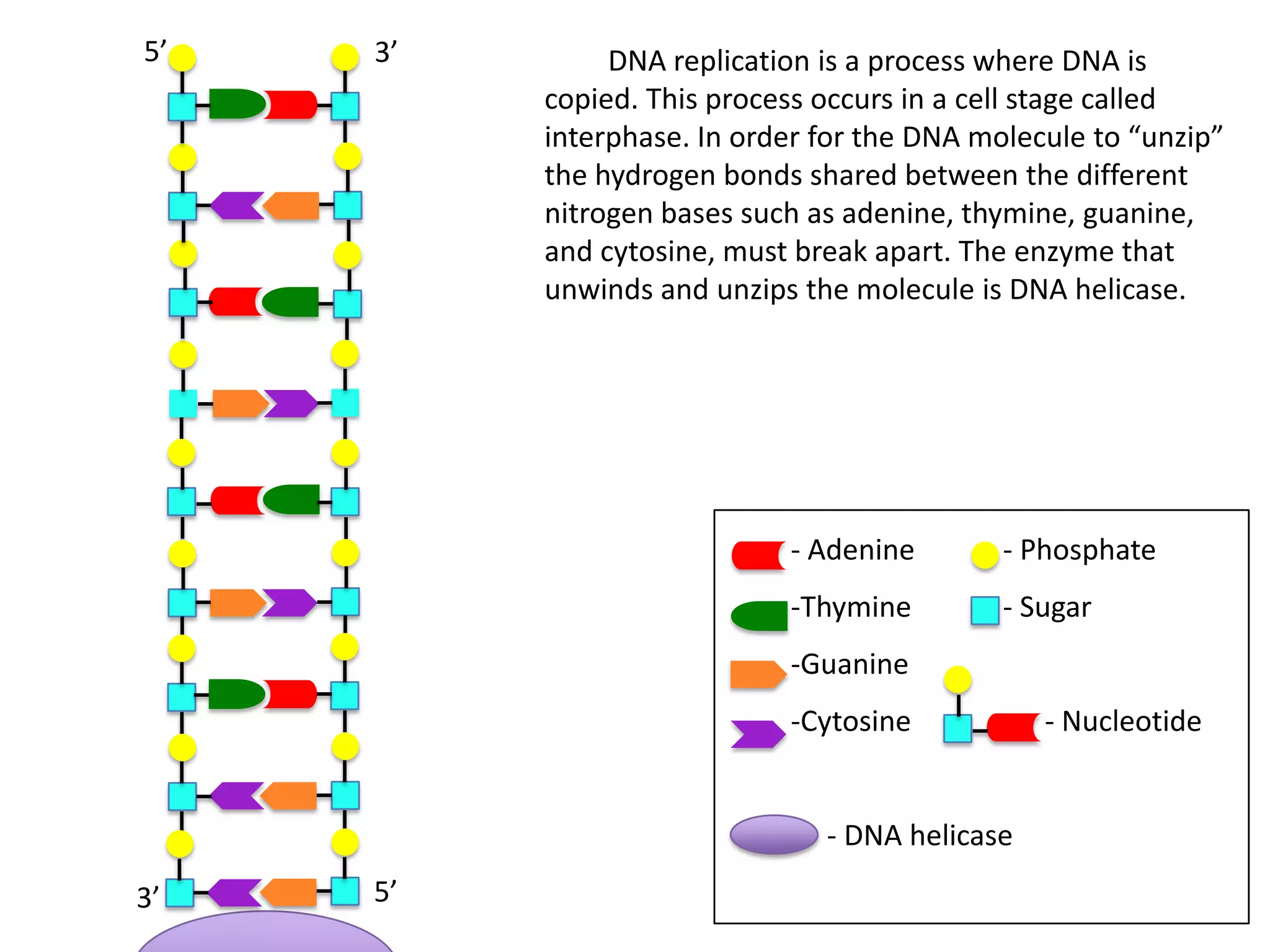
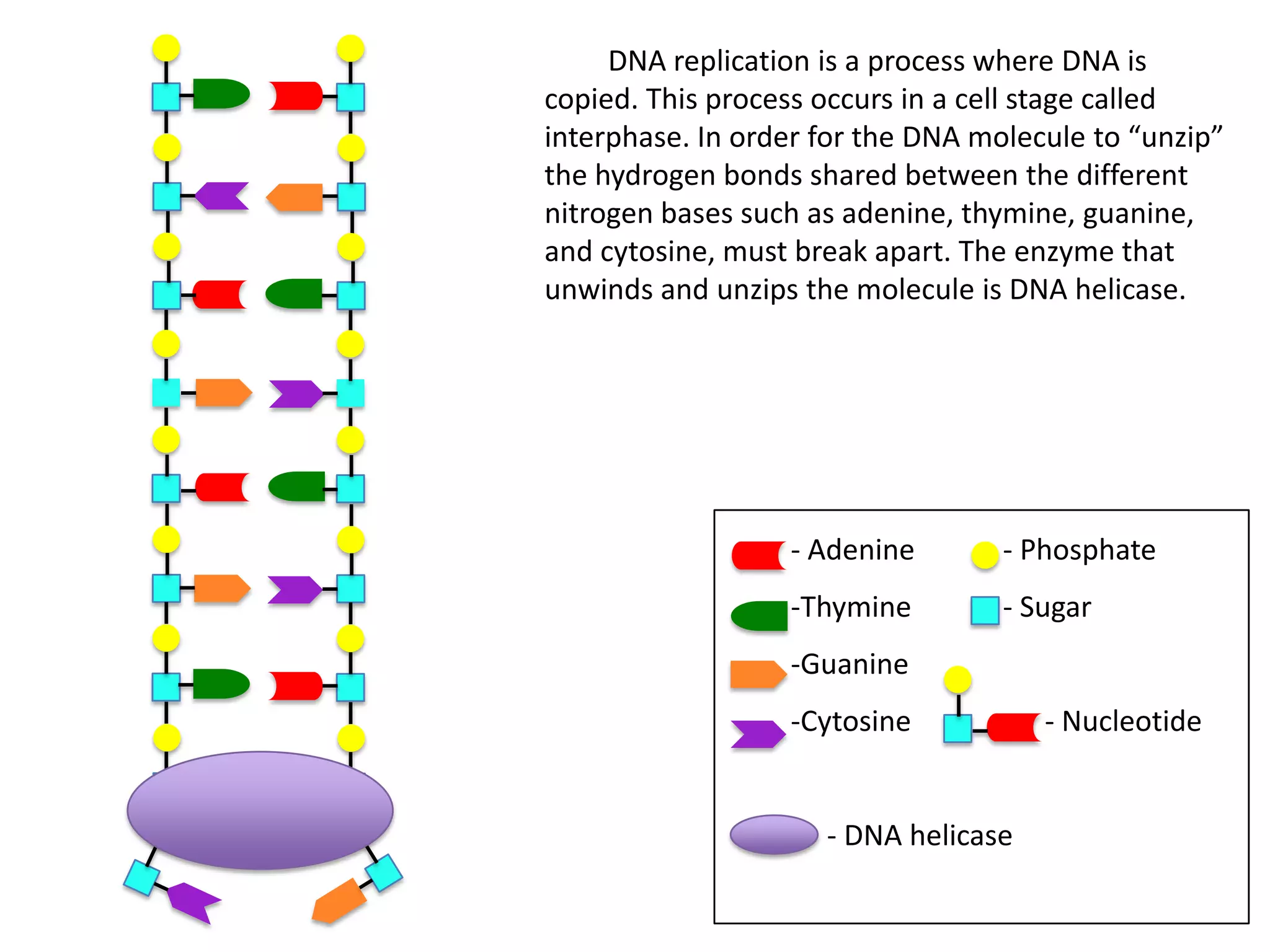
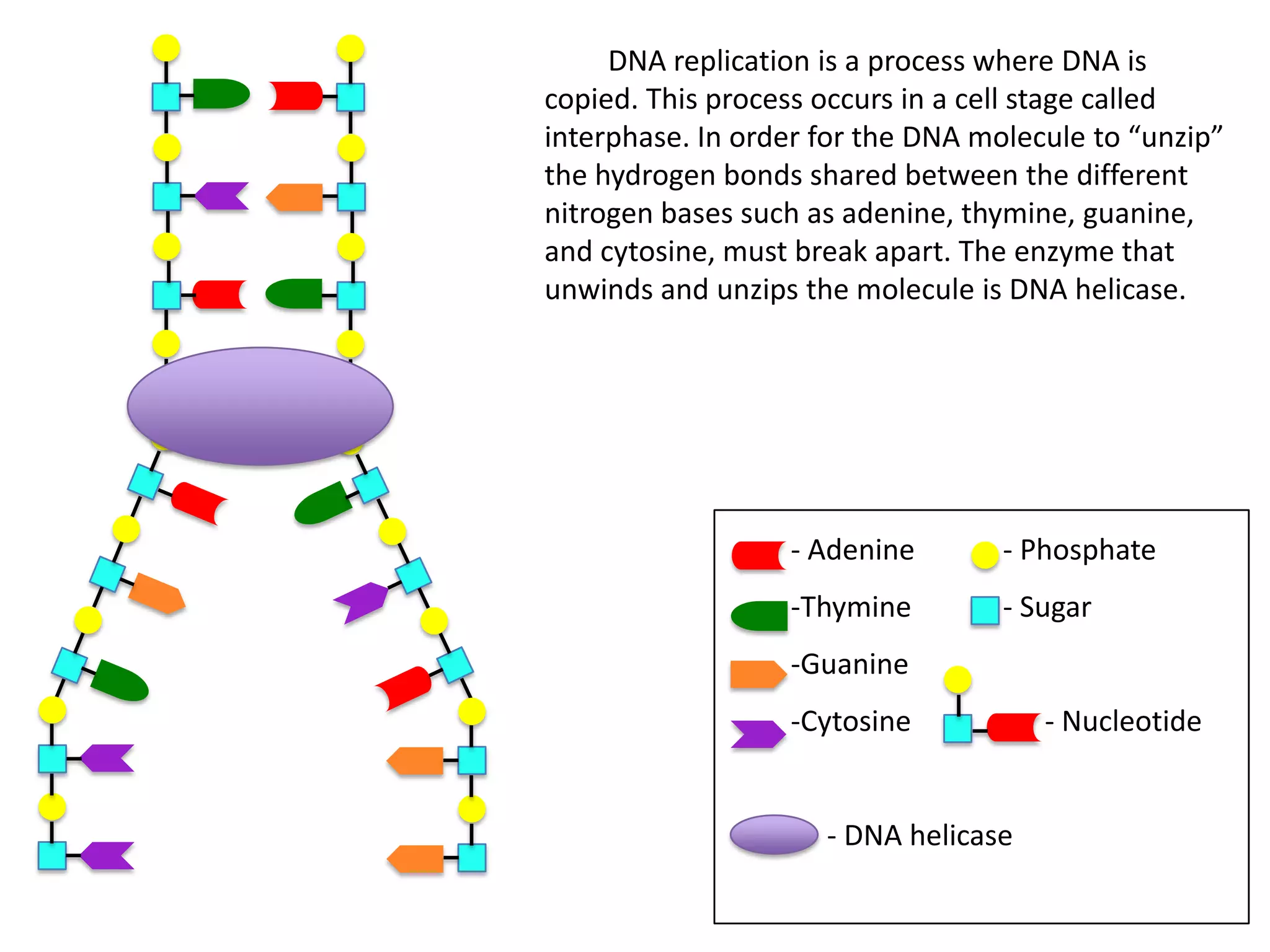
DNA replication is the process by which DNA copies itself. It occurs during the cell's interphase stage. The DNA double helix unwinds due to breaking of hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases. The enzyme DNA helicase unwinds and unzips the DNA molecule. New nucleotides are then linked together by DNA polymerase to make identical copies of the DNA strands. This results in two identical DNA molecules from the original single DNA molecule.