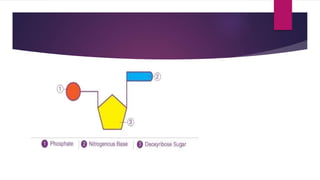
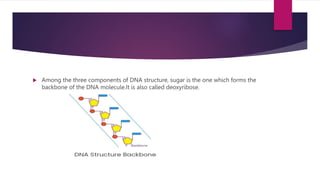
DNA is a molecule that carries genetic instructions from parents to offspring. It has a double helix structure and is composed of nucleotides containing deoxyribose, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine). The bases pair up (A-T, C-G) to form the sides of the DNA ladder. DNA stores genetic information that directs protein synthesis, cell division, and other functions essential for life. It exists in various forms (A, B, Z DNA) and is found in the nuclei and mitochondria of cells.