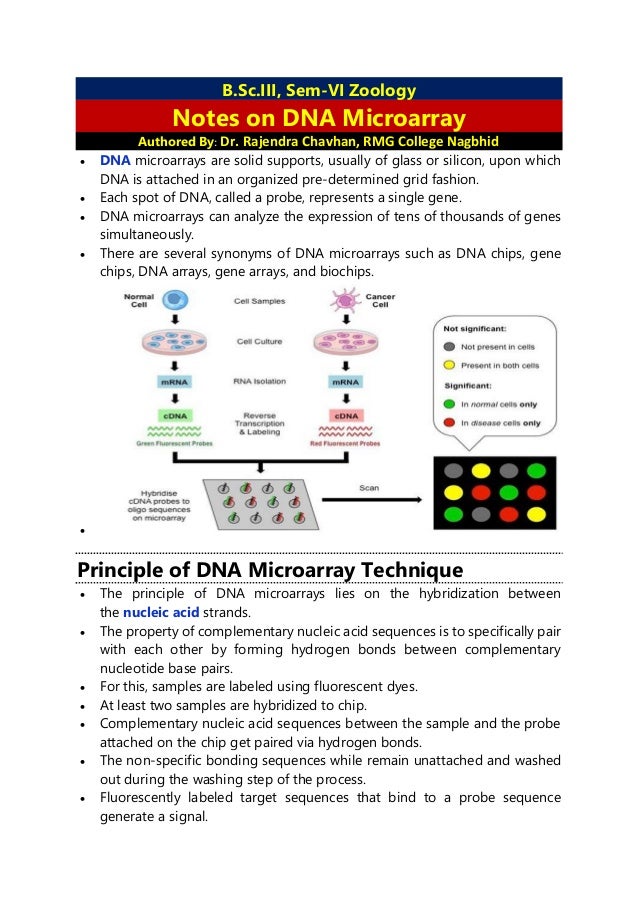
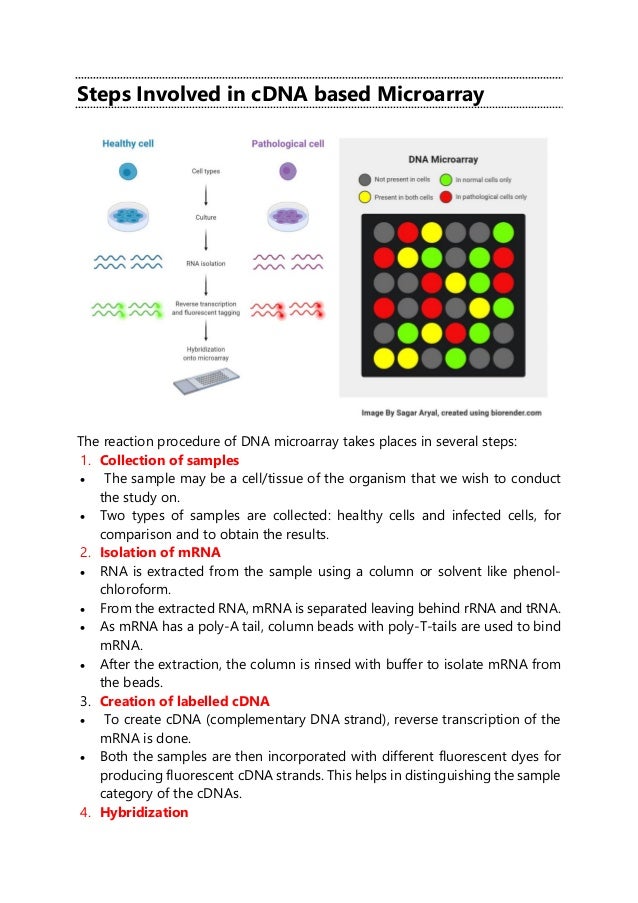
DNA microarrays are glass or silicon supports with organized DNA probes that analyze thousands of genes simultaneously, utilizing hybridization principles and fluorescent labeling. There are two main types: cDNA-based and oligonucleotide-based microarrays, each with distinct preparation methods. They have significant applications in medicine and research but also come with advantages like rapid data generation and disadvantages such as high cost and complexity in data analysis.