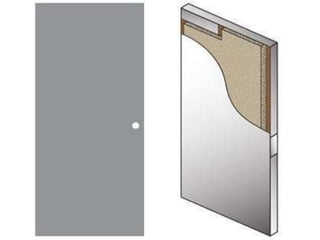
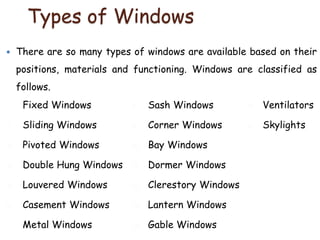
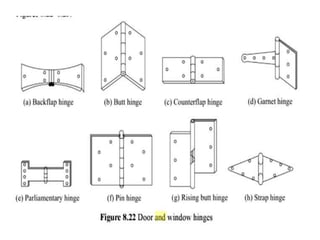
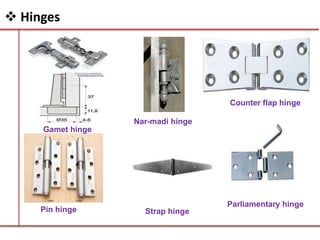
This document provides an overview of building construction materials with a focus on doors and windows. It discusses the definitions, components, sizes, types and selection criteria for doors and windows. For doors, it describes common types like framed doors, flush doors, and metal doors. For windows, it outlines fixed, sliding, pivoted, double hung and other types. Factors for selecting appropriate window types based on location, climate and other considerations are also summarized.